 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
The potency of N, N'-diphenyl-1,4-phenylenediamine and adipose-derived stem cell co-administration in alleviating hepatorenal dysfunction complications associated with type 1 diabetes mellitus in rats
1 Department of Chemistry, College of Science, King Faisal University, Al-Ahsa, Saudi Arabia
2 Chemistry Department, Faculty of Science, Sohag University, Sohag, Egypt
3 Department of Biology, College of Science, University of Jeddah, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia
4 Department of Biotechnology, College of Science, Taif University, Taif, Saudi Arabia
5 Fellow of Biochemistry, Genetic Unit, Children Hospital, Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura University, Mansoura, Egypt
6 Chemistry Department (Biochemistry Branch), Faculty of Science, Suez University, Suez, Egypt
7 Department of Clinical Laboratories Sciences, College of Applied Medical Sciences, Shaqra University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
8 Biology Department, Faculty of Science, Mansoura University, Mansoura, Egypt
9 Department of Chemistry, Organic Chemistry Division, College of Science, Mansoura University, Mansoura, Egypt
10 Zoology Department, Faculty of Science, Arish University, North Sinai, Egypt
* Corresponding Authors: HANY M. ABD EL-LATEEF. Email: ; SHADY G. EL-SAWAH. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Cell-Based Regenerative Therapies)
BIOCELL 2023, 47(8), 1885-1895. https://doi.org/10.32604/biocell.2023.030680
Received 18 April 2023; Accepted 01 June 2023; Issue published 28 August 2023
Abstract
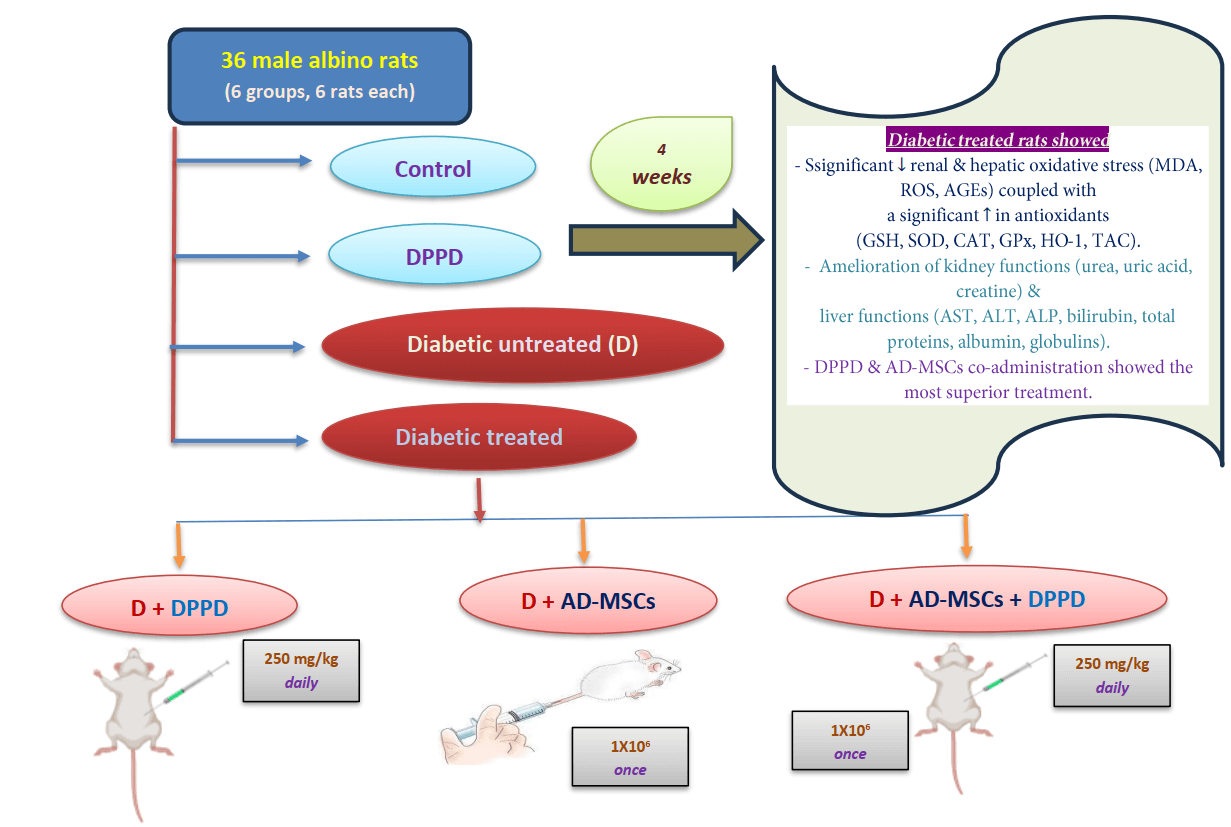
Background: The increasing occurrence of diabetes mellitus (DM) noted worldwide has considerably elicited concern in the recent past. DM is associated with elevated vascular complications, morbidity, mortality, and poor quality of life. In this context, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have shown significant therapeutic potentialities in managing and curing type 1 DM owing to their self-renewable, immunosuppressive, and differentiation capacities. We investigated the potential action of N, N′-diphenyl-1,4-phenylenediamine (DPPD), a well-known synthetic antioxidant to enhance the therapeutic ability of the adipose-derived stem cells (AD-MSCs) in alleviating kidney and liver complications in diabetic rats. Methods: Over the four weeks of experiments, albino male rats (n = 36) were split into six test groups: control, DPPD (250 mg/kg, i.p.), STZ-diabetic (D), D+DPPD, D+AD-MSCs (1 × 10 cell/rat, i.v.), and D+AD-MSCs+DPPD treated groups. Results: Significant declines in the renal and hepatic oxidative stress markers (MDA, ROS, and AGEs) were observed coupled with a significant elevation in many antioxidant marker levels (GSH, SOD, CAT, GPx, HO-1, and TAC) in the diabetic rats treated with either DPPD or AD-MSCs or their co-administered injection compared to the diabetic untreated rats. This was suggested to be the leading cause of amelioration of the kidney functions (as measured by urea, uric acid, and creatine levels) and liver functions (as evidenced by the levels of AST, ALT, ALP, bilirubin, total proteins, albumin, and globulins). Conclusion: DPPD and AD-MSCs co-administration showed superior results in terms of the enhancement of the relative hepato-renal function, indicating the beneficial role of DPPD supplementation in increasing the therapeutic potential of AD-MSCs.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material FileCite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools