 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Design and Research of Eco-Friendly Biodegradable Composites Based on Renewable Biopolymer Materials, Reed, and Hemp Waste
1 The Department of Plastics and Biologically Active Polymers Technology, National Technical University (Kharkiv Polytechnic Institute), Kharkiv, 61002, Ukraine
2 Department of Oil, Gas and Solid Fuel Refining Technologies, National Technical University (Kharkiv Polytechnic Institute), Kharkiv, 61002, Ukraine
3 Coal Department, The Ukrainian Research Coal-Chemistry Institute, Kharkiv, 61023, Ukraine
4 Department of Industrial and Biomedical Electronics, National Technical University (Kharkiv Polytechnic Institute), Kharkiv, 61002, Ukraine
5 Department of Engineering Technology and Cutting Machines, National Technical University (Kharkiv Polytechnic Institute), Kharkiv, 61002, Ukraine
6 Department of Chemical Technology of Oil and Gas Processing, Lviv Polytechnic National University, Lviv, 79013, Ukraine
* Corresponding Author: Serhiy Pyshyev. Email:
Journal of Renewable Materials 2025, 13(8), 1645-1660. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0049
Received 03 March 2025; Accepted 13 May 2025; Issue published 22 August 2025
Abstract
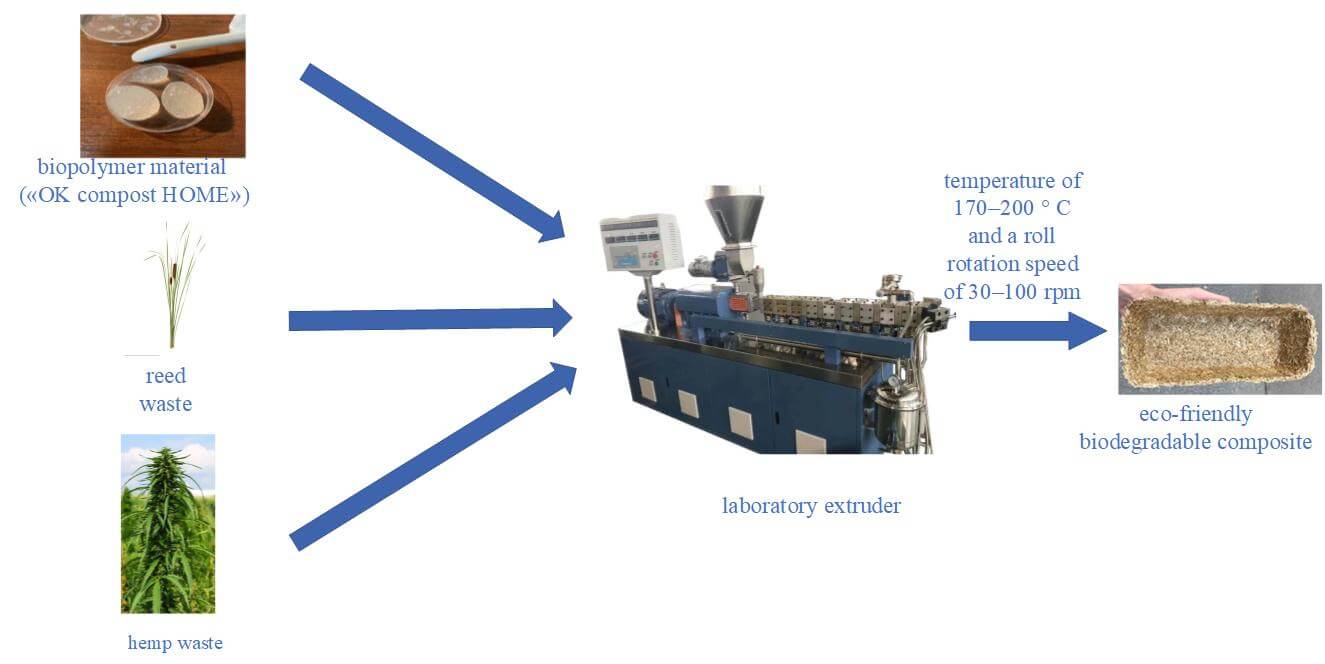
Nowadays, the development of effective bioplastics aims to combine traditional plastics’ functionality with environmentally friendly properties. The most effective and durable modern bioplastics are made from the edible part of crops. This forces bioplastics to compete with food production because the crops that produce bioplastics can also be used for human nutrition. That is why the article’s main focus is on creating bioplastics using renewable, non-food raw materials (cellulose, lignin, etc.). Eco-friendly composites based on a renewable bioplastic blend of polybutylene adipate-co-terephthalate, corn starch, and poly(lactic acid) with reed and hemp waste as a filler. The physic-chemical features of the structure and surface, as well as the technological characteristics of reed and hemp waste as the organic fillers for renewable bioplastic blend of polybutylene adipate-co-terephthalate, corn starch, and poly(lactic acid), were studied. The effect of the fractional composition analysis, morphology, and nature of reed and hemp waste on the quality of the design of eco-friendly biodegradable composites and their ability to disperse in the matrix of renewable bioplastic blend of polybutylene adipate-co-terephthalate, corn starch and poly(lactic acid) was carried out. The influence of different content and morphology of reed and hemp waste on the composite characteristics was investigated. It is shown that the most optimal direction for obtaining strong eco-friendly biodegradable composites based on a renewable bioplastic blend of polybutylene adipate-co-terephthalate, corn starch, and poly(lactic acid) is associated with the use of waste reed stalks, with its optimal content at the level of 50 wt.%.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools