
A Proud Tradition
Established in 1904, Energy Engineering has a history of more than 120 years, making it one of the long-standing journals in the field. Throughout its long history, the journal has evolved alongside advances in energy science and technology, consistently serving as a catalyst for innovation and progress. In recent years, it has achieved steady improvements in academic quality, editorial standards, and international influence, and continues to move toward becoming a leading international journal.
Multi-faceted scholarship
Energy Engineering is an open-access, peer-reviewed journal focusing on the engineering aspects of energy research. It provides a global platform for researchers, engineers, scientists, and policy makers to publish original studies across a broad range of energy topics, including energy generation, conversion, conservation, utilization, storage, transmission, systems, technologies, management and sustainability. The journal also explores the societal impacts of energy use and policy, showcasing research that advances sustainable development and supports the transition to cleaner energy systems.
Ei Compendex/Engineering Village (Elsevier); Scopus (Elsevier); WorldCat (OCLC); Google Scholar; ResearchGate; SCImago (SJR); Crossref; Sherpa/RoMEO; Letpub; Elektronische; Genamics JournalSeek; Dimensions; Portico, etc...
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Energy Engineering, Vol.123, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.064353 - 27 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Selected Papers from the SDEWES 2024 Conference on Sustainable Development of Energy, Water and Environment Systems)
Abstract Decarbonising the building sector, particularly residential heating, represents a critical challenge for achieving carbon-neutral energy systems. Efficient solutions must integrate both technological performance and renewable energy sources while considering operational constraints of existing systems. This study investigates a hybrid heating system combining a natural gas boiler (NGB) with an air-to-water heat pump (AWHP), evaluated through a combination of laboratory experiments and dynamic modelling. A prototype developed in the Electrical and Energy Engineering Laboratory enabled the characterization of both heat generators, the collection of experimental data, and the calibration of a MATLAB/Simulink model, including emissions and… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Energy Engineering, Vol.123, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.070715 - 27 January 2026
Abstract In the pursuit of carbon peaking and neutrality goals, multi-energy parks, as major energy consumers and carbon emitters, urgently require low-carbon operational strategies. This paper proposes an electricity-carbon synergy-driven optimization method for the low-carbon operation of multi-energy parks. The method integrates multi-energy complementary scheduling with a tiered carbon trading mechanism to balance operational security, economic efficiency, and environmental objectives. A mixed-integer linear programming model is developed to characterize the coupling relationships and dynamic behaviors of key equipment, including photovoltaic systems, ground-source heat pumps, thermal storage electric boilers, combined heat and power units, and electrical energy… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Energy Engineering, Vol.123, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.073303 - 27 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advancements in Energy Resources and Their Processes, Systems, Materials and Policies for Affordable Energy Sustainability)
Abstract Gas Turbines are among the most important energy systems for aviation and thermal-based power generation. The performance of gas turbine intakes with S-shaped diffusers is vulnerable to flow separation, reversal flow, and pressure distortion, mainly in aggressive S-shaped diffusers. Several methods, including vortex generators and energy promoters, have been proposed and investigated both experimentally and numerically. This paper compiles a review of experimental investigations that have been performed and reported to mitigate flow separation and restore system performance. The operational principles, classifications, design geometries, and performance parameters of S-shaped diffusers are presented to facilitate the… More >
Graphic Abstract
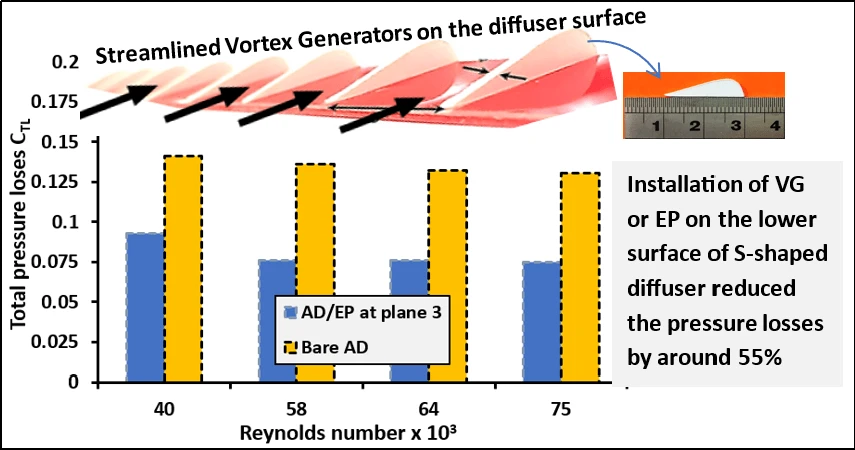
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Energy Engineering, Vol.123, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.068894 - 27 January 2026
Abstract The author proposes a dual layer source grid load storage collaborative planning model based on Benders decomposition to optimize the low-carbon and economic performance of the distribution network. The model plans the configuration of photovoltaic (3.8 MW), wind power (2.5 MW), energy storage (2.2 MWh), and SVC (1.2 Mvar) through interaction between upper and lower layers, and modifies lines 2–3, 8–9, etc. to improve transmission capacity and voltage stability. The author uses normal distribution and Monte Carlo method to model load uncertainty, and combines Weibull distribution to describe wind speed characteristics. Compared to the traditional… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Energy Engineering, Vol.123, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.070530 - 27 January 2026
Abstract Energy storage-equipped photovoltaic (PV-storage) systems can meet frequency regulation requirements under various operating conditions, and their coordinated support for grid frequency has become a future trend. To address frequency stability issues caused by low inertia and weak damping, this paper proposes a multi-timescale frequency regulation coordinated control strategy for PV-storage integrated systems. First, a self-synchronizing control strategy for grid-connected inverters is designed based on DC voltage dynamics, enabling active inertia support while transmitting frequency variation information. Next, an energy storage inertia support control strategy is developed to enhance the frequency nadir, and an active frequency… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Energy Engineering, Vol.123, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.070190 - 27 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Solar and Thermal Energy Systems)
Abstract The technical, economic, and environmental performance of solar hot-water (SWH) systems for Swedish residential apartments—where approximately 80% of household energy is devoted to space heating and sanitary hot-water production—was assessed. Two collector types, flat plate (FP) and evacuated tube (ET), were simulated in TSOL Pro 5.5 for five major cities (Stockholm, Göteborg, Malmö, Uppsala, Linköping). Climatic data and cold-water temperatures were sourced from Meteonorm 7.1, and economic parameters were derived from recent national statistics and literature. All calculations explicitly accounted for heat losses from collectors, storage tanks, and internal and external piping systems, and established… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Energy Engineering, Vol.123, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.070934 - 27 January 2026
Abstract With the rapid development of large-scale offshore wind farms, efficient and reliable power transmission systems are urgently needed. Hybrid high-voltage direct current (HVDC) configurations combining a diode rectifier unit (DRU) and a modular multilevel converter (MMC) have emerged as a promising solution, offering advantages in cost-effectiveness and control capability. However, the uncontrollable nature of the DRU poses significant challenges for system stability under offshore AC fault conditions, particularly due to its inability to provide fault current or voltage support. This paper investigates the offshore AC fault characteristics and fault ride-through (FRT) strategy of a hybrid… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Energy Engineering, Vol.123, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.069323 - 27 January 2026
Abstract The increasing intelligence of power systems is transforming distribution networks into Cyber-Physical Distribution Systems (CPDS). While enabling advanced functionalities, the tight interdependence between cyber and physical layers introduces significant security challenges and amplifies operational risks. To address these critical issues, this paper proposes a comprehensive risk assessment framework that explicitly incorporates the physical dependence of information systems. A Bayesian attack graph is employed to quantitatively evaluate the likelihood of successful cyber attacks. By analyzing the critical scenario of fault current path misjudgment, we define novel system-level and node-level risk coupling indices to precisely measure the… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Energy Engineering, Vol.123, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.069495 - 27 January 2026
Abstract Addressing the limitations of inadequate stochastic disturbance characterization during wind turbine degradation processes that result in constrained modeling accuracy, replacement-based maintenance practices that deviate from actual operational conditions, and static maintenance strategies that fail to adapt to accelerated deterioration trends leading to suboptimal remaining useful life utilization, this study proposes a Time-Based Incomplete Maintenance (TBIM) strategy incorporating reliability constraints through stochastic differential equations (SDE). By quantifying stochastic interference via Brownian motion terms and characterizing nonlinear degradation features through state influence rate functions, a high-precision SDE degradation model is constructed, achieving 16% residual reduction compared to… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Energy Engineering, Vol.123, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.070501 - 27 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Artificial Intelligence-Driven Advanced Wave Energy Control Technology)
Abstract Wave energy is a promising form of marine renewable energy that offers a sustainable pathway for electricity generation in coastal regions. Despite Malaysia’s extensive coastline, the exploration of wave energy in Sarawak remains limited due to economic, technical, and environmental challenges that hinder its implementation. Compared to other renewable energy sources, wave energy is underutilized largely because of cost uncertainties and the lack of local performance data. This research aims to identify the most suitable coastal zone in Sarawak that achieves an optimal balance between energy potential, cost-effectiveness, and environmental impact, particularly in relation to… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Energy Engineering, Vol.123, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.068653 - 27 January 2026
Abstract The deep coal reservoir in Linxing-Shenfu block of Ordos Basin is an important part of China’s coalbed methane resources. In the process of reservoir reconstruction, the artificial fracture morphology of coal seam with gangue interaction is significantly different, which affects the efficient development of coalbed methane resources in this area. In this paper, the surface outcrop of Linxing-Shenfu block is selected, and three kinds of interaction modes between gangue and coal seam are set up, including single-component coal rock sample, coal rock sample with different thicknesses of gangue layer and coal rock sample with different… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Energy Engineering, Vol.123, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.069878 - 27 January 2026
Abstract To enhance the low-carbon economic efficiency and increase the utilization of renewable energy within integrated energy systems (IES), this paper proposes a low-carbon dispatch model integrating power-to-gas (P2G), carbon capture and storage (CCS), hydrogen fuel cell (HFC), and combined heat and power (CHP). The P2G process is refined into a two-stage structure, and HFC is introduced to enhance hydrogen utilization. Together with CCS and CHP, these devices form a multi-energy conversion system coupling electricity, heat, cooling, and gas. A ladder-type carbon trading approach is adopted to flexibly manage carbon output by leveraging marginal cost adjustments.… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Energy Engineering, Vol.123, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.070290 - 27 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Green and Low-Carbon Pipeline Transportation Theory and Technology for Petroleum, Natural Gas, and Unconventional Media)
Abstract Shock waves in the nozzle during supersonic separation under different conditions can disrupt the flow field’s thermodynamic equilibrium. While it contributes to the recovery of pressure energy, it also leads to the dissipation of mechanical energy. This study aimed to investigate the effects of changes in back pressure on the shock wave position and its subsequent impact on the refrigeration performance of nozzles. A mathematical model for the supersonic gas in a nozzle was established and evaluated via experiments. The results show that when the back pressure is less than 0.2 MPa, no shock wave… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Energy Engineering, Vol.123, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.073313 - 27 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advancements in Energy Resources and Their Processes, Systems, Materials and Policies for Affordable Energy Sustainability)
Abstract In the present study, researchers examined a solar off-grid-connected photovoltaic system for a family house in the city of Baghdad. The design was created with the help of the “How to Design PV Program” and the “Renewable Energy Investment Calculator (REICAL)” software (Version 1.1). In Iraq, the national grid provides around 71% of the overall electricity demand, though this drops to nearly 50% during extremely hot and cold months, where the supply alternates between four hours on and four hours off. During the off periods, power is generated by local generators at high costs. To… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Energy Engineering, Vol.123, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.070733 - 27 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Grid Integration of Intermittent Renewable Energy Resources: Technologies, Policies, and Operational Strategies)
Abstract The construction of spot electricity markets plays a pivotal role in power system reforms, where market clearing systems profoundly influence market efficiency and security. Current clearing systems predominantly adopt a single-system architecture, with research focusing primarily on accelerating solution algorithms through techniques such as high-efficiency parallel solvers and staggered decomposition of mixed-integer programming models. Notably absent are systematic studies evaluating the adaptability of primary-backup clearing systems in contingency scenarios—a critical gap given redundant systems’ expanding applications in operational environments. This paper proposes a comprehensive evaluation framework for analyzing dual-system adaptability, demonstrated through an in-depth case… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Energy Engineering, Vol.123, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.070750 - 27 January 2026
Abstract Hydraulic fracturing serves as a critical technology for reservoir stimulation in deep coalbed methane (CBM) development, where the mechanical properties of gangue layers exert a significant control on fracture propagation behavior. To address the unclear mechanisms governing fracture penetration across coal-gangue interfaces, this study employs the Continuum-Discontinuum Element Method (CDEM) to simulate and analyze the vertical propagation of hydraulic fractures initiating within coal seams, based on geomechanical parameters derived from the deep Benxi Formation coal seams in the southeastern Ordos Basin. The investigation systematically examines the influence of geological and operational parameters on cross-interfacial fracture… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Energy Engineering, Vol.123, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.073329 - 27 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Recent Advance and Development in Solar Energy)
Abstract The aim of this study is to design, build, and evaluate an indirect forced convection solar dryer adapted to semi-arid climate, such as that of Béchar situated in the west south region of Algeria. The tested drying system consists of a flat-plate solar collector, an insulated two-chamber drying unit, and an Arduino-controlled device that ensures uniform temperature distribution and real-time monitoring using DHT22 sensors. Drying tests were conducted on locally grown beet slices at air temperatures of 45°C, 60°C, and 80°C, with a constant air velocity of 1.2 m/s and a mass flow rate of… More >
Graphic Abstract

 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Energy Engineering, Vol.123, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.073991 - 27 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Revolution in Energy Systems: Hydrogen and Beyond)
Abstract To address the issues of insufficient and imbalanced data samples in proton exchange membrane fuel cell (PEMFC) performance degradation prediction, this study proposes a data augmentation-based model to predict PEMFC performance degradation. Firstly, an improved generative adversarial network (IGAN) with adaptive gradient penalty coefficient is proposed to address the problems of excessively fast gradient descent and insufficient diversity of generated samples. Then, the IGAN is used to generate data with a distribution analogous to real data, thereby mitigating the insufficiency and imbalance of original PEMFC samples and providing the prediction model with training data rich More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Energy Engineering, Vol.123, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.073483 - 27 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advancements in Energy Resources and Their Processes, Systems, Materials and Policies for Affordable Energy Sustainability)
Abstract This paper presents an experimental analysis of a solar-assisted powered underfloor heating system, designed primarily to boost energy efficiency and achieve reliable desired steady-state temperature in buildings. We thoroughly tested the system’s thermal and operational features by subjecting it to three distinct scenarios that mimicked diverse solar irradiance and environmental conditions. Our findings reveal a strong correlation between variations in solar input and overall system performance. The Solar Fraction (SF), our key energy efficiency metric, varied significantly across the cases, ranging from 63.1% up to 88.7%. This high reliance on renewables resulted in a substantial… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Energy Engineering, Vol.123, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.072631 - 27 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Innovative Renewable Energy Systems for Carbon Neutrality: From Buildings to Large-Scale Integration)
Abstract Data center industries have been facing huge energy challenges due to escalating power consumption and associated carbon emissions. In the context of carbon neutrality, the integration of data centers with renewable energy has become a prevailing trend. To advance the renewable energy integration in data centers, it is imperative to thoroughly explore the data centers’ operational flexibility. Computing workloads and refrigeration systems are recognized as two promising flexible resources for power regulation within data center micro-grids. This paper identifies and categorizes delay-tolerant computing workloads into three types (long-running non-interruptible, long-running interruptible, and short-running) and develops… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Energy Engineering, Vol.123, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.070905 - 27 January 2026
Abstract In view of the insufficient utilization of condition-monitoring information and the improper scheduling often observed in conventional maintenance strategies for photovoltaic (PV) modules, this study proposes a predictive maintenance (PdM) strategy based on Remaining Useful Life (RUL) estimation. First, a RUL prediction model is established using the Transformer architecture, which enables the effective processing of sequential degradation data. By employing the historical degradation data of PV modules, the proposed model provides accurate forecasts of the remaining useful life, thereby supplying essential inputs for maintenance decision-making. Subsequently, the RUL information obtained from the prediction process is… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Energy Engineering, Vol.123, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.073702 - 27 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advancements in Energy Resources and Their Processes, Systems, Materials and Policies for Affordable Energy Sustainability)
Abstract Improving energy efficiency and lowering negative environmental impact through waste heat recovery (WHR) is a critical step toward sustainable cement manufacturing. This study analyzes advanced cogeneration systems for recovering waste heat from the Fallujah White Cement Plant in Iraq. The novelty of this work lies in its direct application and comparative thermodynamic analysis of three distinct cogeneration cycles—the Organic Rankine Cycle, the Single-Flash Steam Cycle, and the Dual-Pressure Steam Cycle—within the Iraqi cement industry, a context that has not been widely studied. The main objective is to evaluate and compare these models to determine the… More >
Graphic Abstract
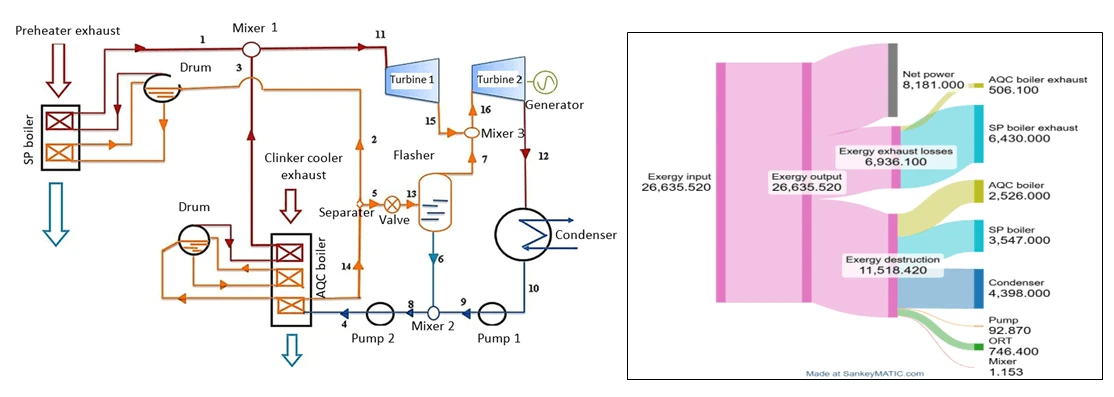
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Energy Engineering, Vol.123, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.068106 - 27 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advanced Analytics on Energy Systems)
Abstract In the quest to enhance energy efficiency and reduce environmental impact in the transportation sector, the recovery of waste heat from diesel engines has become a critical area of focus. This study provided an exhaustive thermodynamic analysis optimizing Organic Rankine Cycle (ORC) systems for waste heat recovery from diesel engines. The study assessed the performance of five candidate working fluids—R11, R123, R113, R245fa, and R141b—under a range of operating conditions, specifically varying overheat temperatures and evaporation pressures. The results indicated that the choice of working fluid substantially influences the system’s exergetic efficiency, net output power,… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Energy Engineering, Vol.123, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.070957 - 27 January 2026
Abstract In order to enhance the off-peak performance of gas turbine combined cycle (GTCC) units, a novel collaborative power generation system (CPG) was proposed. During off-peak operation periods, the remaining power of the GTCC was used to drive the adiabatic compressed air energy storage (ACAES), while the intake air of the GTCC was heated by the compression heat of the ACAES. Based on a 67.3 MW GTCC, under specific demand load distribution, a CPG system and a benchmark system (BS) were designed, both of which used 9.388% of the GTCC output power to drive the ACAES.… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Energy Engineering, Vol.123, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.073940 - 27 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advancements in Energy Resources and Their Processes, Systems, Materials and Policies for Affordable Energy Sustainability)
Abstract Operating Lithium-ion batteries at their temperature limits is a challenging design task due to explosion risk at high temperatures and rapid degradation at low temperatures. Depending on the battery package design, those risks can be solved with passive solutions, which require no active cooling or heating. The current work aims to optimize the pack design and materials of the type-NCR18650B battery based on a wide range of operation temperature. The lower limit was denoted by cold case while the maximum limit was expressed by hot case. A combined analytical-numerical approach was developed to model the… More >