 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
A Data-Driven Systematic Review of the Metaverse in Transportation: Current Research, Computational Modeling, and Future Trends
1 Centre of Mathematics, Universidade do Minho, Braga, 4710-057, Portugal
2 School of Industrial Engineering, Pontificia Universidad Católica de Valparaíso, Valparaíso, 2362807, Chile
3 Instituto Sistemas Complejos de Ingeniería, Santiago, 8320000, Chile
* Corresponding Author: Victor Leiva. Email:
Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences 2025, 144(2), 1481-1543. https://doi.org/10.32604/cmes.2025.067992
Received 18 May 2025; Accepted 21 July 2025; Issue published 31 August 2025
Abstract
Metaverse technologies are increasingly promoted as game-changers in transport planning, connected-autonomous mobility, and immersive traveler services. However, the field lacks a systematic review of what has been achieved, where critical technical gaps remain, and where future deployments should be integrated. Using a transparent protocol-driven screening process, we reviewed 1589 records and retained 101 peer-reviewed journal and conference articles (2021–2025) that explicitly frame their contributions within a transport-oriented metaverse. Our review reveals a predominantly exploratory evidence base. Among the 101 studies reviewed, 17 (16.8%) apply fuzzy multi-criteria decision-making, 36 (35.6%) feature digital-twin visualizations or simulation-based testbeds, 9 (8.9%) present hardware-in-the-loop or field pilots, and only 4 (4.0%) report performance metrics such as latency, throughput, or safety under realistic network conditions. Over time, the literature evolves from early conceptual sketches (2021–2022) through simulation-centered frameworks (2023) to nascent engineering prototypes (2024–2025). To clarify persistent gaps, we synthesize findings into four foundational layers—geometry and rendering, distributed synchronization, cryptographic integrity, and human factors—enumerating essential algorithms (homogeneous transforms, Lamport clocks, Raft consensus, Merkle proofs, sweep-and-prune collision culling, Q-learning, and real-time ergonomic feedback loops). A worked bus-fleet prototype illustrates how blockchain-based ticketing, reinforcement learning-optimized traffic signals, and extended reality dispatch can be integrated into a live digital twin. This prototype is supported by a three-phase rollout strategy. Advancing the transport metaverse from blueprint to operation requires open data schemas, reproducible edge–cloud performance benchmarks, cross-disciplinary cyber-physical threat models, and city-scale sandboxes that apply their mathematical foundations in real-world settings.Graphic Abstract
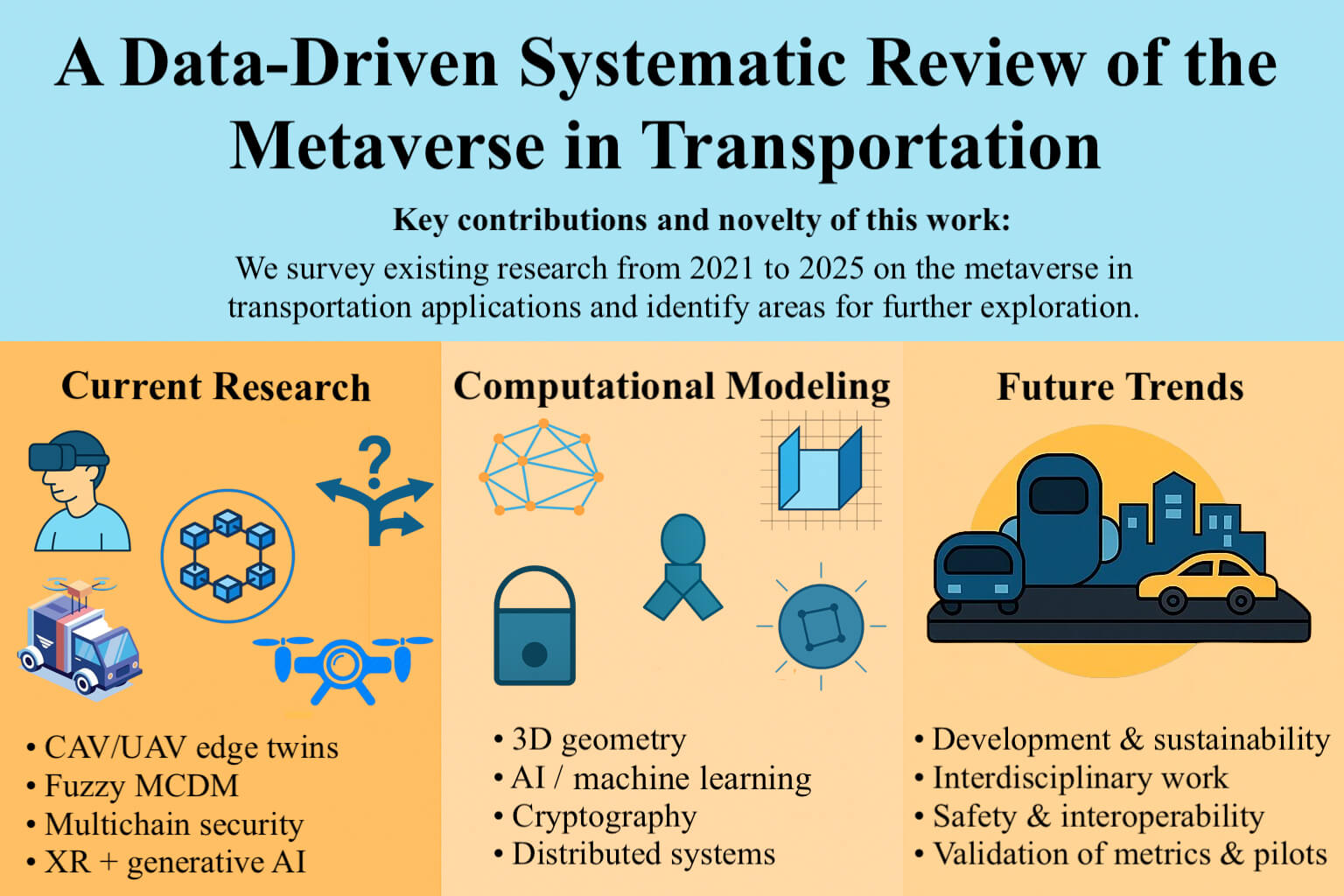
Keywords
Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material FileCite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools