 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
C-Phycocyanin–Cisplatin Combination Targeting Redox Balance for Enhanced Efficacy Against Glioblastoma Cells
1 Laboratory of Genetics Immunology and Human Pathology, Biology Department, Faculty of Sciences of Tunis, University of Tunis El Manar, Tunis, 2092, Tunisia
2 Faculté des Sciences Médicales et Paramédicales, Institut de NeuroPhysiopathologie (INP), UMR 7051, CNRS, Aix Marseille Université, Marseille, 13005, France
3 Confocal Microscopy Unit, Faculty of Medicine of Tunis, University Tunis El Manar, Tunis, 1007, Tunisia
4 Laboratory of Neurophysiology, Cellular Physiopathology and Biomolecules Valorisation, LR18ES03, Faculty of Sciences of Tunis, University of Tunis El Manar, Tunis, 2092, Tunisia
* Corresponding Authors: Hervé Kovacic. Email: ; Asma Gati. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Mechanisms of Reactive Oxygen Species Modulation in Cancer Therapy)
Oncology Research 2025, 33(12), 3887-3906. https://doi.org/10.32604/or.2025.070729
Received 22 July 2025; Accepted 22 September 2025; Issue published 27 November 2025
Abstract
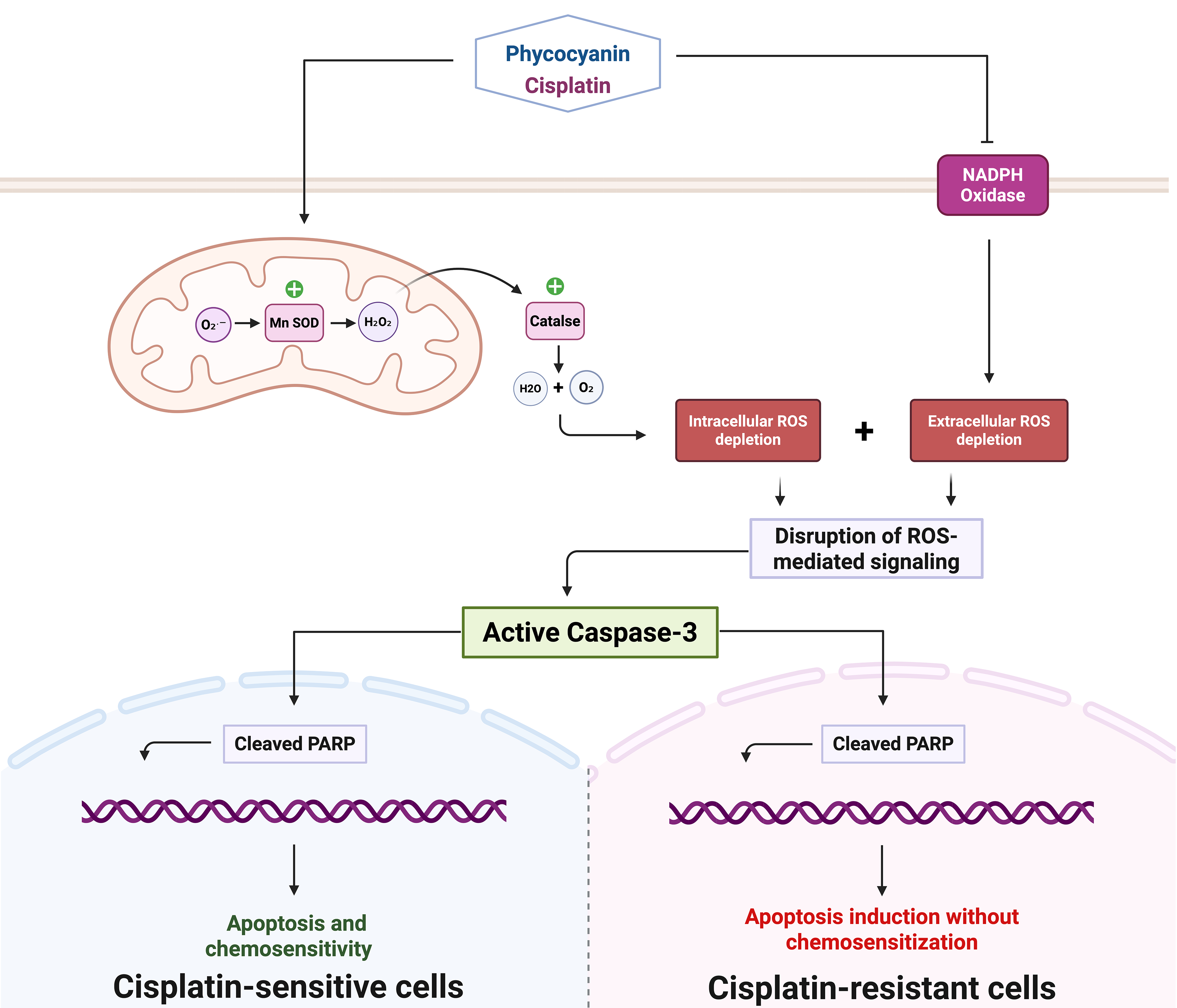
Objectives: Cisplatin (CDDP) therapy for glioblastoma (GBM) is linked with several limitations, which include poor penetration of the blood-brain barrier (BBB), systemic toxicity, and the development of drug resistance mechanisms implicating oxidative stress dysregulation and compromised apoptotic pathways. This study evaluates C-Phycocyanin (C-PC) as a potential adjuvant to enhance CDDP efficacy by modulating redox balance and apoptosis. Methods: GBM cells (U87 and U87-EGFRvIII) were treated with CDDP, C-PC, or their combination. Cell viability was assessed by MTT assay; apoptosis was evaluated by DAPI staining and Western blot analysis of cleaved Caspase-3 and poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP). Both intracellular and extracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) were measured using 2′,7′-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate (DCF-DA) fluorescence and lucigenin chemiluminescence, respectively. Catalase activity was quantified via hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) decomposition assay, and manganese superoxide dismutase (MnSOD) expression by Western blot. Results: C-PC selectively decreased U87 GBM cell viability while sparing normal cells. C-PC enhanced CDDP cytotoxicity, reducing viability to 26.5% vs. 53.2% for CDDP alone. This effect correlated with increased apoptosis, evidenced by DNA fragmentation and higher cleaved caspase-3 and PARP levels. Combined treatment lowered ROS below survival thresholds while upregulating MnSOD and catalase activity. In U87-EGFRvIII cells, CDDP reduced viability modestly (85.2%), C-PC alone decreased viability significantly (51.5%) and induced cell death, but the combination did not further increase apoptosis. Here, C-PC’s pro-apoptotic effects, alone or with CDDP, were also associated with reduced oxidative stress in cells. Conclusion: We demonstrate that C-PC enhances CDDP cytotoxicity in sensitive U87 cells by promoting apoptosis and modulating ROS, suggesting potential for improved therapeutic efficacy with reduced systemic toxicity. Compared to the combination, C-PC monotherapy achieves superior cytotoxicity in CDDP-resistant U87-EGFRvIII cells, underscoring its potential as a standalone therapeutic approach for chemotherapy-resistant glioblastoma subtypes.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools