 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Goodness Adediran1, Kenny Awuson-David2, Yussuf Ahmed1,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.077606
Abstract Amazon Web Services (AWS) CloudTrail auditing service provides detailed records of operational and security events, enabling cloud administrators to monitor user activity and manage compliance. Although signature-based threat detection methods have been enhanced with machine learning and Large Language Models (LLMs), these approaches remain limited in addressing emerging threats. This study evaluates a two-step Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) approach using Gemini 2.5 Pro to enhance threat detection accuracy and contextual relevance. The RAG system integrates external cybersecurity knowledge sources including the MITRE ATT&CK framework, AWS Threat Technique Catalogue, and threat reports to overcome limitations of… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Nahdi Saubari1,2,*, Kunfeng Wang1,*, Rachmat Muwardi3,*, Andri Pranolo4
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.077087
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Novel Methods for Image Classification, Object Detection, and Segmentation, 2nd Edition)
Abstract This study proposes an Adaptive Pooling method based on an alpha (α) parameter to enhance the effectiveness and stability of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) in image classification tasks. Conventional pooling techniques, such as max pooling and average pooling, often exhibit limited adaptability when applied to datasets with heterogeneous distributions and varying levels of complexity. To address this limitation, the proposed approach introduces an α parameter ranging from 0 to 1 that continuously regulates the contribution of maximum-based and average-based pooling operations in a unified and flexible framework. The proposed method is evaluated using two benchmark… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Hao Li1,2, Zhoujingzi Qiu1,2, Jianxiao Zou1,2, Haojie Wu1, Shicai Fan1,2,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.076784
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Intelligent Video Object Tracking and Scene Understanding)
Abstract Self-supervised monocular depth estimation has attracted considerable attention due to its ability to learn without ground-truth depth annotations and its strong scalability. However, existing approaches still suffer from inaccurate object boundaries and limited inference efficiency. To address these issues, we present a Lightweight Conditional Diffusion Model for Monocular Depth Estimation (LCDM-Mono). The proposed framework integrates an efficient diffusion inference strategy with a knowledge distillation scheme, enabling the model to generate high-quality depth maps with only two sampling steps during inference. This design substantially reduces computational overhead and ensures real-time performance on resource-constrained platforms. In addition, More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Oksana Ivanova*, Roman Cherepanov, Sergey Zelepugin
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075451
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Perspective Materials for Science and Industrial: Modeling and Simulation)
Abstract This study presents an investigation into shock-induced exothermic reactions within three distinct aluminum-based energetic mixtures: aluminum/sulfur (Al/S), aluminum/copper oxide (Al/CuO), and aluminum/polytetrafluoroethylene (Al/PTFE). A challenge in current modeling efforts is accurately capturing the complex physical and chemical coupling under extreme loading, especially the influence of rapidly forming gaseous products in Al/PTFE mixtures on material integrity. To address this, a wide-range numerical model based on the Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH) method was developed. This mesh-free approach manages large deformations and incorporates elastic-plastic flow, heat transfer, component diffusion, and chemical kinetics simulated using both zero- and first-order… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Qian Zhang1, Lei Fu1,2, Renzhou Chen3, Xu Zhan4,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.074939
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Additive Manufacturing: Advances in Computational Modeling and Simulation)
Abstract Triply periodic minimal surface (TPMS) structures are widely utilized in engineering and biomedical fields owing to their superior mechanical and functional properties. However, limited by the current additive manufacturing (AM) techniques, insufficient wall thickness often leads to poor forming quality or even printing failure. Therefore, accurate prediction of wall thickness parameters during the design stage is essential. This study proposes a prediction approach for the wall thickness parameters of TPMS models by integrating a Convolutional Neural Network–Support Vector Regression (CNN-SVM) framework with Multiple Linear Regression (MLR). A total of 152 TPMS models were randomly generated,… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Adam Dudáš*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.076507
Abstract It is known that correlation does not imply causality. Some relationships identified in the analysis of data are coincidental or unknown, and some are produced by real-world causality of the situation, which is problematic, since there is a need to differentiate between these two scenarios. Until recently, the proper−semantic−causality of the relationship could have been determined only by human experts from the area of expertise of the studied data. This has changed with the advance of large language models, which are often utilized as surrogates for such human experts, making the process automated and readily… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Udit Mamodiya1,*, Indra Kishor2, P. Satish Reddy3, K. Lakshmi Kalpana3, Radha Seelaboyina4, Harish Reddy Gantla5
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.076464
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: AI and Multiscale Modeling in the Development of Optoelectronic and Thermoelectric Materials)
Abstract The direct conversion of solid-state heat to electricity using thermoelectric materials has attracted attention; however, their effective application is limited because of the challenge of ensuring a balance between the microstructural features at the quantum, mesoscale, and continuum scales. Current computational and machine-learning methods have a small design space, wherein few to no interactions between the electronic structure, phonon transport, and device-level are considered. This makes it difficult to discover stable high-figure of merit (ZT) settings that are manufacturable and strong in the actual working environment. This study presents a multiscale hybrid optimization framework that… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Raed Alotaibi1,*, Muhammad Atta Othman Ahmed2, Omar Reyad3,4,*, Nahla Fathy Omran5
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.076156
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Fake News Detection in the Era of Social Media and Generative AI)
Abstract The widespread use of social media has made assessing users’ tastes and preferences increasingly complex and important. At the same time, the rapid dissemination of misinformation on these platforms poses a critical challenge, driving significant efforts to develop effective detection methods. This study offers a comprehensive analysis leveraging advanced Machine Learning (ML) techniques to classify news articles as fake or true, contributing to discourse on media integrity and combating misinformation. The suggested method employed a diverse dataset encompassing a wide range of topics. The method evaluates the performance of five ML models: Artificial Neural Networks… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Cheng Yang, Xianghong Tang*, Jianguang Lu, Chaobin Wang
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.076126
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Artificial Intelligence Methods and Techniques to Cybersecurity)
Abstract Graph neural networks (GNNs) have demonstrated impressive capabilities in processing graph-structured data, yet their vulnerability to adversarial perturbations poses serious challenges to real-world applications. Existing defense methods often fail to handle diverse types of attacks and adapt to dynamic adversarial strategies because they typically rely on static defense mechanisms or focus narrowly on a single robustness dimension. To address these limitations, we propose an adversarial attention-based robustness strategy (AARS), which is a unified framework designed to enhance the robustness of GNNs against structural and feature perturbations. AARS operates in two stages: the first stage employs More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yanping Chen1, Zhengxin Zhan1, Xiaohui Yan1, Le Zou1,*, Yucheng Zhong1, Hailei Wang2
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075459
Abstract With the increasing complexity of substation inspection tasks, achieving efficient and safe path planning for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles in densely populated and structurally complex three-dimensional (3D) environments remains a critical challenge. To address this problem, this paper proposes an improved path planning algorithm—Random Geometric Graph (RGG)-guided Rapidly-exploring Random Tree (R-RRT)—based on the classical Rapidly-exploring Random Tree (RRT) framework. First, a refined 3D occupancy grid map is constructed from Light Detection and Ranging point cloud data through ground filtering, noise removal, coordinate transformation, and obstacle inflation using spherical structuring elements. During the planning stage, a dynamic… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Bofan Yang, Bingbing Li, Chuanping Hu*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.077697
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Artificial Intelligence Methods and Techniques to Cybersecurity)
Abstract The rapid evolution of malware obfuscation and packing techniques significantly undermines the effectiveness of traditional static detection approaches. Transforming malware binaries into grayscale or RGB images enables learning-based classification, yet existing CNN- and ViT-based models depend heavily on fixed-resolution inputs and exhibit poor robustness under cross-resolution distortions. This study proposes a lightweight and sample-adaptive Multi-Scale Vision Transformer (MSA-ViT) for efficient and robust malware image classification. MSA-ViT leverages a fixed set of input scales and integrates them using a Scale-Attention Fusion (SAF) module, where the largest-scale CLS token serves as the query to dynamically aggregate cross-scale More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Ching-Lung Fan*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.077260
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Development and Application of Deep Learning and Image Processing)
Abstract Unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) images have high spatial resolution and are cost-effective to acquire. UAV platforms are easy to control, and the prevalence of UAVs has led to an emerging field of remote sensing technologies. However, the details of high-resolution images often lead to fragmented classification results and significant scale differences between objects. Additionally, distinguishing between objects on the basis of shape or textural characteristics can be difficult. Conventional classification methods based on pixels and objects can indeed be ineffective at detecting complex and fine-scale land use and land cover (LULC) features. Therefore, in this More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Zuoquan Zhu*, Menghan Wang, Xinyu Li, Mengxin Zhao
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.076418
Abstract Investigating the deformation behavior of graphene-reinforced composite structures holds significant engineering implications, while the rapid advancement of machine learning has introduced new technical approaches to structural bending analysis. In this study, we investigate the mechanical bending behavior of graphene origami (GOri)-enabled auxetic metamaterial beams using a physics-informed neural network (PINN). GOri-enabled auxetic metamaterials represent an innovative composite system characterized by a negative Poisson’s ratio (NPR) and superior mechanical performance. Here, we propose a composite beam model incorporating the modified coupled stress theory (MCST) and employing the PINN method to solve higher-order bending governing equations. Compared More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Abdulaziz A. Alsulami1,*, Badraddin Alturki2, Ahmad J. Tayeb2, Rayan A. Alsemmeari2, Raed Alsini1
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.076413
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in IoT Security: Challenges, Solutions, and Future Applications)
Abstract Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) play a critical role in protecting networked environments from cyberattacks. They have become increasingly important in smart environments such as the Internet of Things (IoT) systems. However, IDS for IoT networks face critical challenges due to hardware constraints, including limited computational resources and storage capacity, which lead to high feature dimensionality, prediction uncertainty, and increased processing cost. These factors make many conventional detection approaches unsuitable for real-time IoT deployment. To address these challenges, this paper proposes an adaptive intrusion detection framework that intelligently balances detection accuracy and computational efficiency. The proposed… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Hongjiang Wang1, Jian Yu2, Tian Zhang3, Na Ren4, Nan Zhang2, Zhenyu Liu1,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.077997
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Intelligent Computation and Large Machine Learning Models for Edge Intelligence in industrial Internet of Things)
Abstract The rapid deployment of Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) systems, such as large-scale photovoltaic (PV) power stations in modern power grids, has created a strong demand for edge-intelligent fault localization methods that can operate reliably under strict computational and memory constraints. In this work, we propose an edge-intelligent photovoltaic fault localization framework that integrates intelligent computation with classical sub-pixel optimization. The framework adopts a modular, edge-oriented design in which a radial basis function (RBF) network is first employed as a lightweight screening module to enable conditional execution, thereby reducing unnecessary computation for non-faulty samples. For… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Chung-Wei Kuo1,2,*, Cheng-Xuan Wu1
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.076767
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Secure and Intelligent Intrusion Detection for IoT and Cloud-Integrated Environments)
Abstract The rapid proliferation of the Internet of Things (IoT) has not only reshaped the digital ecosystem but also significantly widened the attack surface, leading to a surge in network traffic and diverse security threats. Deploying effective defense mechanisms in such environments is challenging, as conventional Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) often struggle to balance computational efficiency with the reliable detection of low-frequency, high-impact threats, particularly within the tight resource constraints of edge devices. To address these limitations, we propose a lightweight, high-efficiency IDS framework specifically optimized for edge-based IoT applications, incorporating Mutual Information (MI)-based feature selection… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Chia-Hui Liu1, Zhen-Yu Wu2,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075495
Abstract Federated Learning (FL) enables collaborative medical model training without sharing sensitive patient data. However, existing FL systems face increasing security risks from post quantum adversaries and often incur non-negligible computational and communication overhead when encryption is applied. At the same time, training high performance AI models requires large volumes of high quality data, while medical data such as patient information, clinical records, and diagnostic reports are highly sensitive and subject to strict privacy regulations, including HIPAA and GDPR. Traditional centralized machine learning approaches therefore pose significant challenges for cross institutional collaboration in healthcare. To address… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Chen Yu, Jingjing Tan, Wenwu Zhao, Ke Gu*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075457
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Towards Privacy-preserving, Secure and Trustworthy AI-enabled Systems)
Abstract Although federated learning (FL) improves privacy-preserving by updating parameters without collecting original user data, their shared gradients still leak sensitive user information. Existing differential privacy and encryption techniques typically focus on whether the aggregated gradient is correctly processed and verified only, rather than whether each user is honestly trained locally. To address these above issues, we propose a gradient feature-based collaborative filtering scheme in verification federated learning, where the authenticity of user training is verified using the collaborative filtering (CF) method based on gradient features. Compared with single user gradient detection (such as similarity detection More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yuanmeng Chang, Hongmei Liu*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.074204
Abstract Driven by rapid advances in deep learning, object detection has been widely adopted across diverse application scenarios. However, in low-light conditions, critical visual cues of target objects are severely degraded, posing a significant challenge for accurate low-light object detection. Existing methods struggle to preserve discriminative features while maintaining semantic consistency between low-light and normal-light images. For this purpose, this study proposes a DL-YOLO model specially tailored for low-light detection. To mitigate target feature attenuation introduced by repeated downsampling, we design a Multi-Scale Feature Convolution (MSF-Conv) module that captures rich, multi-level details via multi-scale feature learning, More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Wasfieh Nazzal1, Ezequiel López-Rubio1,2,3, Miguel A. Molina-Cabello1,2,3, Karl Thurnhofer-Hemsi1,2,3,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.077561
Abstract Automatic and accurate medical image segmentation remains a fundamental task in computer-aided diagnosis and treatment planning. Recent advances in foundation models, such as the medical-focused Segment Anything Model (MedSAM), have demonstrated strong performance but face challenges in many medical applications due to anatomical complexity and a limited domain-specific prompt. This work introduces a methodology that enhances segmentation robustness and precision by automatically generating multiple informative point prompts, rather than relying on single inputs. The proposed approach randomly samples sets of spatially distributed point prompts based on image features, enabling MedSAM to better capture fine-grained anatomical… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Yihao Kuang1,2, Hong Zhang1,2, Jiaqi Wang1,2, Lingyu Jin1,2, Bo Huang1,2,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.076652
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Video Object Tracking: Methods, Challenges, and Applications)
Abstract 3D single object tracking (SOT) based on point clouds is a fundamental task for environmental perception in autonomous driving and dynamic scene understanding in robotics. Recent technological advancements in this field have significantly bolstered the environmental interaction capabilities of intelligent systems. This field faces persistent challenges, including feature degradation induced by point cloud sparsity, representation drift caused by non-rigid deformation, and occlusion in complex scenarios. Traditional appearance matching methods, particularly those relying on Siamese networks, are severely constrained by point cloud characteristics, often failing under rapid motions or structural ambiguities among similar objects. In response,… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yuchuan Gu1,2, Lusheng Wang1,*, Jun Ding1, Yanhong Peng1, Changgeng Li3,*, Shaojie Gu4,5
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075939
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Computational Materials Design and Intelligent Processing for Advanced Alloys and Manufacturing Systems)
Abstract In materials science and engineering design, high-fidelity and high-efficiency numerical simulation has become a driving force for innovation and practical implementation. To address longstanding bottlenecks in the development of conventional material constitutive models—such as lengthy modeling cycles and difficulties in numerical implementation—this study proposes an intelligent modeling and code generation approach powered by large language models. A structured knowledge base integrating constitutive theory, numerical algorithms, and UMAT (User Material) interface specifications is constructed, and a retrieval-augmented generation strategy is employed to establish an end-to-end workflow spanning experimental data parsing, constitutive model formulation, and automatic UMAT… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Saeid Sheikhi*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.077788
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Artificial Intelligence Algorithms and Applications, 2nd Edition)
Abstract Metaheuristic optimization algorithms continue to be essential for solving complex real-world problems, yet existing methods often struggle with balancing exploration and exploitation across diverse problem landscapes. This paper proposes a novel nature-inspired metaheuristic optimization algorithm named the Painted Wolf Optimization (PWO) algorithm. The main inspiration for the PWO algorithm is the group behavior and hunting strategy of painted wolves, also known as African wild dogs in the wild, particularly their unique consensus-based voting rally mechanism, a behavior fundamentally distinct from the social dynamics of grey wolves. In this innovative process, pack members explore different areas… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Anandkumar Balasubramaniam, Seung Yeob Nam*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.077582
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence for Intrusion Detection Systems)
Abstract The increasing connectivity of modern vehicles exposes the in-vehicle controller area network (CAN) bus to various cyberattacks, including denial-of-service, fuzzy injection, and spoofing attacks. Existing machine learning and deep learning intrusion detection systems (IDS) often rely on labeled data, struggle with class imbalance, lack interpretability, and fail to generalize well across different datasets. This paper proposes a lightweight and interpretable IDS framework based on non-negative matrix factorization (NMF) to address these limitations. Our contributions include: (i) evaluating NMF as both a standalone unsupervised detector and an interpretable feature extractor (NMF-W) for classical, unsupervised, and deep… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Fengqi Hao1,2,3, Yawen Hou2,3, Conghui Gao2,3, Jinqiang Bai2,3, Gang Liu4, Hoiio Kong1,*, Xiangjun Dong1,2,3
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.077252
Abstract Field–road classification, a fine-grained form of agricultural machinery operation-mode identification, aims to use Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) trajectory data to assign each trajectory point a semantic label indicating whether the machine is performing field work or travelling on roads. Existing methods struggle with highly imbalanced class distributions, noisy measurements, and intricate spatiotemporal dependencies. This paper presents AgroGeoDB-Net, a unified framework that combines a residual BiLSTM backbone with two tightly coupled innovations: (i) a Density-Aware Local Interpolator (DALI), which balances the minority road class via density-aware interpolation while preserving road-segment structure; and (ii) a geometry-aware… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Wenxuan Yu1, Wenjing Gao1, Jiuru Wang2, Rong Hao1,*, Jia Yu1,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.076731
Abstract Non-negative Matrix Factorization (NMF) is a computationally intensive matrix operation that resource-constrained clients struggle to complete locally. Privacy-preserving outsourcing allows clients to offload heavy computing tasks to powerful servers, effectively solving the problem of local computing difficulties. However, the existing privacy-preserving NMF outsourcing schemes only allow one server to perform outsourcing computation, resulting in low efficiency on the server side. In order to improve the efficiency of outsourcing computation, we propose a privacy-preserving parallel NMF outsourcing scheme with multiple edge servers. We adopt the matrix blocking technique to divide the computation task into multiple subtasks, More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yuzhou Han1,*, Zhuoran Li1, Ahmad Gendia2,3, Teruji Ide4, Osamu Muta2,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.076555
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advancements in Mobile Computing for the Internet of Things: Architectures, Applications, and Challenges)
Abstract Spectrum sensing is an indispensable core part of cognitive radio dynamic spectrum access (DSA) and a key approach to alleviating spectrum scarcity in the Internet of Things (IoT). The key issue in practical IoT networks is robust sensing under the coexistence of low signal-to-noise ratios (SNRs) and non-Gaussian impulsive noise, where observations may be distorted differently across feature modalities, making conventional fusion unstable and degrading detection reliability. To address this challenge, the generalized Gaussian distribution (GGD) is adopted as the noise model, and a multimodal fusion framework termed BCAM-Net (bidirectional cross-attention multimodal network) is proposed.… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Azhar G. Hamad1, Nasser Firouzi2,*, Yousef S. Al Rjoub3
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075840
Abstract The accurate mechanical analysis of thick-walled pressure vessel structures composed of advanced materials, such as hyperelastic and functionally graded materials (FGMs), is critical for ensuring their safety and optimizing their design. However, conventional numerical methods can face challenges with the non-linearities inherent in hyperelasticity and the complex spatial variations in FGMs. This paper presents a novel hybrid numerical approach combining Physics-Informed Neural Networks (PINNs) with Finite Element Method (FEM) derived data for the robust analysis of thick-walled, axisymmetric, heterogeneous, hyperelastic pressure vessels with elliptical geometries. A PINN framework incorporating neo-Hookean constitutive relations is developed in… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Fang Hao1, Puyuan Hu2, Yumo Jiang2, Ruonan Liu2,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075655
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advancements in Mobile Computing for the Internet of Things: Architectures, Applications, and Challenges)
Abstract Industrial fault diagnosis is a critical challenge in complex systems, where sensor data is often noisy and interdependencies between components are difficult to capture. Traditional methods struggle to effectively model these complexities. This paper presents a novel approach by transforming fault diagnosis into a graph recognition task, using sensor data represented as graph-structured data with the k-nearest neighbors (KNN) algorithm. A Graph Transformer is applied to extract node and graph features, with a combined loss function of cross-entropy and weighted consistency loss to stabilize graph representations. Experiments on the TFF dataset show that Graph Transformer More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Xinyue Zhang1, Yuxuan Zhao2, Jeremy S. Smith3, Yuechun Wang4, Gabriela Mogos5, Ka Lok Man1, Yutao Yue6,7,8,9, Young-Ae Jung10,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075415
Abstract Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS) represent a cornerstone in modern traffic management, leveraging surveillance cameras as primary visual sensors to monitor road conditions. However, the fixed characteristics of public surveillance cameras, coupled with inherent image resolution limitations, pose significant challenges for Small Object Detection (SOD) in traffic surveillance. To address these challenges, this paper proposes Ghost-Attention YOLO (GA-YOLO), a lightweight model derived from YOLOv8 and specifically designed for traffic SOD. To enhance the attention of small targets and critical features, a novel channel-spatial attention mechanism, termed Small-object Extend Attention (SEA), is introduced. In addition, the original… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Zhe Ding1,2, Hao Yi3,4,*, Wenrui Xie3,4, Ming Zhang1, Yuxuan Xiao1, Qixu Wang1,2, Qing Chen5, Zhiguang Qin1, Dajiang Chen1
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.074244
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Deep Learning and Neural Networks: Architectures, Applications, and Challenges)
Abstract Federated semi-supervised learning (FSSL) has garnered substantial attention for enabling collaborative global model training across multiple clients to address the scarcity of labeled data and to preserve data privacy. However, FSSL is plagued by formidable challenges stemming from cross-client data heterogeneity, as existing methods fail to achieve effective fusion of feature subspaces across distinct clients. To address this issue, we propose a novel FSSL framework, named FedSPQR, which is explicitly tailored for the label-at-server scenario. On the server side, FedSPQR adopts subspace clustering and fusion method based on the Grassmann manifold to construct a unified More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Soo-Yeon Jeong1, Ho-Yeon Jeong2, Sun-Young Ihm3,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.074016
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Additive Manufacturing: Advances in Computational Modeling and Simulation)
Abstract Sign language is a primary mode of communication for individuals with hearing impairments, conveying meaning through hand shapes and hand movements. Contrary to spoken or written languages, sign language relies on the recognition and interpretation of hand gestures captured in video data. However, sign language datasets remain relatively limited compared to those of other languages, which hinders the training and performance of deep learning models. Additionally, the distinct word order of sign language, unlike that of spoken language, requires context-aware and natural sentence generation. To address these challenges, this study applies data augmentation techniques to… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yuechuan Zhang1,2, Mingshu Zhang1,2,*, Bin Wei1,2, Hongyu Jin1,2, Yaxuan Wang1,2
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.073996
Abstract Detecting fake news in multimodal and multilingual social media environments is challenging due to inherent noise, inter-modal imbalance, computational bottlenecks, and semantic ambiguity. To address these issues, we propose SparseMoE-MFN, a novel unified framework that integrates sparse attention with a sparse-activated Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture. This framework aims to enhance the efficiency, inferential depth, and interpretability of multimodal fake news detection. SparseMoE-MFN leverages LLaVA-v1.6-Mistral-7B-HF for efficient visual encoding and Qwen/Qwen2-7B for text processing. The sparse attention module adaptively filters irrelevant tokens and focuses on key regions, reducing computational costs and noise. The sparse MoE module dynamically… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Basudev Nath1, Deepak Sahoo1, Sudhansu Shekhar Patra2, Hassan Alkhiri3, Subrata Chowdhury4, Sheraz Aslam5,6,*, Kainat Mustafa7
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.073486
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Deep Learning and Neural Networks: Architectures, Applications, and Challenges)
Abstract Accurate, up to date, and quick information related to any disaster supports disaster management team/authorities to perform quick, easy, and cost-effective response to enhance rescue operations to alleviate the possible loss of lives, financial risks, and properties. Due to damaged infrastructure in disaster-affected areas, social media is the only way to share/ exchange real time information. Therefore, ‘X’ (formerly Twitter) has become a major platform for disseminating real-time information during disaster events or emergencies, i.e., floods and earthquake. Rapid identification of actionable content is critical for effective humanitarian response; however, the brief and noisy nature… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Jinwei Mao1,2, Wang Luo1,2,*, Jiangtao Xu3, Daohua Zhu3, Wei Liang3, Zhechen Huang3, Bao Feng1,2, Shuang Yang1,2
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.072505
Abstract With the rapid development of power Internet of Things (IoT) scenarios such as smart factories and smart homes, numerous intelligent terminal devices and real-time interactive applications impose higher demands on computing latency and resource supply efficiency. Multi-access edge computing technology deploys cloud computing capabilities at the network edge; constructs distributed computing nodes and multi-access systems and offers infrastructure support for services with low latency and high reliability. Existing research relies on a strong assumption that the environmental state is fully observable and fails to thoroughly consider the continuous time-varying features of edge server load fluctuations,… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yang Lei1,2, Kangshuo Zhu3,4,*, Bo Jiang1, Yaodong Wang3,4, Feiyu Jia1, Zhaoning Wang1, Falin Qi1, Qiming Qu1
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.077314
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Intelligent Transportation System (ITS) Safety and Security)
Abstract The safe operation of railway systems necessitates efficient and automated inspection of tunnel defects. While deep learning offers solutions, a clear pathway for selecting and optimizing the latest object detectors for distinct defects under strict speed constraints is lacking. This paper presents a two-stage, task-specific framework for high-speed tunnel defect detection. First, this study conducts a comprehensive comparative analysis of state-of-the-art YOLO models (YOLOv5s, YOLOv8s, YOLOv10s, YOLOv11s) on self-constructed datasets. This systematic comparison identifies YOLOv5s as the optimal model for crack detection, achieving an mAP@0.5 of 0.939 at 77.5 FPS, sufficient for inspection at 50… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Chan-Woo Kim#, Sung-Jun Lee#, Chang-Lae Kim*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.077143
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Computational Approaches for Tribological Materials and Surface Engineering)
Abstract Epoxy resins are widely used as protective coatings due to their excellent adhesion and chemical resistance; however, their inherent brittleness and susceptibility to shear stress-induced crack propagation limit their tribological performance. This study investigates the stress distribution mechanisms governing the wear resistance of solvent-textured epoxy coatings using finite element analysis (FEA) and experimental validation. Three solvents with distinct volatilities—acetone, methyl ethyl ketone (MEK), and ethyl acetate (EA)—generated characteristic surface morphologies through Marangoni convection, with roughness ranging from Ra = 0.17 μm (EA) to 0.66 μm (acetone). X-ray diffraction (XRD) and Fourier-transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy confirmed… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Mohamed Diouf1, Elisée Toe1,*, Manel Grichi2, Haïfa Nakouri1,3, Fehmi Jaafar1
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.077139
Abstract Software security bugs present significant security risks to modern systems, leading to unauthorized access, data breaches, and severe operational and financial consequences. Early prediction of such vulnerabilities is therefore essential for strengthening software reliability and reducing remediation costs. This study investigates the extent to which static software quality metrics can identify vulnerable code and evaluates the effectiveness of machine learning models for large-scale security-bug prediction. We analyze a dataset of 338,442 source files, including 33,294 buggy files, collected from seven major open-source ecosystems. These ecosystems include GitHub Security Advisories (GHSA), Python Package Index (PyPI), OSS-Fuzz… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Pratik Goswami1,#, Hamid Naseem2,#, Khizar Abbas3,*, Kwonhue Choi1,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.077012
Abstract In a distributed edge computing environment, Internet of Things (IoT) and Vehicular-IoT (V-IoT) devices communicate through Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) by collecting and transmitting data from different environments. Although energy efficiency is always a critical challenge in WSN due to limited battery power, along with the demand for fast communication over edge devices in 5G and beyond 5G scenarios. Therefore, to overcome the challenges, an advanced hierarchical agent-based power management scheme is proposed for WSNs that optimizes energy distribution while maintaining reliable communication. The proposed model employs Master Agents (MAs), Coordination Agents (CoAs), and Task More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Pablo Guillén1, Enrique Frias-Martinez2,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.076400
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Bridging the Gap: AutoML and Explainable AI for Industrial and Healthcare Innovations)
Abstract Alzheimer’s disease (AD) diagnosis and prognosis increasingly rely on machine learning (ML) models. Although these models provide good results, clinical adoption is limited by the need for technical expertise and the lack of trustworthy and consistent model explanations. SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations) is commonly used to interpret AD models, but existing studies tend to focus on explanations for isolated tasks, providing little evidence about their robustness across disease stages, model architectures, or prediction objectives. This paper proposes a multi-level explainability framework that measures the coherence, stability and consistency of explanations by integrating: (1) within-model coherence… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Mirna Yunita1, Xiabi Liu1,*, Zhaoyang Hai1, Rachmat Muwardi2
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075073
Abstract Designing appropriate loss functions is critical to the success of supervised learning models. However, most conventional losses are fixed and manually designed, making them suboptimal for diverse and dynamic learning scenarios. In this work, we propose an Adaptive Meta-Loss Network (Adaptive-MLN) that learns to generate task-agnostic loss functions tailored to evolving classification problems. Unlike traditional methods that rely on static objectives, Adaptive-MLN treats the loss function itself as a trainable component, parameterized by a shallow neural network. To enable flexible, gradient-free optimization, we introduce a hybrid evolutionary approach that combines Genetic Algorithms (GA) for global More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yong Hu1, Weifan Xu2, Xiangtong Du3,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.074437
Abstract Deep learning-based methods have shown great potential in intelligent bearing fault diagnosis. However, most existing approaches suffer from the scarcity of labeled data, which often results in insufficient robustness under complex working conditions and a general lack of interpretability. To address these challenges, we propose a physics-informed multimodal fault diagnosis framework based on few-shot learning, which integrates a 2D time-frequency image encoder and a 1D vibration signal encoder. Specifically, we embed prior knowledge of multi-resolution analysis from signal processing into the model by designing a Laplace Wavelet Convolution (LWC) module, which enhances interpretability since wavelet More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Wajdan Al Malwi1, Fatima Asiri1, Nazik Alturki2, Noha Alnazzawi3, Dimitrios Kasimatis4, Nikolaos Pitropakis5,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.074274
Abstract The expansion of 5G-enabled Internet of Things (IoT) networks, while enabling transformative applications, significantly increases the attack surface and necessitates security solutions that extend beyond traditional intrusion detection. Existing intrusion detection systems (IDSs) mainly operate in an open-loop manner, excelling at classification but lacking the ability for autonomous, safety-aware remediation. This gap is particularly critical in 5G environments, where manual intervention is too slow and naive automation can lead to severe service disruptions. To address this issue, we propose a novel Self-Healing Intrusion Detection System (SH-IDS) framework that develops a closed-loop cyber defense mechanism. The… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Moises Jimenez-Martinez1,*, Gael Ramirez2, Giancarlo Marchetta-Cruz3, Manuel Coca-Gonzalez1
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.074260
Abstract Most failures in component operation occur due to cyclic loads. Validation has been performed under quasistatic loads, but the fatigue life of components under dynamic loads should be predicted to prevent failures during component service life. Fatigue is a damage accumulation process where loads degrade the material, depending on the characteristics and number of repetitions of the load. Studies on the mechanical fatigue of 3D-printed Onyx are limited. In this paper, the strength of 3D-printed Onyx components under dynamic conditions (repetitive loads) is estimated. Fatigue life prediction is influenced by manufacturing processes, material properties, and… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Bakhtawar Gul1, Atif Elahi1,2, Tahir Saleem3, Noor Gul1, Fahad Algarni4, Insaf Ullah5,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.069776
Abstract Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) enables efficient Dynamic Spectrum Access (DSA) but suffers from high sidelobe that causes excessive out-of-band (OOB) emissions and expose the system to spectrum-layer cyberattacks such as man-in-the-middle (MITM), eavesdropping, and primary user emulation (PUE) attacks. To address both spectral leakage and its security implications, this paper introduces a secure and intelligent hybrid optimization strategy that combinesan Eigenspace-based Generalized Sidelobe Canceller (ES-GSC) with a Genetic Algorithm (GA), to derive optimally weighted cancellation carriers. The proposed method jointly suppresses sidelobes and reinforces resistance to leakage-based attacks. MATLAB Simulation demonstrate considerable reductions in More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Seohyun Yoo, Joonseo Hyeon, Jaehyuk Cho*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.077579
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Bridging the Gap: AutoML and Explainable AI for Industrial and Healthcare Innovations)
Abstract Despite remarkable advances in medical large language models (LLMs), their deployment in real clinical settings remains impractical due to prohibitive computational requirements and privacy regulations that restrict cloud-based solutions. Small LLMs (sLLMs) offer a promising alternative for on-premise deployment, yet they require domain-specific fine-tuning that still exceeds the hardware capacity of most healthcare institutions. Furthermore, the impact of multilingual data composition on medical sLLM performance remains poorly understood. We present a resource-efficient fine-tuning pipeline that integrates Quantized Low-Rank Adaptation (QLoRA), Fully Sharded Data Parallelism (FSDP), and Sequence Packing, validated across two model scales: MedGemma 4B… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Kexin Jiang1,2, Yong Fan2, Liang Wen1, Zhigang Xie1, Enzhi Dong1, Bo Zhu1, Zhonghua Cheng1,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.077392
Abstract With the growing deployment of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), reliable engine health state assessment (HSA) requires methods that are interpretable, auditable, and transferable under noisy data and varying operating conditions. This paper proposes an AHP-enhanced, data-driven HSA framework that builds a unified health vector from four indicators—remaining useful life (RUL) health, absolute state, relative degradation, and condition health. Indicator weights are derived using AHP with consistency checking, and the resulting continuous health index is mapped through nonlinear stretching and four-level thresholds to produce actionable health grades. Experiments on the NASA CMAPSS benchmark (FD001) evaluate conventional More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Manh-Tuan Ha1, Nhu-Nghia Bui2, Dinh-Quy Vu1,*, Thai-Viet Dang2,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.077237
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Video Object Tracking: Methods, Challenges, and Applications)
Abstract In the realm of unmanned surface vehicle (USV) operations, leveraging environmental factors to enhance situational awareness has garnered significant academic attention. Developing vision systems for USVs presents considerable challenges, mainly due to variable observational conditions and angular vibrations caused by hydrodynamic forces. The paper proposed a novel MDGAN-DIFI network for end-to-end multi-object tracking (MOT), specifically designed for camera systems mounted on USVs. Beyond enhancing traditional MOT models, the proposed MDGAN-DIFI includes preprocessing modules designed to enhance the efficiency of processing input signal quality. Initially, a Deep Iterative Frame Interpolation (DIFI) module is used to stabilize… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Hye-Min Kwon, Sung-Jun Lee, Chang-Lae Kim*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.077155
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Computational Approaches for Tribological Materials and Surface Engineering)
Abstract UV-curable acrylic polymers are promising for advanced coating applications; however, they suffer from low mechanical strength and wear resistance. This study investigated the effects of zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticle incorporation (0, 1, 3, and 5 wt.%) on mechanical, surface, and tribological properties of UV-curable acrylic polymer nanocomposites. The elastic modulus increased from 9.41 MPa (bare polymer) to 22.39 MPa (5 wt.% ZnO), a 138% improvement. X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis confirmed the formation of a crystalline region at the polymer-ZnO interface, with crystallite sizes reaching 121.94 nm compared to 7.95 nm for the bare-polymer. Surface roughness More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Lan Xiong, Liang Wan*, Jingxia Ren
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.076986
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence for Intrusion Detection Systems)
Abstract The semantic complexity of large-scale malicious payloads in modern network traffic severely limits the robustness and generalization of existing Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS). This limitation presents a major challenge to network security. This paper proposes a dual-branch intrusion detection method called CPS-IDS. This method fuses deep semantic features with statistical features. The first branch uses the DeBERTav2 module. It performs deep semantic modeling on the session payload. This branch also incorporates a Time Encoder. The Time Encoder models the temporal behavior of the packet arrival interval time series. A Cross-Attention mechanism achieves the joint modeling… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Thi-Loan Nguyen1,2,*, Huy-Nam Chu3, The-Thanh Hua3, Trung-Nghia Phung2, Van-Hung Le3,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.076732
Abstract To support the process of grasping objects on a tabletop for the blind or robotic arm, it is necessary to address fundamental computer vision tasks, such as detecting, recognizing, and locating objects in space, and determining the position of the grasping information. These results can then be used to guide the visually impaired or to execute grasping tasks with a robotic arm. In this paper, we collected, annotated, and published the benchmark TQU-GraspingObject dataset for testing, validation, and evaluation of deep learning (DL) models for detecting, recognizing, and localizing grasping objects in 2D and 3D… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Sara Tehsin1,*, Inzamam Mashood Nasir1, Wiem Abdelbaki2, Fadwa Alrowais3, Reham Abualhamayel4, Abdulsamad Ebrahim Yahya5, Radwa Marzouk6
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.076514
Abstract The rapid proliferation of multimodal misinformation on social media demands detection frameworks that are not only accurate but also robust to noise, adversarial manipulation, and semantic inconsistency between modalities. Existing multimodal fake news detection approaches often rely on deterministic fusion strategies, which limits their ability to model uncertainty and complex cross-modal dependencies. To address these challenges, we propose Q-ALIGNer, a quantum-inspired multimodal framework that integrates classical feature extraction with quantum state encoding, learnable cross-modal entanglement, and robustness-aware training objectives. The proposed framework adopts quantum formalism as a representational abstraction, enabling probabilistic modeling of multimodal alignment… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Hongtao Guo1, Shuai Li2, Shu Li1,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.076492
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Machine Learning Methods in Materials Science)
Abstract This paper reviews the research progress and application prospects of machine learning technologies in the field of polymer materials. Currently, machine learning methods are developing rapidly in polymer material research; although they have significantly accelerated material prediction and design, their complexity has also caused difficulties in understanding and application for researchers in traditional fields. In response to the above issues, this paper first analyzes the inherent challenges in the research and development of polymer materials, including structural complexity and the limitations of traditional trial-and-error methods. To address these problems, it focuses on introducing key basic… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
A-Seong Moon, Haesung Kim, Ye-Chan Park, Jaesung Lee*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.076411
Abstract Multimodal emotion recognition has emerged as a key research area for enabling human-centered artificial intelligence, supported by the rapid progress in vision, audio, language, and physiological modeling. Existing approaches integrate heterogeneous affective cues through diverse embedding strategies and fusion mechanisms, yet the field remains fragmented due to differences in feature alignment, temporal synchronization, modality reliability, and robustness to noise or missing inputs. This survey provides a comprehensive analysis of MER research from 2021 to 2025, consolidating advances in modality-specific representation learning, cross-modal feature construction, and early, late, and hybrid fusion paradigms. We systematically review visual,… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Salma Akther1, Wencheng Yang1,*, Song Wang2, Shicheng Wei1, Ji Zhang1, Xu Yang3, Yanrong Lu4, Yan Li1
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.076358
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Artificial Intelligence Methods and Techniques to Cybersecurity)
Abstract As deep learning (DL) models are increasingly deployed in sensitive domains (e.g., healthcare), concerns over privacy and security have intensified. Conventional penetration testing frameworks, such as OWASP and NIST, are effective for traditional networks and applications but lack the capabilities to address DL-specific threats, such as model inversion, membership inference, and adversarial attacks. This review provides a comprehensive analysis of penetration testing for the privacy of DL models, examining the shortfalls of existing frameworks, tools, and testing methodologies. Through systematic evaluation of existing literature and empirical analysis, we identify three major contributions: (i) a critical… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Qiuxiao Mou, Haoyu Gui, Xianghong Tang*, Jianguang Lu
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.076251
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Time Series Analysis, Modelling and Forecasting)
Abstract Electrocardiogram (ECG) is a widely used non-invasive tool for diagnosing cardiovascular diseases. ECG zero-shot classification involves pre-training a model on a large dataset to classify unknown disease categories. However, existing ECG feature extraction networks often neglect key lead signals and spatial topology dependencies during cross-modal alignment. To address these issues, we propose a multimodal channel compression graph attention alignment network (MCCGAA). MCCGAA incorporates a channel attention module (CAM) to effectively integrate key lead features and a graph attention-based alignment network to capture spatial dependencies, enhancing cross-modal alignment. Additionally, MCCGAA employs a log-sum-exp loss function, improving More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Zhi Zhang1,2, Bingyu Sun1,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.076236
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Bridging the Gap: AutoML and Explainable AI for Industrial and Healthcare Innovations)
Abstract In facial landmark detection, shape deviations induced by large poses and exaggerated expressions often prevent existing algorithms from simultaneously achieving fine-grained local accuracy and holistic global shape constraints. To address this, we propose a Transformer-Conv Attention-based Method (TCAM). Built upon a hybrid coordinate-heatmap regression backbone, TCAM integrates the long-range dependency modeling of Transformers with the local feature extraction advantages of Depthwise Convolution (DWConv). Specifically, by partitioning feature maps into sub-regions and applying Transformer modeling, the module enforces sparse linear constraints on global information, effectively mitigating the issues caused by discontinuous landmark distributions. Experimental results on More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Zhu Fang1,2,*, Zhengquan Xu1,2, Weizhen He3, Bohao Xu3
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.076043
Abstract In view of the problem that the IP address jump law is easy to predict in the current mobile target defense, this paper proposes a network address jump active defense method based on a dynamic random graph, designed to improve the unpredictability of IP address translation. Firstly, in order to make IP address transformation unpredictable in space and time, a random graph model is designed to generate a pseudo-random sequence of IP address randomization; these pseudo-random can meet the unpredictability of IP address translation in both space and time. Then, based on these pseudo-random sequences… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Run Jiao, Qingyuan Hou, Ziyu Jiang, Hongxia Wang*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075967
Abstract Mesh models are among the primary representations for storing 3-D objects, encapsulating detailed geometric information. 3-D mesh watermarking, in particular, plays a central role in the protection of 3-D content. However, frequency-domain methods rely on complex parameterization and spectral decomposition, which are sensitive to mesh topology and resolution and often introduce perceptible artifacts. Spatial-domain techniques, on the other hand, typically embed watermarks in global or randomly selected regions, leading to visible distortions and reduced robustness. To address the above limitations and protect model copyright without compromising the original aesthetic quality, we propose a deterministice PCA-synchronized… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Shuai Li1, Dongrong Liu1, Shu Li2,*, Minghua Chen2
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075830
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Machine Learning Methods in Materials Science)
Abstract The exploration of high-performance materials presents a fundamental challenge in materials science, particularly in predicting properties for materials beyond the known range of target property values (extrapolation). This study formally investigated the interpolation-extrapolation trade-off phenomenon in the prediction capabilities of machine learning (ML) models. A new ML scheme was proposed, featuring a newly developed ML model and forward cross-validation-based hyperparameter optimization, which demonstrated superior extrapolation prediction across multiple materials datasets. Based on this ML scheme, multi-objective optimization was performed to systematically identify lightweight Mg-Zn-Al alloys with both high bulk modulus and high Debye temperature. Subsequently, More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Suman Sukhavasi, Thinagaran Perumal*, Norwati Mustapha, Razali Yaakob
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075613
Abstract The Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem is inherently heterogeneous, comprising diverse devices that must interoperate seamlessly to enable federated message and data exchange. However, as the number of service requests grows, existing approaches suffer from increased discovery time and degraded Quality of Service (QoS). Moreover, the massive data generated by heterogeneous IoT devices often contain redundancy and noise, posing challenges to efficient data management. To address these issues, this paper proposes a lightweight ontology-based architecture that enhances service discovery and QoS-aware semantic data management. The architecture employs Modified-Ordered Points to Identify the Clustering Structure (M-OPTICS)… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Chenglong Lu1, Jiehui Li1, Tonglin Chen1,2,*, Changhua Zhou1, Yixin Fan1, Xinlin Ren1, Ziyi Ju1, Wei Wang1
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075400
Abstract Existing methods for tracing water pollution sources typically integrate three-dimensional excitation-emission matrix (3D-EEM) fluorescence spectroscopy with similarity-based matching algorithms. However, these approaches exhibit high error rates in borderline cases and necessitate expert manual review, which limits scalability and introduces inconsistencies between algorithmic outputs and expert judgment. To address these limitations, we propose a large vision-language model (VLM) designed as an “expert agent” to automatically refine similarity scores, ensuring alignment with expert decisions and overcoming key application bottlenecks. The model consists of two core components: (1) rule-based similarity calculation module generate initial spectral similarity scores, and More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Ahmad Salehiyan1, Nuria Serrano2, Francisco Hernando-Gallego3, Diego Martín2,*, José Vicente Álvarez-Bravo2
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075336
Abstract The increasing integration of cyber-physical components in Industry 4.0 water infrastructures has heightened the risk of false data injection (FDI) attacks, posing critical threats to operational integrity, resource management, and public safety. Traditional detection mechanisms often struggle to generalize across heterogeneous environments or adapt to sophisticated, stealthy threats. To address these challenges, we propose a novel evolutionary optimized transformer-based deep reinforcement learning framework (Evo-Transformer-DRL) designed for robust and adaptive FDI detection in smart water infrastructures. The proposed architecture integrates three powerful paradigms: a transformer encoder for modeling complex temporal dependencies in multivariate time series, a… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yujie Tian1, Ming Zhu1, Jing Li1,*, Cong Liu2, Ziyang Zhang1
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075063
Abstract Workflow scheduling is critical for efficient cloud resource management. This paper proposes Tunicate Swarm-Highest Response Ratio Next, a novel scheduler that synergistically combines the Tunicate Swarm Algorithm with the Highest Response Ratio Next policy. The Tunicate Swarm Algorithm generates a cost-minimizing task-to-VM mapping scheme, while the Highest Response Ratio Next dynamically dispatches tasks in the ready queue with the highest-priority. Experimental results demonstrate that the Tunicate Swarm-Highest Response Ratio Next reduces costs by up to 94.8% compared to meta-heuristic baselines. It also achieves competitive cost efficiency vs. a learning-based method while offering superior operational simplicity More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Chu Thi Minh Hue1, Nguyen Minh Quy2,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.074398
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: AI-Driven Next-Generation Networks: Innovations, Challenges, and Applications)
Abstract Nowadays, Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) are making increasingly important contributions to numerous applications that enhance human quality of life, such as sensing and data collection, computing, and communication. However, communication between UAVs still faces challenges due to high-dynamic topology, volatile wireless links, and strict energy budgets. In this work, we introduce an improved communication scheme, namely Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO). Our solution casts hop–by–hop relay selection as a Markov decision process and develops a decentralized Proximal Policy Optimization framework in an actor–critic form. A key novelty is the design of the reward function, which jointly More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Sumbul Azeem1, Shazia Javed1,*, Farheen Ibraheem2, Uzma Bashir1, Nazar Waheed3, Khursheed Aurangzeb4
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.071977
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advancing Feature Engineering for Knowledge Discovery and Explainable AI)
Abstract Data serves as the foundation for training and testing machine learning and artificial intelligence models. The most fundamental part of data is its attributes or features. The feature set size changes from one dataset to another. Only the relevant features contribute meaningfully to classification accuracy. The presence of irrelevant features reduces the system’s effectiveness. Classification performance often deteriorates on high-dimensional datasets due to the large search space. Thus, one of the significant obstacles affecting the performance of the learning process in the majority of machine learning and data mining techniques is the dimensionality of the… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Abuzar Khan1, Abid Iqbal2,*, Ghassan Husnain1,*, Fahad Masood1, Mohammed Al-Naeem3, Sajid Iqbal4
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.077222
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Cloud Computing Security and Privacy: Advanced Technologies and Practical Applications)
Abstract Cloud computing now supports large-scale maritime analytics, yet offloading rich Automatic Identification
System (AIS) data to the cloud exposes sensitive operational patterns and complicates compliance withcross-border privacy regulations. This work addresses the gap between growing demand for AI-driven vessel intelligence
and the limited availability of practical, privacy-preserving cloud solutions. We introduce a privacy-by-designedge-cloud framework in which ports and vessels serve as federated clients, training vessel-type classifiers on local AIStrajectories while transmitting only clipped, Gaussian-perturbed updates to a zero-trust cloud coordinator employingsecure and robust aggregation. Using a public AIS corpus with realistic non-IID client partitions, our… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Hitesh Mohapatra*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.076726
Abstract This review examines current approaches to real-time decision-making and task optimization in Internet of Things systems through the application of machine learning models deployed at the network edge. Existing literature shows that edge-based distributed intelligence reduces cloud dependency. It addresses transmission latency, device energy use, and bandwidth limits. Recent optimization strategies employ dynamic task offloading mechanisms to determine optimal workload placement across local devices and edge servers without centralized coordination. Empirical findings from the literature indicate performance improvements with latency reductions of approximately 32.8% and energy efficiency gains of 27.4% compared to conventional cloud-centric models.… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Ying Yao1, Le Tian1,2,3, Yuxiang Hu1,2,3,*, Pengshuai Cui1,2,3
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075747
Abstract In the process of programmable networks simplifying network management and increasing network flexibility through custom packet behavior, security incidents caused by human logic errors are seriously threatening their safe operation, robust verification methods are required to ensure their correctness. As one of the formal methods, symbolic execution offers a viable approach for verifying programmable networks by systematically exploring all possible paths within a program. However, its application in this field encounters scalability issues due to path explosion and complex constraint-solving. Therefore, in this paper, we propose NetVerifier, a scalable verification system for programmable networks. To… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Wenchao Shi1, Tao Wei2, Chuan Yang3, Qichao Fan3, Hongxi Liu4, Bin Shao5,*, Peng Jing4,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075293
Abstract Enhancing the strength of nanotwinned aluminum (Al) is essential for the development of next-generation high-end chip technology. To better understand the detwinning behavior of nanotwinned Al under conditions with no resolved shear stress acting on the twin boundaries, we conducted molecular dynamics simulations of uniaxial tensile deformation in nanotwinned single-crystal Al at room temperature. Detwinning is observed only when the twin boundary spacing is 7.01 Å. At larger spacings, twin boundaries remain parallel to the loading direction, with no rotation or bending, indicating negligible migration. Detwinning is triggered by localized stress from dislocation interactions, with More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Qi Wang, Kelvin Amos Nicodemas*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.074305
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Time Series Analysis, Modelling and Forecasting)
Abstract Multivariate time series forecasting plays a crucial role in decision-making for systems like energy grids and transportation networks, where temporal patterns emerge across diverse scales from short-term fluctuations to long-term trends. However, existing Transformer-based methods often process data at a single resolution or handle multiple scales independently, overlooking critical cross-scale interactions that influence prediction accuracy. To address this gap, we introduce the Hierarchical Attention Transformer (HAT), which enables direct information exchange between temporal hierarchies through a novel cross-scale attention mechanism. HAT extracts multi-scale features using hierarchical convolutional-recurrent blocks, fuses them via temperature-controlled mechanisms, and optimizes More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Qian Hu, Lei Tan*, Qingjun Yuan, Zong Zuo, Yan Li
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.076137
Abstract Multi-behavior recommendation methods leverage various types of user interaction behaviors to make personalized recommendations. Behavior paths formed by diverse user interactions reveal distinctive patterns between users and items. Modeling these behavioral paths captures multidimensional behavioral features, which enables accurate learning of user preferences and improves recommendation accuracy. However, existing methods share two critical limitations: (1) Lack of modeling for the diversity of behavior paths; (2) Ignoring the impact of item attribute information on user behavior paths. To address these issues, we propose a Directed Behavior path graph-based Multi-behavior Recommendation method (DBMR). Specifically, we first construct… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Dmytro Tymoshchuk1,*, Oleh Yasniy1, Iryna Didych2, Pavlo Maruschak3,*, Yuri Lapusta4
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.077062
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Machine Learning in the Mechanics of Materials and Structures)
Abstract This article presents an approach to predicting the hysteresis behavior of shape memory alloys (SMAs) using a Temporal Convolutional Network (TCN) deep learning model, followed by the interpretation of the results using Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) methods. The experimental dataset was prepared based on cyclic loading tests of nickel-titanium wire at loading frequencies of 0.3, 0.5, 1, 3, and 5 Hz. For training, validation, and testing, 100–250 loading-unloading cycles were used. The input features of the models were stress σ (MPa), cycle number (Cycle parameter), and loading-unloading stage indicator, while the output variable was strain… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yan-Hao Huang*, Yu-Tse Huang
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.076800
Abstract Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) is a common microvascular complication of diabetes that progressively damages the retinal blood vessels and, without timely treatment, can lead to irreversible vision loss. In clinical practice, DR is typically diagnosed by ophthalmologists through visual inspection of fundus images, a process that is time-consuming and prone to inter- and intra-observer variability. Recent advances in artificial intelligence, particularly Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Transformer-based models, have shown strong potential for automated medical image classification and decision support. In this study, we propose a Position-Wise Attention-Enhanced Vision Transformer (PWAE-ViT), which integrates a positional attention… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Sara Tehsin1,*, Muhammad John Abbas2, Inzamam Mashood Nasir1, Fadwa Alrowais3, Reham Abualhamayel4, Abdulsamad Ebrahim Yahya5, Radwa Marzouk6
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.076515
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Bridging the Gap: AutoML and Explainable AI for Industrial and Healthcare Innovations)
Abstract Globally, diabetes and glaucoma account for a high number of people suffering from severe vision loss and blindness. To treat these vision disorders effectively, proper diagnosis must occur in a timely manner, and with conventional methods such as fundus photography, optical coherence tomography (OCT), and slit-lamp imaging, much depends on an expert’s interpretation of the images, making the systems very labor-intensive to operate. Moreover, clinical settings face difficulties with inter-observer variability and limited scalability with these diagnostic devices. To solve these problems, we have developed the Efficient Channel-Spatial Attention Network (ECSA-Net), a new deep learning-based… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Rama Gautam1,*, Nikhil Marriwala1, Reeta Devi1, Dhariya Singh Arya2
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.076136
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advanced Computational Modeling and Simulations for Engineering Structures and Multifunctional Materials: Bridging Theory and Practice)
Abstract In this study, the multi-scale (meso and macro) modelling was used to predict the electric response of the material. Porosity was introduced through a sugar-templating process to enhance compressibility and sensitivity. Mean-field homogenization was employed to predict the electrical conductivity of the nanocomposites, which was validated experimentally through I–V characterisation, confirming stable Ohmic behavior. The homogenised material parameters were incorporated into COMSOL Multiphysics to simulate diaphragm deflection and capacitance variation under applied pressure. Experimental results showed a linear and stable capacitance response at the force magnitude of 0–7 N. The Graphene nanoplatelets (GnP)–Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) sensor demonstrated More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Hongyu Xu1,*, Xiaofeng Liu1, Zhao Li1, Shuai Zhang2, Jintao Cui1, Zongshuai Zhou1, Longlong Chen1, Mengen Zhang1
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075413
Abstract In two-scale topology optimization, enhancing the connectivity between adjacent microstructures is crucial for achieving the collaborative optimization of micro-scale performance and macro-scale manufacturability. This paper proposes a two-scale concurrent topology optimization strategy aimed at improving the interface connection strength. This method employs a parametric approach to explicitly divide the micro-design domain into a “boundary connection region” and a “free design domain” at the initial stage of optimization. The boundary connection region is used to generate a connection layer that enhances the interface strength, while the free design domain is not constrained by this layer, thus… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Chunqian Guo*, Gang Chen
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072184
Abstract Despite the ability of the anonymous communication system The Onion Router (Tor) to obscure the content of communications, prior studies have shown that passive adversaries can still infer the websites visited by users through website fingerprinting (WF) attacks. Conventional WF methodologies demonstrate optimal performance in scenarios involving single-tab browsing. Conventional WF methods achieve optimal performance primarily in scenarios involving single-tab browsing. However, in real-world network environments, users often engage in multi-tab browsing, which generates overlapping traffic patterns from different websites. This overlap has been shown to significantly degrade the performance of classifiers that rely on… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Rafika Harrabi1,2,*, Slim Ben Chaabane1,2, Hassene Seddik2
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.072054
Abstract Securing restricted zones such as airports, research facilities, and military bases requires robust and reliable access control mechanisms to prevent unauthorized entry and safeguard critical assets. Face recognition has emerged as a key biometric approach for this purpose; however, existing systems are often sensitive to variations in illumination, occlusion, and pose, which degrade their performance in real-world conditions. To address these challenges, this paper proposes a novel hybrid face recognition method that integrates complementary feature descriptors such as Fuzzy-Gabor 2D Fisher Linear Discriminant (FG-2DFLD), Generalized 2D Linear Discriminant Analysis (G2DLDA), and Modular-Local Binary Patterns (Modular-LBP)… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Jingjing Liu1, Chuanyang Liu1,2,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075348
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Deep Learning and Neural Networks: Architectures, Applications, and Challenges)
Abstract Intelligent inspection of transmission lines enables efficient automated fault detection by integrating artificial intelligence, robotics, and other related technologies. It plays a key role in ensuring power grid safety, reducing operation and maintenance costs, driving the digital transformation of the power industry, and facilitating the achievement of the dual-carbon goals. This review focuses on vision-based power line inspection, with deep learning as the core perspective to systematically analyze the latest research advancements in this field. Firstly, at the technical foundation level, it elaborates on deep learning algorithms for intelligent transmission line inspection based on image… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Nurbek Sissenov1,*, Gulden Ulyukova1,*, Dina Satybaldina2, Nikolaj Goranin3
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075504
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Software, Algorithms and Automation for Industrial, Societal and Technological Sustainable Development)
Abstract The reliability of information systems (IS) is a key factor in the sustainable operation of modern digital services. However, existing assessment methods remain fragmented and are often limited to individual indicators or expert judgments. This paper proposes a hybrid methodology for a comprehensive assessment of IS reliability based on the integration of the international standard ISO/IEC 25010:2023, multicriteria analysis methods (ARAS, CoCoSo, and TOPSIS), and the XGBoost machine learning algorithm for missing data imputation. The structure of the ISO/IEC 25010 standard is used to formalize reliability criteria and subcriteria, while the AHP method allows for… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Trong-Thua Huynh1,*, De-Thu Huynh2, Du-Thang Phu1, Hong-Son Nguyen1, Quoc H. Nguyen3
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.076623
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Deep Learning: Emerging Trends, Applications and Research Challenges for Image Recognition)
Abstract This paper introduces MobiIris, a lightweight deep network for mobile iris recognition that enhances attention and specifically addresses the balance between accuracy and efficiency on devices with limited resources. The proposed model is based on the large version of MobileNetV3 and adds more spatial attention blocks and an embedding-based head that was trained using margin-based triplet learning, enabling fine-grained modeling of iris textures in a compact representation. To further improve discriminability, we design a training pipeline that combines dynamic-margin triplet loss, a staged hard/semi-hard negative mining strategy, and feature-level knowledge distillation from a ResNet-50 teacher.… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yanming Chen1, Fuxiang Yuan2,*, Zekang Wang2
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075072
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Cyberspace Mapping and Anti-Mapping Techniques)
Abstract Network topology obfuscation is a technique aimed at protecting critical nodes and links from disruptions such as Link Flooding Attack (LFA). Currently, there are limited topology obfuscation methods for protecting critical nodes, and the existing approaches mainly achieve obfuscation by extensively modifying network links, resulting in high costs. To address this issue, this paper proposes a low-cost network topology obfuscation method dedicated to critical node protection, with its core innovation lying in a lightweight obfuscation architecture based on Fake Node Clusters (FNCs). Firstly, the protected network is modeled as an undirected graph, and an adjacency… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Malik Al-Essa1,*, Mohammad Qatawneh2,1, Ahmad Sami Al-Shamayleh3, Orieb Abualghanam1, Wesam Almobaideen4,1
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.076608
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Bridging the Gap: AutoML and Explainable AI for Industrial and Healthcare Innovations)
Abstract Machine Learning (ML) intrusion detection systems (IDS) are vulnerable to manipulations: small, protocol-valid manipulations can push samples across brittle decision boundaries. We study two complementary remedies that reshape the learner in distinct ways. Adversarial Training (AT) exposes the model to worst-case, in-threat perturbations during learning to thicken local margins; Counterfactual Augmentation (CF-Aug) adds near-boundary exemplars that are explicitly constrained to be feasible, causally consistent, and operationally meaningful for defenders. The main goal of this work is to investigate and compare how AT and CF-Aug can reshape the decision surface of the IDS. eXplainable Artificial Intelligence More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Adeel Iqbal1,#, Tahir Khurshaid2,#, Syed Abdul Mannan Kirmani3, Mohammad Arif4,*, Muhammad Faisal Siddiqui5,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075819
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Vehicular Ad-Hoc Networks (VANETs) for Intelligent Transportation Systems)
Abstract Vehicular Internet of Things (V-IoT) networks need intelligent and adaptive spectrum access methods for ensuring ultra-reliable and low-latency communication (URLLC) in highly dynamic environments. Traditional reinforcement learning (RL)-based algorithms, such as Q-Learning and Double Q-Learning, are often characterized by unstable convergence and inefficient exploration in the presence of stochastic vehicular traffic and interference. This paper proposes Adaptive Reinforcement Q-learning with Upper Confidence Bound (ARQ-UCB), a lightweight and reliability-aware RL framework, which explicitly reduces interruption and blocking probabilities while improving throughput and delay across diverse vehicular traffic conditions. This proposed ARQ-UCB algorithm extends the basic Q-updates More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Somia A. Abd El-Mottaleb1, Amira G. Mohamed2, Mehtab Singh3, Hassan Yousif Ahmed4, Medien Zeghid4, Abu Sufian A. Osman5,*, Sami Mourou5
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075669
Abstract This paper presents an image encryption scheme for underwater optical wireless communication (UOWC) systems based on dynamically generated hyperchaotic S-boxes, aiming to enhance both data security and transmission performance in underwater environments. The proposed encryption approach provides strong confusion and diffusion properties and is evaluated over five Jerlov water types with different optical attenuation characteristics. Security analysis demonstrates that the encrypted images achieve information entropy values close to the ideal value of 8 (7.9925–7.9993), with very low correlation coefficients in horizontal, vertical, and diagonal directions, as well as the system achieves high values in key… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Ho Hai Quan1,2, Le Huu Binh1,*, Nguyen Dinh Hoa Cuong3, Le Duc Huy4
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075549
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: AI-Driven Next-Generation Networks: Innovations, Challenges, and Applications)
Abstract Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) play a crucial role in numerous Internet of Things (IoT) applications and next-generation communication systems, yet they continue to face challenges in balancing energy efficiency and reliable connectivity. This study proposes SAC-HTC (Soft Actor-Critic-based High-performance Topology Control), a deep reinforcement learning (DRL) method based on the Actor-Critic framework, implemented within a Software Defined Wireless Sensor Network (SDWSN) architecture. In this approach, sensor nodes periodically transmit state information, including coordinates, node degree, transmission power, and neighbor lists, to a centralized controller. The controller acts as the reinforcement learning (RL) agent, with the… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Chih-Yung Huang*, Hong-Ru Shi, Min-Yan Xie
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075398
Abstract Quality control plays a critical role in modern manufacturing. With the rapid development of electric vehicles, 5G communications, and the semiconductor industry, high-speed and high-precision detection of surface defects on silicon carbide (SiC) wafers has become essential. This study developed an automated inspection framework for identifying surface defects on SiC wafers during the coarse grinding stage. The complex machining textures on wafer surfaces hinder conventional machine vision models, often leading to misjudgment. To address this, deep learning algorithms were applied for defect classification. Because defects are rare and imbalanced across categories, data augmentation was performed… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
HeeSeok Choi1, Joon-Min Gil2,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.074511
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Integrating Computing Technology of Cloud-Fog-Edge Environments and its Application)
Abstract Given the growing number of vehicle accidents caused by unintended acceleration and braking failure, verifying Sudden Unintended Acceleration (SUA) incidents has become a persistent challenge. A central issue of debate is whether such events stem from mechanical malfunctions or driver pedal misapplications. However, existing verification procedures implemented by vehicle manufacturers often involve closed tests after vehicle recalls; thus raising ongoing concerns about reliability and transparency. Consequently, there is a growing need for a user-driven framework that enables independent data acquisition and verification. Although previous studies have addressed SUA detection using deep learning, few have explored… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Lin-Hui Liu1, Dong-Jie Liu1,*, Yin-Yan Zhang1, Xiao-Bo Jin2, Xiu-Cheng Wu3, Guang-Gang Geng1
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.074253
Abstract Phishing email detection represents a critical research challenge in cybersecurity. To address this, this paper proposes a novel Double-S (statistical-semantic) feature model based on three core entities involved in email communication: the sender, recipient, and email content. We employ strategic game theory to analyze the offensive strategies of phishing attackers and defensive strategies of protectors, extracting statistical features from these entities. We also leverage the Qwen large language model to excavate implicit semantic features (e.g., emotional manipulation and social engineering tactics) from email content. By integrating statistical and semantic features, our model achieves a robust More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Atef Gharbi1, Mohamed Ayari2, Nasser Albalawi3, Ahmad Alshammari3, Nadhir Ben Halima4,*, Zeineb Klai3
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075474
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Control Theory and Application of Multi-Agent Systems)
Abstract This paper presents Dual Adaptive Neural Topology (Dual ANT), a distributed dual-network meta-adaptive framework that enhances ant-colony-based multi-agent coordination with online introspection, adaptive parameter control, and privacy-preserving interactions. This approach improves standard Ant Colony Optimization (ACO) with two lightweight neural components: a forward network that estimates swarm efficiency in real time and an inverse network that converts these descriptors into parameter adaptations. To preserve the privacy of individual trajectories in shared pheromone maps, we introduce a locally differentially private pheromone update mechanism that adds calibrated noise to each agent’s pheromone deposit while preserving the efficacy More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Dina S. M. Hassan*, Reem Ibrahim Alkanhel, Thuraya Alrumaih, Shiyam Alalmaei
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.074751
Abstract The sustainability of the Internet of Things (IoT) involves various issues, such as poor connectivity, scalability problems, interoperability issues, and energy inefficiency. Although the Sixth Generation of mobile networks (6G) allows for Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communication (URLLC), enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB), and massive Machine-Type Communications (mMTC) services, it faces deployment challenges such as the short range of sub-THz and THz frequency bands, low capability to penetrate obstacles, and very high path loss. This paper presents a network architecture to enhance the connectivity of wireless IoT mesh networks that employ both 6G and Wi-Fi technologies. In this… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Rui Yao1,2, Yuye Wang1,2,*, Fei Yu1,2,3,*, Hongrun Wu1,2, Zhenya Diao1,2
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.073861
Abstract Path planning for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) in complex environments presents several challenges. Traditional algorithms often struggle with the complexity of high-dimensional search spaces, leading to inefficiencies. Additionally, the non-linear nature of cost functions can cause algorithms to become trapped in local optima. Furthermore, there is often a lack of adequate consideration for real-world constraints, for example, due to the necessity for obstacle avoidance or because of the restrictions of flight safety. To address the aforementioned issues, this paper proposes a dynamic weighted spherical particle swarm optimization (DW-SPSO) algorithm. The algorithm adopts a dual Sigmoid-based More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Hoyoon Lee1, Jeonghoon Jee1, Hoseon Kim2, Cheol Oh1,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.076980
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: AI-Driven Big Data Analytics for Sustainable Mixed Traffic and Mobility Systems)
Abstract Analyzing the driving behavior of autonomous vehicles (AV) in mixed traffic conditions at urban intersections has become increasingly important for improving intersection design, providing infrastructure-based guidance information, and developing capability-enhanced AV perception systems. This study investigated the contributing factors affecting AV driving behavior using the Waymo Open Dataset. Binarized autonomous driving stability metrics, derived via a kernel density estimation, served as the target variables for a random forest classification model. The model’s input variables included 15 factors divided into four types: intersection-related, surrounding object-related, road infrastructure-related, and time-of-day-related types. The random forest classification model was… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Mohammed M. Alenazi*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075966
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Integrating Computing Technology of Cloud-Fog-Edge Environments and its Application)
Abstract Multimodal spatiotemporal data from smart city consumer electronics present critical challenges including cross-modal temporal misalignment, unreliable data quality, limited joint modeling of spatial and temporal dependencies, and weak resilience to adversarial updates. To address these limitations, EdgeST-Fusion is introduced as a cross-modal federated graph transformer framework for context-aware smart city analytics. The architecture integrates cross-modal embedding networks for modality alignment, graph transformer encoders for spatial dependency modeling, temporal self-attention for dynamic pattern learning, and adaptive anomaly detection to ensure data quality and security during aggregation. A privacy-preserving federated learning protocol with differential privacy guarantees enables… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Randika K. Makumbura1, Hasanthi Wijesundara2, Hirushan Sajindra1, Upaka Rathnayake1,*, Vikram Kumar3, Dineshbabu Duraibabu1, Sumit Sen3
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075539
Abstract Accurate streamflow prediction is essential for flood warning, reservoir operation, irrigation scheduling, hydropower planning, and sustainable water management, yet remains challenging due to the complexity of hydrological processes. Although data-driven models often outperform conventional physics-based hydrological modelling approaches, their real-world deployment is limited by cost, infrastructure demands, and the interdisciplinary expertise required. To bridge this gap, this study developed QPred, a regional, lightweight, cost-effective, web-delivered application for daily streamflow forecasting. The study executed an end-to-end workflow, from field data acquisition to accessible web-based deployment for on-demand forecasting. High-resolution rainfall data were recorded with tipping-bucket gauges… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Xuehan Li1, Tao Jing2, Yang Wang2, Bo Gao3, Jing Ai4, Minghao Zhu5,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075426
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Integrating Computing Technology of Cloud-Fog-Edge Environments and its Application)
Abstract With the deep integration of cloud computing, edge computing and the Internet of Things (IoT) technologies, smart manufacturing systems are undergoing profound changes. Over the past ten years, an extensive body of research on cloud-edge-end systems has been generated. However, challenges such as heterogeneous data fusion, real-time processing and system optimization still exist, and there is a lack of systematic review studies. In this paper, we review a cloud-edge-end collaborative sensing-communication-computing-control (
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Hamad Ali Abosaq1, Jarallah Alqahtani1,*, Fahad Masood2, Alanoud Al Mazroa3, Muhammad Asad Khan4, Akm Bahalul Haque5
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075250
Abstract The technological advancement of the vehicular Internet of Things (IoT) has revolutionized Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS) into next-generation ITS. The connectivity of IoT nodes enables improved data availability and facilitates automatic control in the ITS environment. The exponential increase in IoT nodes has significantly increased the demand for an energy-efficient, mobility-aware, and secure system for distributed intelligence. This article presents a mobility-aware Deep Reinforcement Learning based Federated Learning (DRL-FL) approach to design an energy-efficient and threat-resilient ITS. In this approach, a Policy Proximal Optimization (PPO)-based DRL agent is first employed for adaptive client selection. Second, More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Shtwai Alsubai1, Abdullah Al Hejaili2, Najib Ben Aoun3,4,*, Amina Salhi5, Vincent Karovič6,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.074057
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Action Recognition: Algorithms, Applications, and Emerging Trends)
Abstract The concept of Human Activity Recognition (HAR) is integral to applications based on Internet of Things (IoT)-enabled devices, particularly in healthcare, fitness tracking, and smart environments. The streams of data from wearable sensors are rich in information, yet their high dimensionality and variability pose a significant challenge to proper classification. To address this problem, this paper proposes hybrid architectures that integrate traditional machine learning models with a deep neural network (DNN) to deliver improved performance and enhanced capabilities for HAR tasks. Multi-sensor HAR data were used to systematically test several hybrid models, including: RF +… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Xiaocong Wang1, Jiajian Li1, Peng Zhao1, Hui Lian2, Yanjun Shi1,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075202
Abstract With the widespread deployment of assembly robots in smart manufacturing, efficiently offloading tasks and allocating resources in highly dynamic industrial environments has become a critical challenge for Mobile Edge Computing (MEC). To address this challenge, this paper constructs a cloud-edge-end collaborative MEC system that enables assembly robots to offload complex workflow tasks via multiple paths (horizontal, vertical, and hybrid collaboration). To mitigate uncertainties arising from mobility, the location prediction module is employed. This enables proactive channel-quality estimation, providing forward-looking insights for offloading decisions. Furthermore, we propose a fairness-aware joint optimization framework. Utilizing an improved Multi-Agent More >
Graphic Abstract
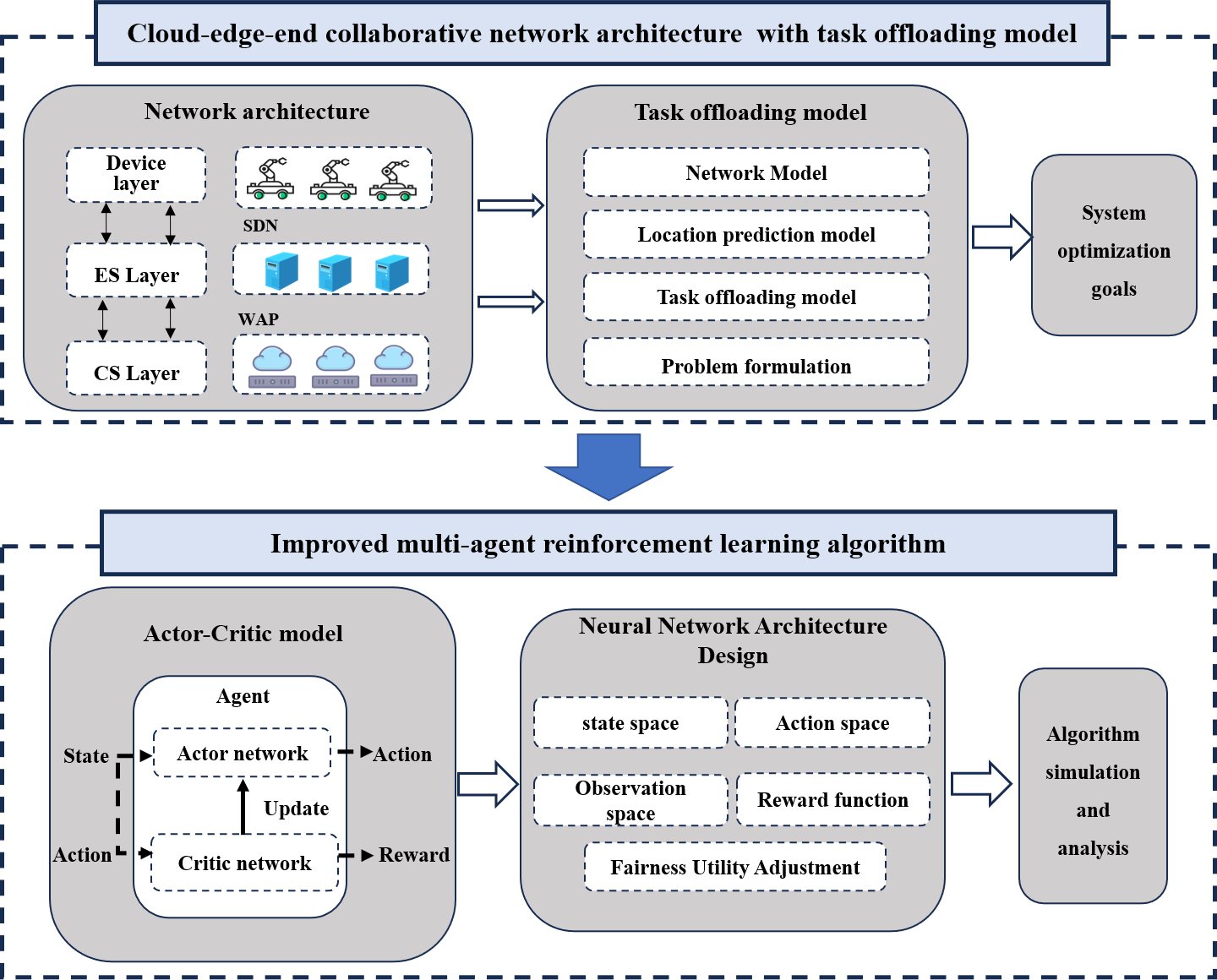
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Awais Ahmad1, Fakhri Alam Khan2,3, Awais Ahmad4, Gautam Srivastava5,6,7, Syed Atif Moqurrab8,*, Abdul Razaque9, Dina S. M. Hassan10,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.076104
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Complex Network Approaches for Resilient and Efficient Urban Transportation Systems)
Abstract Collision avoidance is recognized as a critical challenge in Vehicular Ad-Hoc Networks (VANETs), which demand real-time decision-making. It plays a vital role in ensuring road safety and traffic efficiency. Traditional approaches like rule-based systems and heuristic methods fail to provide optimal solutions in dynamic and unpredictable traffic scenarios. They cannot balance multiple objectives like minimizing collision risk, ensuring passenger comfort, and optimizing fuel efficiency, leading to suboptimal performance in real-world conditions. To tackle collision avoidance, this paper introduces a novel approach by defining the issue as an optimal control problem and solving it using the… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Shasha Li, Bin Ji*, Xiaodong Liu, Jun Ma, Jie Yu*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.076083
Abstract Aligning natural language with operating system (OS) commands allows users to perform complex computer tasks through simple natural language descriptions. However, due to the complex nature of natural language, it still remains challenging to achieve precise alignment. In this paper, we present ComAlign, a Chinese benchmark dataset that pairs Chinese natural language descriptions with corresponding OS commands. ComAlign covers a broad range of
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Peiying Zhang1,2, Yihong Yu1,2, Jia Luo3,4,*, Nguyen Gia Ba5, Lizhuang Tan6,7, Lei Shi8
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.076690
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: AI-Driven Next-Generation Networks: Innovations, Challenges, and Applications)
Abstract Next-Generation Networks (NGNs) demand high resilience, dynamic adaptability, and efficient resource utilization to enable ubiquitous connectivity. In this context, the Space-Air-Ground Integrated Network (SAGIN) architecture is uniquely positioned to meet these requirements. However, conventional NGN routing algorithms often fail to account for SAGIN’s intrinsic characteristics, such as its heterogeneous structure, dynamic topology, and constrained resources, leading to suboptimal performance under disruptions such as node failures or cyberattacks. To meet these demands for SAGIN, this study proposes a resilience-oriented routing optimization framework featuring dynamic weighting and multi-objective evaluation. Methodologically, we define three core routing performance metrics,… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Lei Sun1,2, Jingwen Wang2,*, Peng Hu2, Xiuqing Mao1,2, Cuiyun Hu1,2, Zhihong Wang2
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.073657
Abstract Transformer models face significant computational challenges in private inference (PI). Existing optimization methods often rely on isolated techniques, neglecting joint structural and operational improvements. We propose IG-3D, a unified framework that integrates structured compression and operator approximation through accurate importance assessment. Our approach first evaluates attention head importance using Integrated Gradients (IG), offering greater stability and theoretical soundness than gradient-based methods. We then apply a three-dimensional optimization: (1) structurally pruning redundant attention heads; (2) replacing Softmax with adaptive polynomial approximation to avoid exponential computations; (3) implementing layer-wise GELU substitution to accommodate different layer characteristics. A More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yao-Hsin Chou1, Cheng-Yen Hua1, Ru-Wei Tseng1, Shu-Yu Kuo2,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.075705
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Heuristic Algorithms for Optimizing Network Technologies: Innovations and Applications)
Abstract The rapid growth of mobile and Internet of Things (IoT) applications in dense urban environments places stringent demands on future Beyond 5G (B5G) or Beyond 6G (B6G) networks, which must ensure high Quality of Service (QoS) while maintaining cost-efficiency and sustainable deployment. Traditional strategies struggle with complex 3D propagation, building penetration loss, and the balance between coverage and infrastructure cost. To address this challenge, this study presents the first application of a Global-best Guided Quantum-inspired Tabu Search with Quantum-Not Gate (GQTS-QNG) framework for 3D base-station deployment optimization. The problem is formulated as a multi-objective model… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Heesoo Kim1, Minwook Kim1, Hyorim Han2, Soongbong Lee2, Tai-jin Song1,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.074802
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: AI-Driven Big Data Analytics for Sustainable Mixed Traffic and Mobility Systems)
Abstract Autonomous vehicles operate without direct human intervention, which introduces safety risks that differ from those of conventional vehicles. Although many studies have examined safety issues related to autonomous driving, high-risk situations have often been defined using single indicators, making it difficult to capture the complex and evolving nature of accident risk. To address this limitation, this study proposes a structured framework for defining and analyzing high-risk situations throughout the traffic accident process. High-risk situations are described using three complementary indicators: accident likelihood, accident severity, and accident duration. These indicators explain how risk emerges, increases, and… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Mohammad Nauman*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.077259
Abstract Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly utilized for semantic understanding and reasoning, yet their use in sensitive settings is limited by privacy concerns. This paper presents In-Mig, a mobile-agent architecture that integrates LLM reasoning within agents that can migrate across organizational venues. Unlike centralized approaches, In-Mig performs reasoning in situ, ensuring that raw data remains within institutional boundaries while allowing for cross-venue synthesis. The architecture features a policy-scoped memory model, utility-driven route planning, and cryptographic trust enforcement. A prototype using JADE for mobility and quantized Mistral-7B demonstrates practical feasibility. Evaluation across various scenarios shows that In-Mig achieves More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Xi Cai, Xiaoqiang Wang, Huiying Zhao, Guang Han*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075756
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Development and Application of Deep Learning and Image Processing)
Abstract Low-light image enhancement (LLIE) remains challenging due to underexposure, color distortion, and amplified noise introduced during illumination correction. Existing deep learning–based methods typically apply uniform enhancement across the entire image, which overlooks scene semantics and often leads to texture degradation or unnatural color reproduction. To overcome these limitations, we propose a Semantic-Guided Visual Mamba Network (SGVMNet) that unifies semantic reasoning, state-space modeling, and mixture-of-experts routing for adaptive illumination correction. SGVMNet comprises three key components: (1) a semantic modulation module (SMM) that extracts scene-aware semantic priors from pretrained multimodal models—Large Language and Vision Assistant (LLaVA) and… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Guotai Huang, Xiyu Gao, Peng Liu, Liming Zhou*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.074941
Abstract To address the insufficient prediction accuracy of multi-state parameters in electro-hydraulic servo material fatigue testing machines under complex loading and nonlinear coupling conditions, this paper proposes a multivariate sequence-to-sequence prediction model integrating a Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) encoder, a Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU) decoder, and a multi-head attention mechanism. This approach enhances prediction accuracy and robustness across different control modes and load spectra by leveraging multi-channel inputs and cross-variable feature interactions, thereby capturing both short-term high-frequency dynamics and long-term slow drift characteristics. Experiments using long-term data from real test benches demonstrate that the model achieves… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Samia Allaoua Chelloug1,*, Ahmed A. Abd El-Latif2,3,*, Samah AlShathri1, Mohamed Hammad2,4
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.074485
Abstract Scene recognition is a critical component of computer vision, powering applications from autonomous vehicles to surveillance systems. However, its development is often constrained by a heavy reliance on large, expensively annotated datasets. This research presents a novel, efficient approach that leverages multi-model transfer learning from pre-trained deep neural networks—specifically DenseNet201 and Visual Geometry Group (VGG)—to overcome this limitation. Our method significantly reduces dependency on vast labeled data while achieving high accuracy. Evaluated on the Aerial Image Dataset (AID) dataset, the model attained a validation accuracy of 93.6% with a loss of 0.35, demonstrating robust performance More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Wang Cheng1, Zhuodong Liu2, Xiangyu Li3,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.074250
Abstract Smart pest control is crucial for building farm resilience and ensuring sustainable agriculture in the face of climate change and environmental challenges. To achieve effective intelligent monitoring systems, agricultural pest and disease detection must overcome three fundamental challenges: feature degradation in dense vegetation environments, limited detection capability for sub-
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Seunggyu Byeon1, Jung-hun Lee2, Jong-Deok Kim3,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.074033
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Recent Fuzzy Techniques in Image Processing and its Applications)
Abstract This paper introduces a fuzzy C-means-based pooling layer for convolutional neural networks that explicitly models local uncertainty and ambiguity. Conventional pooling operations, such as max and average, apply rigid aggregation and often discard fine-grained boundary information. In contrast, our method computes soft memberships within each receptive field and aggregates cluster-wise responses through membership-weighted pooling, thereby preserving informative structure while reducing dimensionality. Being differentiable, the proposed layer operates as standard two-dimensional pooling. We evaluate our approach across various CNN backbones and open datasets, including CIFAR-10/100, STL-10, LFW, and ImageNette, and further probe small training set restrictions More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Anfeng Yang, Fei Kang, Wenjuan Bu*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073979
Abstract Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated significant capabilities in semantic understanding and code generation. However, cybersecurity tasks often require prompting the adaptation of open-source models to this domain. Despite their effectiveness, large-parameter LLMs incur substantial memory usage and runtime costs during task inference and downstream fine-tuning for cybersecurity applications. In this study, we fine-tuned six LLMs with parameters under 4 billion using LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation) on specific cybersecurity instruction datasets, employing evaluation metrics similar to Hackmentor. Results indicate that post-fine-tuning, smaller models achieved victory or parity rates up to 85% against larger models like Qwen-1.5-14B… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Lixing Tan1,2, Liusiyu Chen1, Yang Wang1, Zhenyu Song1,*, Zenan Lu1,3,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075959
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advanced Networking Technologies for Intelligent Transportation and Connected Vehicles)
Abstract Anomaly detection is a vibrant research direction in controller area networks, which provides the fundamental real-time data transmission underpinning in-vehicle data interaction for the internet of vehicles. However, existing unsupervised learning methods suffer from insufficient temporal and spatial constraints on shallow features, resulting in fragmented feature representations that compromise model stability and accuracy. To improve the extraction of valuable features, this paper investigates the influence of clustering constraints on shallow feature convergence paths at the model level and further proposes an end-to-end intrusion detection system based on efficient deep embedded subspace clustering (EDESC-IDS). Following the… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Ksenia Kharitonova1, David Pérez-Fernández2, Zoraida Callejas1,3, David Griol1,3,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075777
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Security and Robustness of Large Language Models (LLMs))
Abstract Building reliable intent-based, task-oriented dialog systems typically requires substantial manual effort: designers must derive intents, entities, responses, and control logic from raw conversational data, then iterate until the assistant behaves consistently. This paper investigates how far large language models (LLMs) can automate this development. In this paper, we use two reference corpora, Let’s Go (English, public transport) and MEDIA (French, hotel booking), to prompt four LLM families (GPT-4o, Claude, Gemini, Mistral Small) and generate the core specifications required by the
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Zhengyu Wu1, Kejun Kang2, Yixiu Liu3,*, Chenpu Li3
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075593
Abstract Binary segmentation tasks in computer vision exhibit diverse appearance distributions and complex boundary characteristics. To address the limited generalization and adaptability of existing models across heterogeneous tasks, we propose Abel-Net, an Aggregated Bilateral Edge Localization Network designed as a universal framework for multi-task binary segmentation. Abel-Net integrates global and local contextual cues to enhance feature learning and edge precision. Specifically, a multi-scale feature pyramid fusion strategy is implemented via an Aggregated Skip Connection (ASC) module to strengthen feature adaptability, while the Edge Dual Localization (EDL) mechanism performs coarse-to-fine refinement through edge-aware supervision. Additionally, Edge Attention More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Shih-Ming Cho1, Sung-Wen Wang1, Min-Chie Chiu2,*, Shao-Chun Chen1
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.074911
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Development and Application of Deep Learning based Object Detection)
Abstract To address crop depredation by intelligent species (e.t, macaques) and the habituation from traditional methods, this study proposes an intelligent, closed-loop, adaptive laser deterrence system. A core contribution is an efficient multi-stage Semi-Supervised Learning (SSL) and incremental fine-tuning (IFT) framework, which reduced manual annotation by ~60% and training time by ~68%. This framework was benchmarked against YOLOv8n, v10n, and v11n. Our analysis revealed that YOLOv12n’s high Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) (47.1% retention) pseudo-labels made it the only model to gain performance (+0.010 mAP) from SSL, allowing it to overtake competitors. Subsequently, in the IFT stress test,… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Talha Farooq Khan1, Fahad Ali2, Majid Hussain1, Lal Khan3,*, Hsien-Tsung Chang4,5,6,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.074557
Abstract The outstanding growth in the applications of large language models (LLMs) demonstrates the significance of adaptive and efficient prompt engineering tactics. The existing methods may not be variable, vigorous and streamlined in different domains. The offered study introduces an immediate optimization outline, named PROMPTx-PE, that is going to yield a greater level of precision and strength when it comes to the assignments that are premised on LLM. The proposed system features a timely selection scheme which is informed by reinforcement learning, a contextual layer and a dynamic weighting module which is regulated by Lyapunov-based stability More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Tran Minh Bao1, Kumar Shashvat2, Nguyen Gia Nhu3,*, Dac-Nhuong Le4
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.075161
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Artificial Intelligence Methods and Techniques to Cybersecurity)
Abstract The sudden growth of harmful web pages, including spam and phishing URLs, poses a greater threat to global cybersecurity than ever before. These URLs are commonly utilised to trick people into divulging confidential details or to stealthily deploy malware. To address this issue, we aimed to assess the efficiency of popular machine learning and neural network models in identifying such harmful links. To serve our research needs, we employed two different datasets: the PhiUSIIL dataset, which is specifically designed to address phishing URL detection, and another dataset developed to uncover spam links by examining the… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Zheng Zhao1, Doo Heon Song2, Kwang Baek Kim1,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.073969
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Recent Fuzzy Techniques in Image Processing and its Applications)
Abstract Deep learning attention mechanisms have achieved remarkable progress in computer vision, but still face limitations when handling images with ambiguous boundaries and uncertain feature representations. Conventional attention modules such as SE-Net, CBAM, ECA-Net, and CA adopt a deterministic paradigm, assigning fixed scalar weights to features without modeling ambiguity or confidence. To overcome these limitations, this paper proposes the Fuzzy Attention Network Layer (FANL), which integrates intuitionistic fuzzy set theory with convolutional neural networks to explicitly represent feature uncertainty through membership (
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Oumaima Saidani1, Nazia Azim2, Ateeq Ur Rehman3,*, Akbayan Bekarystankyzy4, Hala AbdelHameed Mostafa5, Mohamed R. Abonazel6, Ehab Ebrahim Mohamed Ebrahim7, Sarah Abu Ghazalah8
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072772
Abstract The convergence of Software Defined Networking (SDN) in Internet of Vehicles (IoV) enables a flexible, programmable, and globally visible network control architecture across Road Side Units (RSUs), cloud servers, and automobiles. While this integration enhances scalability and safety, it also raises sophisticated cyberthreats, particularly Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks. Traditional rule-based anomaly detection methods often struggle to detect modern low-and-slow DDoS patterns, thereby leading to higher false positives. To this end, this study proposes an explainable hybrid framework to detect DDoS attacks in SDN-enabled IoV (SDN-IoV). The hybrid framework utilizes a Residual Network (ResNet)… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yiming Yu1, Yunfei Guo2, Junchen Liu3, Yiping Sun4, Junliang Du5,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.074959
Abstract Graph neural networks (GNNs) have shown notable success in identifying security vulnerabilities within Ethereum smart contracts by capturing structural relationships encoded in control- and data-flow graphs. Despite their effectiveness, most GNN-based vulnerability detectors operate as black boxes, making their decisions difficult to interpret and thus less suitable for critical security auditing. The information bottleneck (IB) principle provides a theoretical framework for isolating task-relevant graph components. However, existing IB-based implementations often encounter unstable optimization and limited understanding of code semantics. To address these issues, we introduce ContractGIB, an interpretable graph information bottleneck framework for function-level vulnerability More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Omar Almomani1,*, Mahran Al-Zyoud1, Ahmad Adel Abu-Shareha2, Ammar Almomani3,4,*, Said A. Salloum5, Khaled Mohammad Alomari6
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.075465
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Heuristic Algorithms for Optimizing Network Technologies: Innovations and Applications)
Abstract In Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs), survivability is a crucial issue that is greatly impacted by energy efficiency. Solutions that satisfy application objectives while extending network life are needed to address severe energy constraints in WSNs. This paper presents an Adaptive Enhanced Grey Wolf Optimizer (AEGWO) for energy-efficient cluster head (CH) selection that mitigates the exploration–exploitation imbalance, preserves population diversity, and avoids premature convergence inherent in baseline GWO. The AEGWO combines adaptive control of the parameter of the search pressure to accelerate convergence without stagnation, a hybrid velocity-momentum update based on the dynamics of PSO, and… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Changxu Zhao1, Jianping Liu1,*, Xiaofeng Wang1, Wei Sun2, Libo Liu3, Haiyu Ren1, Pan Liu1, Qiantong Wang1
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.074409
Abstract Foundation models are reshaping artificial intelligence, yet their deployment in specialised domains such as agricultural question answering (AQA) still faces challenges including data scarcity and barriers to domain-specific knowledge. To systematically review recent progress in this area, this paper adopts a task–paradigm perspective and examines applications across three major AQA task families. For text-based QA, we analyse the strengths and limitations of retrieval-based, generative, and hybrid approaches built on large language models, revealing a clear trend toward hybrid paradigms that balance precision and flexibility. For visual diagnosis, we discuss techniques such as cross-modal alignment and More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yuji Sang1, Lijun Liu1,*, Long Lv1,*, Husheng Wu2, Hemin Yin1
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073837
Abstract Aiming at the challenges of low throughput, excessive consensus latency and high communication complexity in the Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT) algorithm in blockchain networks, its application in identity verification for distributed networking of a drone cluster is limited. Therefore, a lightweight blockchain-based identity authentication model for UAV swarms is designed, and a Credit-score and Grouping-mechanism Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (CG-PBFT) algorithm is proposed. CG-PBFT introduces a reputation score evaluation mechanism, classifies the reputation levels of nodes in the network, and optimizes the consensus process based on grouping consensus and BLS aggregate signature technology. Experimental More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Hafiz Burhan Ul Haq1, Waseem Akram2, Haroon ur Rashid Kayani3, Khalid Mahmood4,*, Chihhsiong Shih5, Rupak Kharel6,7, Amina Salhi8
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073188
Abstract The Internet of Things (IoT) is a new model that evolved with the rapid progress of advanced technology and gained tremendous popularity due to its applications. Anomaly detection has widely attracted researchers’ attention in the last few years, and its effects on diverse applications. This review article covers the various methods and tools developed to perform the task efficiently and automatically in a smart city. In this work, we present a comprehensive literature review (2011 onwards) of three major types of anomalies: network anomalies, sensor anomalies, and video-based anomalies, along with their methods and software… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Qingwen Yang1, Zhi Li2, Jiawei Tang1, Yanyi Liu1, Tiezheng Guo1, Yingyou Wen1,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.074384
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Intelligent Computation and Large Machine Learning Models for Edge Intelligence in industrial Internet of Things)
Abstract Deploying Large Language Model (LLM)-based agents in the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) presents significant challenges, including high latency from cloud-based APIs, data privacy concerns, and the infeasibility of deploying monolithic models on resource-constrained edge devices. While smaller models (SLMs) are suitable for edge deployment, they often lack the reasoning power for complex, multi-step tasks. To address these issues, this paper introduces LEAF, a Lightweight Edge Agent Framework designed for efficiently executing complex tasks at the edge. LEAF employs a novel architecture where multiple expert SLMs—specialized for planning, execution, and interaction—work in concert, decomposing complex… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Saifullah Tumrani1,2,*, Abdul Jabbar Siddiqui2,3,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.075152
Abstract Vehicle re-identification (ReID) is a challenging task in intelligent transportation, and urban surveillance systems due to its complications in camera viewpoints, vehicle scales, and environmental conditions. Recent transformer-based approaches have shown impressive performance by utilizing global dependencies, these models struggle with aspect ratio distortions and may overlook fine-grained local attributes crucial for distinguishing visually similar vehicles. We introduce a framework based on Swin Transformers that addresses these challenges by implementing three components. First, to improve feature robustness and maintain vehicle proportions, our Aspect Ratio-Aware Swin Transformer (AR-Swin) preserve the native ratio via letterbox, uses a… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Faisal Albalwy1,*, Muhannad Almohaimeed2
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.075098
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Artificial Intelligence Methods and Techniques to Cybersecurity)
Abstract Intrusion detection in Internet of Things (IoT) environments presents challenges due to heterogeneous devices, diverse attack vectors, and highly imbalanced datasets. Existing research on the ToN-IoT dataset has largely emphasized binary classification and single-model pipelines, which often show strong performance but limited generalizability, probabilistic reliability, and operational interpretability. This study proposes a stacked ensemble deep learning framework that integrates random forest, extreme gradient boosting, and a deep neural network as base learners, with CatBoost as the meta-learner. On the ToN-IoT Linux process dataset, the model achieved near-perfect discrimination (macro area under the curve = 0.998),… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Mekhled Alharbi1,*, Khalid Haseeb2, Mamoona Humayun3,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073832
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Recent Advances in Blockchain Technology and Applications)
Abstract The Internet of Things (IoT) and cloud computing have significantly contributed to the development of smart cities, enabling real-time monitoring, intelligent decision-making, and efficient resource management. These systems, particularly in IoT networks, rely on numerous interconnected devices that handle time-sensitive data for critical applications. In related approaches, trusted communication and reliable device interaction have been overlooked, thereby lowering security when sharing sensitive IoT data. Moreover, it incurs additional energy consumption and overhead while addressing potential threats in the dynamic environment. In this research, an Artificial Intelligence (AI) recommended fault-tolerant framework is proposed that leverages blockchain More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Zhongbin Luo1,2, Zhaoyang Guan3, Wenxing You2, Yunteng Wang2, Yanqiu Bi4,5,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.075704
Abstract Gait recognition is a key biometric for long-distance identification, yet its performance is severely degraded by real-world challenges such as varying clothing, carrying conditions, and changing viewpoints. While combining silhouette and skeleton data is a promising direction, effectively fusing these heterogeneous modalities and adaptively weighting their contributions in response to diverse conditions remains a central problem. This paper introduces GaitMAFF, a novel Multi-modal Adaptive Feature Fusion Network, to address this challenge. Our approach first transforms discrete skeleton joints into a dense Skeleton Map representation to align with silhouettes, then employs an attention-based module to dynamically More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Weimin Shi1,*, Kuntao Lv1, Chang Xuan1, Ji Wu2
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.075203
Abstract The application of deep learning in fabric defect detection has become increasingly widespread. To address false positives and false negatives in fabric roll seam detection, and to improve automation efficiency and product quality, we propose the Multi-scale Context DeepLabV3+ (MSC-DeepLabV3+), a semantic segmentation network designed for fabric roll seam detection, based on DeepLabV3+. The model improvements include enhancing the backbone performance through optimization of the UIB-MobileNetV2 network; designing the Dynamic Atrous and Sliding-window Fusion (DASF) module to improve adaptability to multi-scale seam structures with dynamic dilation rates and a sliding-window mechanism; and utilizing the Progressive… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Zhichao Yu1, Jiahui Yu1, Simon James Fong1,*, Yaoyang Wu1,2
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.074899
Abstract Accurately recognizing driver distraction is critical for preventing traffic accidents, yet current detection models face two persistent challenges. First, distractions are often fine-grained, involving subtle cues such as brief eye closures or partial yawns, which are easily missed by conventional detectors. Second, in real-world scenarios, drivers frequently exhibit overlapping behaviors, such as simultaneously holding a cup, closing their eyes, and yawning, leading to multiple detection boxes and degraded model performance. Existing approaches fail to robustly address these complexities, resulting in limited reliability in safety-critical applications. To overcome these pain points, we propose YOLO-Drive, a novel… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Jeng-Shyang Pan1,2, Yan-Na Wei3, Ling-Da Chi4, Shu-Chuan Chu1,*, Ru-Yu Wang5, Junzo Watada6
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.074447
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Nature-Inspired and Metaheuristic Optimization Algorithms: Theory, Applications, and Emerging Trends)
Abstract Multilevel image segmentation is a critical task in image analysis, which imposes high requirements on the global search capability and convergence efficiency of segmentation algorithms. In this paper, an improved Artificial Protozoa Optimization algorithm, termed the two-stage Taguchi-assisted Gaussian–Lévy Artificial Protozoa Optimization (TGAPO) algorithm, is proposed and applied to multilevel image segmentation. The proposed algorithm adopts a two-stage evolutionary mechanism. In the first stage, Gaussian perturbation is introduced to enhance local search capability; in the second stage, Lévy flight is incorporated to expand the global search range; and finally, the Taguchi strategy is employed to… More >