 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
The Blockchain Neural Network Superior to Deep Learning for Improving the Trust of Supply Chain
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, National Chung Hsing University, Taichung City, 402202, Taiwan
* Corresponding Author: Der-Chen Huang. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Key Technologies and Applications of Blockchain Technology in Supply Chain Intelligence and Trust Establishment)
Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences 2025, 143(3), 3921-3941. https://doi.org/10.32604/cmes.2025.065627
Received 18 March 2025; Accepted 18 May 2025; Issue published 30 June 2025
Abstract
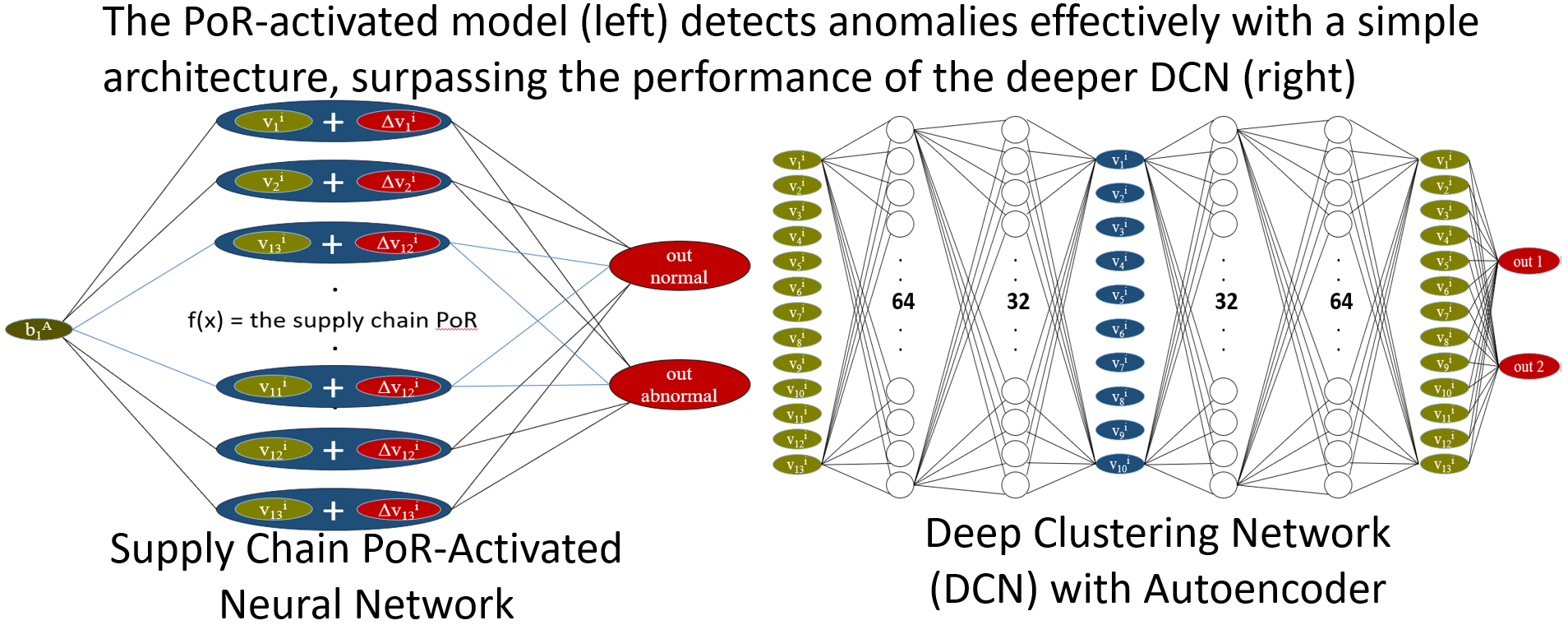
With the increasing importance of supply chain transparency, blockchain-based data has emerged as a valuable and verifiable source for analyzing procurement transaction risks. This study extends the mathematical model and proof of ‘the Overall Performance Characteristics of the Supply Chain’ to encompass multiple variables within blockchain data. Utilizing graph theory, the model is further developed into a single-layer neural network, which serves as the foundation for constructing two multi-layer deep learning neural network models, Feedforward Neural Network (abbreviated as FNN) and Deep Clustering Network (abbreviated as DCN). Furthermore, this study retrieves corporate data from the Chunghwa Yellow Pages online resource and Taiwan Economic Journal database (abbreviated as TEJ). These data are then virtualized using ‘the Metaverse Algorithm’, and the selected virtualized blockchain variables are utilized to train a neural network model for classification. The results demonstrate that a single-layer neural network model, leveraging blockchain data and employing the Proof of Relation algorithm (abbreviated as PoR) as the activation function, effectively identifies anomalous enterprises, which constitute 7.2% of the total sample, aligning with expectations. In contrast, the multi-layer neural network models, DCN and FNN, classify an excessively large proportion of enterprises as anomalous (ranging from one-fourth to one-third), which deviates from expectations. This indicates that deep learning may still be inadequate in effectively capturing or identifying malicious corporate behaviors associated with distortions in procurement transaction data. In other words, procurement transaction blockchain data possesses intrinsic value that cannot be replaced by artificial intelligence (abbreviated as AI).Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools