 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Saccharification of Paper Sludge and Fiber Dust Wastes from the Tissue Paper Industry by Maximyze® Enzymes
1 Cellulose and Paper Department, National Research Centre, Dokki, Giza, 12622, Egypt
2 Advanced Materials and Nanotechnology Group, Centre of Excellence for Advanced Sciences, National Research Centre, Dokki, Giza, 12622, Egypt
3 Chemical Engineering and Pilot Plant Department, National Research Centre, Dokki, Giza, 12622, Egypt
* Corresponding Author: Mohammad Hassan. Email:
Journal of Renewable Materials 2025, 13(6), 1169-1187. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2025.02024-0030
Received 05 November 2024; Accepted 31 December 2024; Issue published 23 June 2025
Abstract
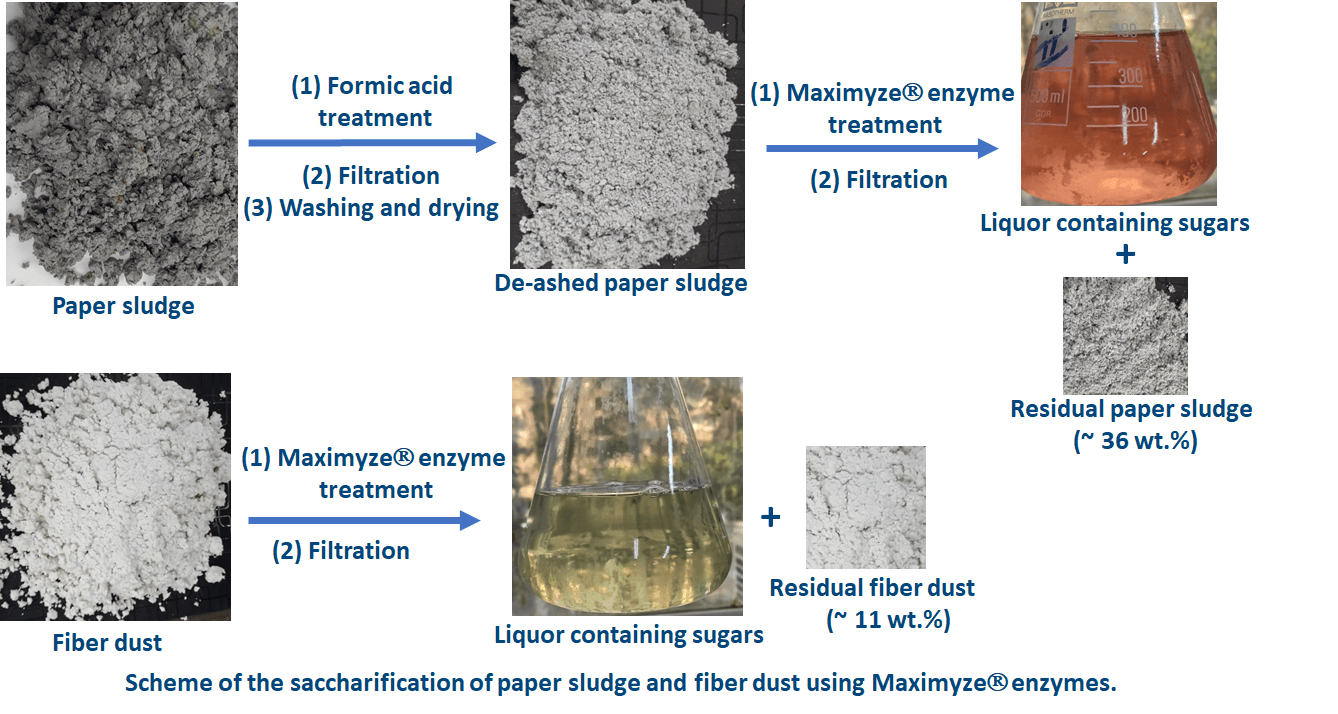
Saccharification of lignocellulosic wastes is the bottleneck of different bio-based chemical industries. Using enzymes for saccharification of lignocellulosic materials has several advantages over using chemicals. In the current work, the application of the Maximyze® enzyme system, which is industrially used in papermaking, was investigated in the saccharification of paper sludge and fiber dust wastes from the tissue paper industry. For optimizing the saccharification process, the effects of the consistency %, enzyme loading, and incubation time were studied and optimized using the Response Surface Methodology. The effect of these factors on the weight loss of paper sludge and total sugars in the hydrolyzate was studied. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) was used to measure the sugars composition of the hydrolyzate. Under the optimized conditions, ~90% and ~66% of the fiber dust and paper sludge could be hydrolyzed into sugars, respectively. The sugar composition was 80.23% glucose, 10.99% xylose, and 8.65% arabinose based on the total sugars in the case of fiber dust. In comparison, 80.63% glucose, 8.43% xylose, and 10.75% arabinose were detected in the case of paper sludge. The results showed the applicability of the Maximyze® commercial enzymes used in the paper industry for efficient saccharification of paper sludge and fiber dust. The presence of non-cellulosic materials in the paper sludge (residual ink, paper additives, and ash) didn’t affect the activity of the enzymes. The study also showed the potential use of fiber dust as a valuable and clean source of sugars that can be used to prepare different bio-based chemicals.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools