Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Kunyi Wu1, Bo Lei1, Yanhua Qiu1, Hui Li2, Shize Wei1, Feng Wang1, Yu Wu1,*, Liming Zhang2,*
FDMP-Fluid Dynamics & Materials Processing, DOI:10.32604/fdmp.2026.076662
Abstract This study investigates in-station pressure drop mechanisms in a shale gas gathering system, providing a quantitative basis for flow system optimization. Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations, based on field-measured parameters related to a representative case (a shale gas platform located in Sichuan, China) are conducted to analyze the flow characteristics of specific fittings and manifolds, and to quantify fitting resistance coefficients and manifold inlet interference. The resulting coefficients are integrated into a full-station gathering network model in PipeSim, which, combined with production data, enables evaluation of pressure losses and identification of equivalent pipeline blockages. The… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Maolei Cui1,2,*, Zengmin Lun1,2, Jie Zhang1,2, Jun Niu1,2, Pufu Xiao1,2
FDMP-Fluid Dynamics & Materials Processing, DOI:10.32604/fdmp.2026.075360
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Multiphase Fluid Flow Behaviors in Oil, Gas, Water, and Solid Systems during CCUS Processes in Hydrocarbon Reservoirs)
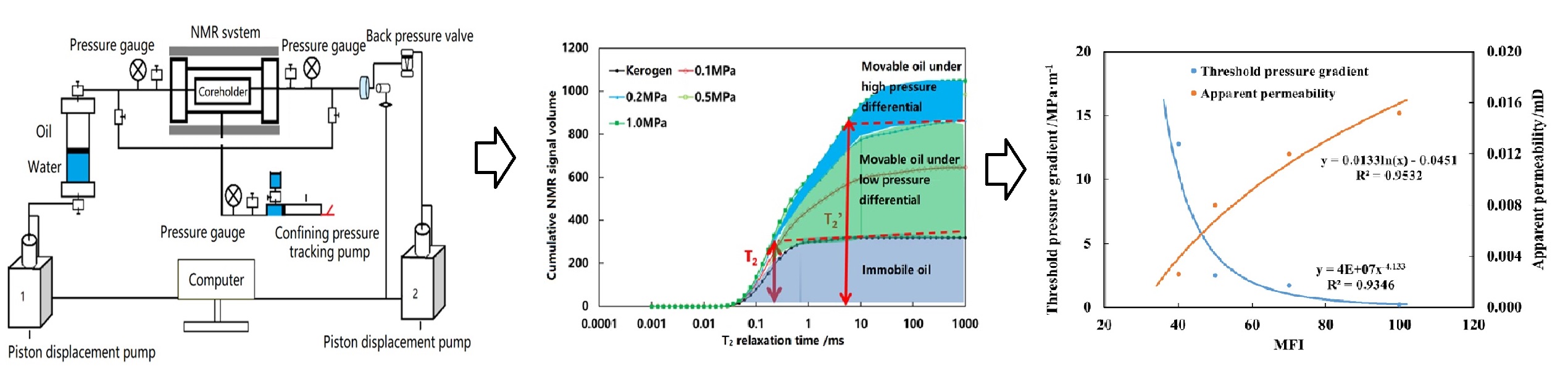
Abstract To clarify fluid flow mechanisms and establish effective development conditions in continental shale oil reservoirs, a high-temperature, high-pressure steady-state flow system integrated with nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) technology has been developed. The apparatus combines sample evacuation, rapid pressurization and saturation, and controlled displacement, enabling systematic investigation of single-phase shale oil flow under representative reservoir conditions. Related experiments allow proper quantification of the activation thresholds and relative contributions of different pore types to flow. A movable fluid index (MFI), defined using dual T2 cutoff values, is introduced accordingly and linked to key flow parameters. The results reveal… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Hongyun Bai1,2, Jianxin Xu1,2,*, Wenbo Shi1,2, Xiaowei Ma3, Jun Ma3, Shaoyin Zhu3, Hua Wang1,2
FDMP-Fluid Dynamics & Materials Processing, DOI:10.32604/fdmp.2026.076265
Abstract Optimizing pyrolysis processes is critical for improving the efficiency of pyrolysis furnaces. This study presents a strategy to enhance heat transfer through agitation, employing Fluent for detailed numerical simulation of the thermal behavior. The simulation results show strong agreement with experimental measurements of localized fluid temperature rise. Forced convection induced by impeller rotation significantly improves heat transfer between the fluid and the furnace walls, effectively reducing thermal stratification. At an impeller speed of 240 RPM, the axial temperature difference decreases from 200 K to 50 K compared with stationary conditions, while the average heat transfer More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Umberto Ravelli1, Silvia Ravelli2,*
FDMP-Fluid Dynamics & Materials Processing, DOI:10.32604/fdmp.2026.075225
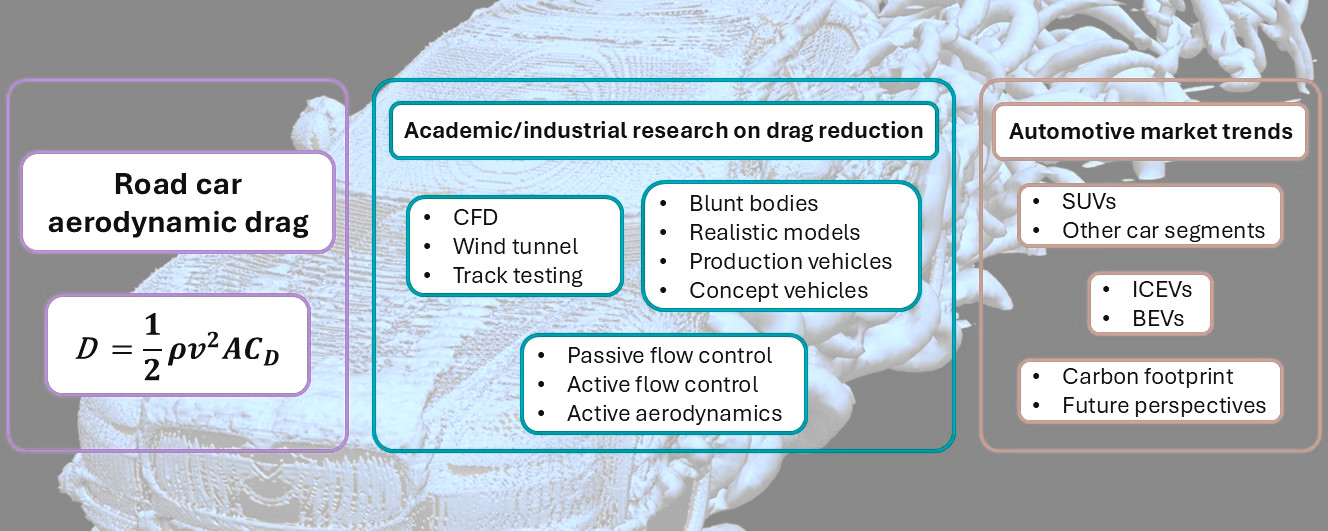
Abstract Aerodynamic research on road cars was reviewed in this work under the thread of reducing drag, with the awareness that this may succeed in effectively decreasing the carbon footprint of transportation. First, a selection of studies was presented to focus on the most important aerodynamic features of the flow around realistic car body shapes. Then, the discussion was organized around three pillars related to passive flow control, active flow control and active aerodynamics. Both experimental and numerical investigations were included to provide a comprehensive overview. A clear distinction was made between simplified and realistic car More >
Graphic Abstract