 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Enhancing the Properties of Biodegradable Food Packaging Films Derived from Agar and Porang-Glucomannan (Amorphophallus oncophyllus) Blends
1 Department Agricultural and Biosystem Engineering, Faculty of Agricultural Technology, Gadjah Mada University, Yogyakarta, 55281, Indonesia
2 Research Center for Food Technology and Processing, National Research and Innovation Agency of the Republic of Indonesia, Yogyakarta, 55861, Indonesia
* Corresponding Authors: Sri Rahayoe. Email: ; Bakti Berlyanto Sedayu. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Polysaccharide-Based Composites: Preparation, Characterization, and Applications )
Journal of Renewable Materials 2025, 13(2), 385-400. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2024.057313
Received 14 August 2024; Accepted 14 September 2024; Issue published 20 February 2025
Abstract
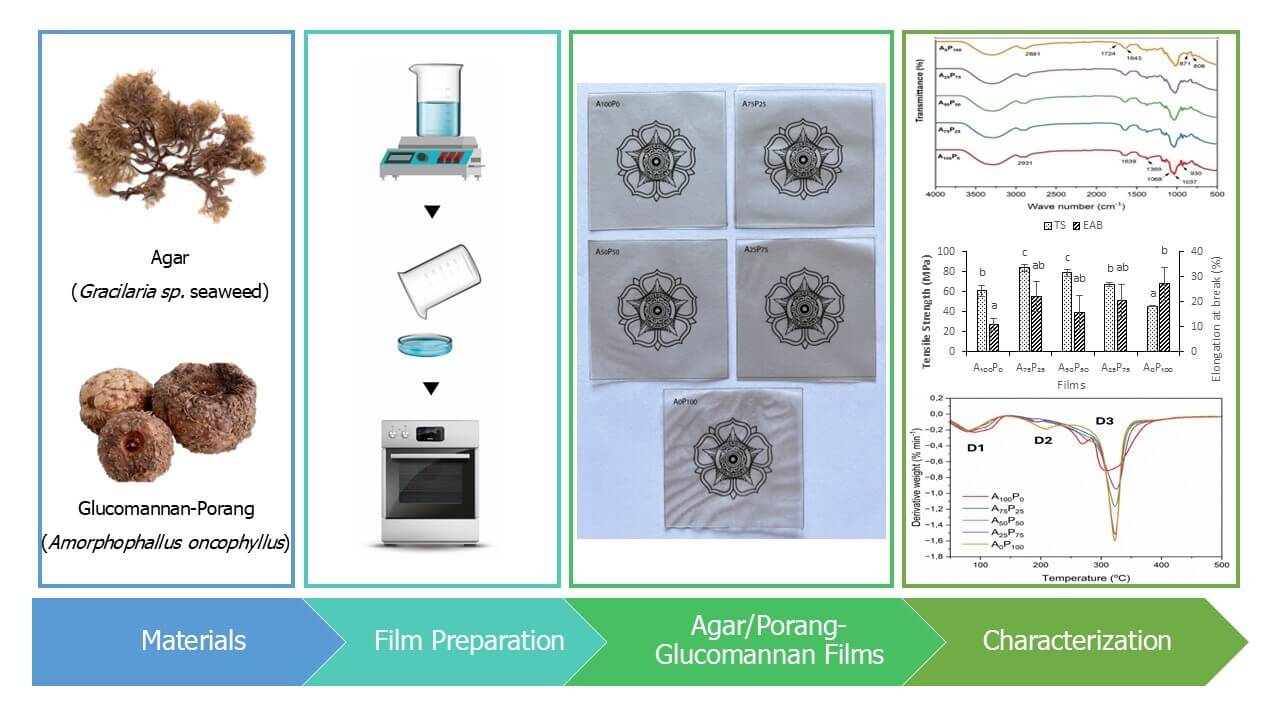
This study aimed to develop and characterize biodegradable packaging film from blends of two natural polysaccharides, i.e., agar and glucomannan. The glucomannan used was derived from the specific tuber plant Amorphophallus oncophyllus (locally known as “porang”), which grows abundantly in Indonesian forests and remains underutilized. Various ratios of agar and porang-glucomannan (PG) proportions were formulated to produce a food packaging film, which was subsequently tested for its mechanical, physical, chemical, and thermal properties. The results showed that the inclusion of PG to the film formulations notably enhanced the stretchability of agar films, achieving maximum a twofold increase, while concurrently reducing their water resistance such as increased water solubility and water swelling for up to 125% and 105%, respectively. The mechanical and thermal properties, as well as the water vapor permeability of the resulting film, were significantly affected by the polymer matrix structure formed by the varying proportions of the two biopolymers. The enhancement of these properties was associated with a more solid/compact film structure, as corroborated by cross-sectional images obtained through SEM analysis. The study’s findings suggest that utilizing agar and porang biomass has significant potential for further development as an environmentally friendly food packaging material.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools