
This journal publishes original research papers of reasonable permanent intellectual value, in the areas of computer modeling in engineering & Sciences, including, but not limited to computational mechanics, computational materials, computational mathematics, computational physics, computational chemistry, and computational biology, pertinent to solids, fluids, gases, biomaterials, and other continua spanning from various spatial length scales (quantum, nano, micro, meso, and macro), and various time scales (picoseconds to hours) are of interest. Papers which deal with multi-physics problems, as well as those which deal with the interfaces of mechanics, chemistry, and biology, are particularly encouraged. Novel computational approaches and state-of-the-art computation algorithms, such as soft computing, artificial intelligence-based machine learning methods, and computational statistical methods are welcome.
Science Citation Index (Web of Science): 2024 Impact Factor 2.5; Current Contents: Engineering, Computing & Technology; Scopus Citescore (Impact per Publication 2024): 4.4; SNIP (Source Normalized Impact per Paper 2024): 0.693; RG Journal Impact (average over last three years); Engineering Index (Compendex); Applied Mechanics Reviews; Cambridge Scientific Abstracts: Aerospace and High Technology, Materials Sciences & Engineering, and Computer & Information Systems Abstracts Database; CompuMath Citation Index; INSPEC Databases; Mathematical Reviews; MathSci Net; Mechanics; Science Alert; Science Navigator; Zentralblatt fur Mathematik; Portico, etc...
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2026.075386 - 26 February 2026
Abstract Vaginal delivery is a fascinating physiological process, but also a high-risk process. Up to 85%–90% of vaginal deliveries lead to perineal trauma, with nearly 11% of severe perineal tearing. It is a common occurrence, especially for first-time mothers. Computational childbirth plays an essential role in the prediction and prevention of these traumas, but fast personalization of the pelvis and floor muscles is challenging due to their anatomical complexity. This study introduces a novel shape-prediction-based personalization of the pelvis and floor muscles for perineal tearing management and childbirth simulation. 300 subjects were selected from public Computed… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2026.077044 - 26 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Data-Driven Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Computational Modelling for Engineering and Applied Sciences)
Abstract Physics-informed neural networks (PINNs) have emerged as a promising class of scientific machine learning techniques that integrate governing physical laws into neural network training. Their ability to enforce differential equations, constitutive relations, and boundary conditions within the loss function provides a physically grounded alternative to traditional data-driven models, particularly for solid and structural mechanics, where data are often limited or noisy. This review offers a comprehensive assessment of recent developments in PINNs, combining bibliometric analysis, theoretical foundations, application-oriented insights, and methodological innovations. A bibliometric survey indicates a rapid increase in publications on PINNs since 2018,… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2026.075433 - 26 February 2026
Abstract Structural Health Monitoring (SHM) plays a critical role in ensuring the safety, integrity, longevity and economic efficiency of civil infrastructures. The field has undergone a profound transformation over the last few decades, evolving from traditional methods—often reliant on visual inspections—to data-driven intelligent systems. This review paper analyzes this historical trajectory, beginning with the approaches that relied on modal parameters as primary damage indicators. The advent of advanced sensor technologies and increased computational power brings a significant change, making Machine Learning (ML) a viable and powerful tool for damage assessment. More recently, Deep Learning (DL) has More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.067108 - 26 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in AI-Driven Computational Modeling for Image Processing)
Abstract Over the years, Generative Adversarial Networks (
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2026.077315 - 26 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: The Evolution of Cybersecurity and AI: Surveys and Tutorials)
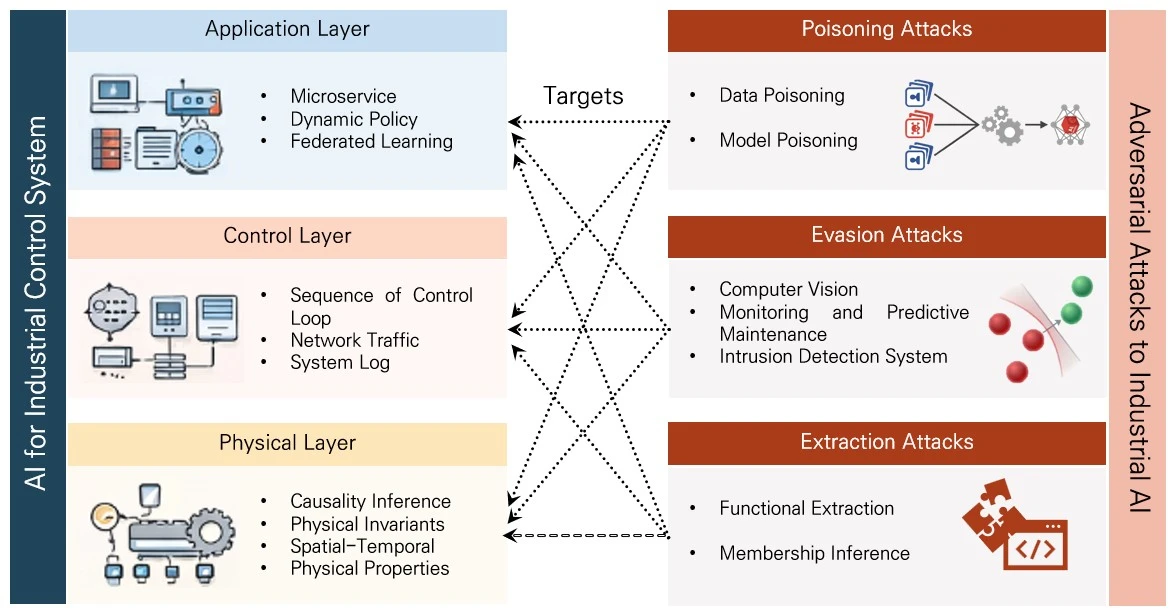
Abstract As attack techniques evolve and data volumes increase, the integration of artificial intelligence-based security solutions into industrial control systems has become increasingly essential. Artificial intelligence holds significant potential to improve the operational efficiency and cybersecurity of these systems. However, its dependence on cyber-based infrastructures expands the attack surface and introduces the risk that adversarial manipulations of artificial intelligence models may cause physical harm. To address these concerns, this study presents a comprehensive review of artificial intelligence-driven threat detection methods and adversarial attacks targeting artificial intelligence within industrial control environments, examining both their benefits and associated… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2026.076299 - 26 February 2026
Abstract Negative Poisson’s ratio materials and structures exhibit lateral expansion under tensile loading, demonstrating significant mechanical advantages over conventional materials. This study systematically investigated three typical two-dimensional negative Poisson’s ratio metamaterial structures (Concave honeycomb, Anti-chiral, and Anti-chiral concave honeycomb hybrid structures) through both experimental tests and numerical analysis. The test specimens were fabricated using selective laser melting (SLM) additive manufacturing technology, and the experimental test was conducted with the use of a DIC strain measurement system. The numerical studies were performed considering both static tensile loading and dynamic impact loading with different strain rates. The deformation More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2026.077949 - 26 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Machine Learning, Data-Driven and Novel Approaches in Computational Mechanics)
Abstract An efficient data-driven numerical framework is developed for transient heat conduction analysis in thin-walled structures. The proposed approach integrates spectral time discretization with neural network approximation, forming a spectral-integrated neural network (SINN) scheme tailored for problems characterized by long-time evolution. Temporal derivatives are treated through a spectral integration strategy based on orthogonal polynomial expansions, which significantly alleviates stability constraints associated with conventional time-marching schemes. A fully connected neural network is employed to approximate the temperature-related variables, while governing equations and boundary conditions are enforced through a physics-informed loss formulation. Numerical investigations demonstrate that the proposed More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2026.076948 - 26 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Scientific Computing and Its Application to Engineering Problems)
Abstract Conformal truss-like lattice structures face significant manufacturability challenges in additive manufacturing due to overhang angle limitations. To address this problem, we propose a novel angle-constrained optimization method grounded in the global adjustment of nodal coordinates. First, a build direction is selected to minimize the number of violating struts. Then, an angular-constraint matrix is assembled from strut direction vectors, and analytical sensitivities with respect to nodal coordinates are derived to enable efficient constrained optimization under nonlinear angular inequality constraints. Numerical studies on two complex curved-surface lattices demonstrate that all overhang violations are eliminated while only minor More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2026.078844 - 26 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Numerical Modeling of Composite Structures and Repairs)
Abstract The increasing occurrence of corrosion-related damage in steel pipelines has led to the growing use of composite-based repair techniques as an efficient alternative to traditional replacement methods. Computer modeling and structural analysis were performed for the repair reinforcement of a steel pipeline with a composite bandage. A preliminary analysis of possible contact interaction schemes was implemented based on the theory of cylindrical shells, taking into account transverse shear deformations. The finite element method was used for a detailed study of the stress state of the composite bandage and the reinforced section of the pipeline. The… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2026.076651 - 26 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Numerical Modeling of Composite Structures and Repairs)
Abstract This study presents a physics-informed modelling framework that combines finite element method (FEM) simulations and supervised machine learning (ML) to predict the self-healing performance of microbial concrete. A FEniCS-based FEM platform resolves multiphysics phenomena including nutrient diffusion, microbial CaCO3 precipitation, and stiffness recovery. These simulations, together with experimental data, are used to train ML models (Random Forest yielding normalized RMSE ≈ 0.10) capable of predicting performance over a wide range of design parameters. Feature importance analysis identifies curing temperature, calcium carbonate precipitation rate, crack width, bacterial strain, and encapsulation method as the most influential parameters. The More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2026.076415 - 26 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Applied Artificial Intelligence: Advanced Solutions for Engineering Real-World Challenges)
Abstract This research centers on structural health monitoring of bridges, a critical transportation infrastructure. Owing to the cumulative action of heavy vehicle loads, environmental variations, and material aging, bridge components are prone to cracks and other defects, severely compromising structural safety and service life. Traditional inspection methods relying on manual visual assessment or vehicle-mounted sensors suffer from low efficiency, strong subjectivity, and high costs, while conventional image processing techniques and early deep learning models (e.g., U-Net, Faster R-CNN) still perform inadequately in complex environments (e.g., varying illumination, noise, false cracks) due to poor perception of fine… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2026.075270 - 26 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Fast Modelling of Fluid-Structure Interaction Based on Computations and Experiments)
Abstract This study presents an implicit multiphysics coupling method integrating Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD), the Multiphase Particle-in-Cell (MPPIC) model, and the Finite Element Method (FEM), implemented with OpenFOAM, CalculiX, and preCICE to simulate fluid-particle-structure interactions with large deformations. Mesh motion in the fluid field is handled using the radial basis function (RBF) method. The particle phase is modeled by MPPIC, where fluid-particle interaction is described through momentum exchange, and inter-particle collisions are characterized by collision stress. The structural field is solved by nonlinear FEM to capture large deformations induced by geometric nonlinearity. Coupling among fields is More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2026.074675 - 26 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Modeling and Applications of Bubble and Droplet in Engineering and Sciences)
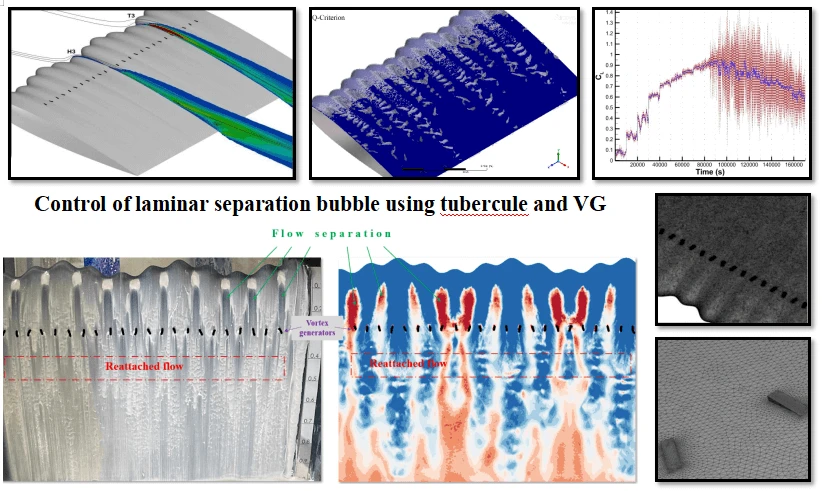
Abstract This paper examines a model that combines vortex generators and leading-edge tubercles for controlling the laminar separation bubble (LSB) over an airfoil at low Reynolds numbers (Re). This new concept of passive flow control technique utilizing a tubercle and vortex generator (VG) close to the leading edge was analyzed numerically for a NACA0015 airfoil. In this study, the Shear Stress Transport (SST) turbulence model was employed in the numerical modelling. Numerical modelling was completed using the ANSYS-Fluent 18.2 solver. Analyses were conducted to investigate the flow pattern and understand the underlying LSB control phenomena that More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2026.077613 - 26 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Computational Intelligent Systems for Solving Complex Engineering Problems: Principles and Applications-III)
Abstract In active noise control, the optimal deployment of secondary sources is a critical factor influencing the noise reduction performance due to the spatial inhomogeneity of the sound field. Traditional methods, which rely on finite element analysis to model the sound field, are accurate but computationally intensive, leading to high costs in solving the deployment optimization problem. To address this issue, this paper proposes an expensive optimization method for secondary source deployment based on Interior Point Method-assisted Differential Evolution with Weibull distribution (IPMDEW). During the optimization process, a Kriging model is employed to construct a response… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2026.077783 - 26 February 2026
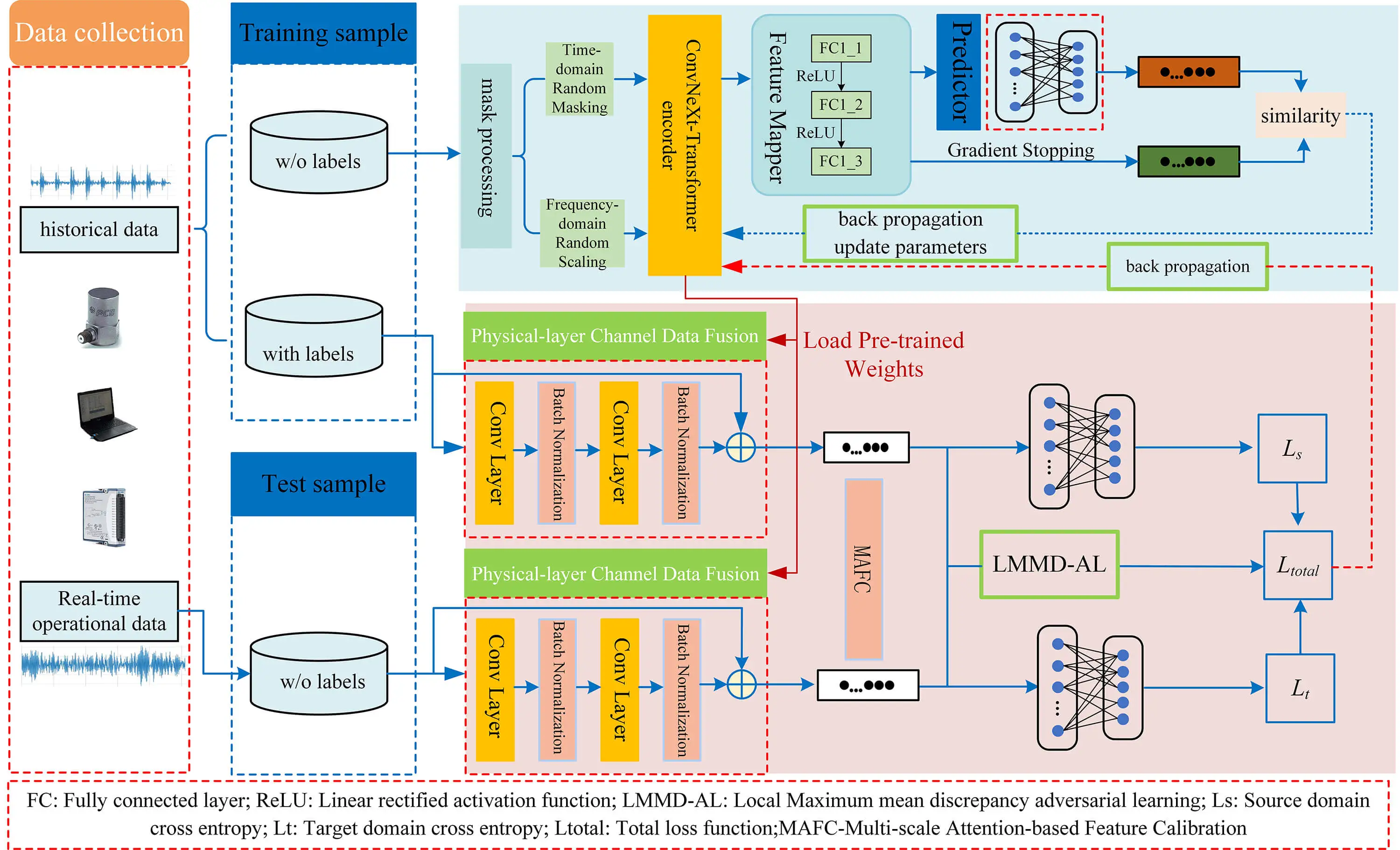
Abstract To address the issue of scarce labeled samples and operational condition variations that degrade the accuracy of fault diagnosis models in variable-condition gearbox fault diagnosis, this paper proposes a semi-supervised masked contrastive learning and domain adaptation (SSMCL-DA) method for gearbox fault diagnosis under variable conditions. Initially, during the unsupervised pre-training phase, a dual signal augmentation strategy is devised, which simultaneously applies random masking in the time domain and random scaling in the frequency domain to unlabeled samples, thereby constructing more challenging positive sample pairs to guide the encoder in learning intrinsic features robust to condition… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2026.075436 - 26 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Intelligent Dynamics Modeling, Predictive Operations & Maintenance, and Control Optimization for Complex Systems)
Abstract To ensure the safe and stable operation of rotating machinery, intelligent fault diagnosis methods hold significant research value. However, existing diagnostic approaches largely rely on manual feature extraction and expert experience, which limits their adaptability under variable operating conditions and strong noise environments, severely affecting the generalization capability of diagnostic models. To address this issue, this study proposes a multimodal fusion fault diagnosis framework based on Mel-spectrograms and automated machine learning (AutoML). The framework first extracts fault-sensitive Mel time–frequency features from acoustic signals and fuses them with statistical features of vibration signals to construct complementary More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2026.077956 - 26 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Deep Learning and Computer Vision for Intelligent Systems: Methods, Applications, and Future Directions)
Abstract Wind turbine blade defect detection faces persistent challenges in separating small, low-contrast surface faults from complex backgrounds while maintaining reliability under variable illumination and viewpoints. Conventional image-processing pipelines struggle with scalability and robustness, and recent deep learning methods remain sensitive to class imbalance and acquisition variability. This paper introduces TurbineBladeDetNet, a convolutional architecture combining dual-attention mechanisms with multi-path feature extraction for detecting five distinct blade fault types. Our approach employs both channel-wise and spatial attention modules alongside an Albumentations-driven augmentation strategy to handle dataset imbalance and capture condition variability. The model achieves 97.14% accuracy, 98.65% More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2026.075720 - 26 February 2026
Abstract Unconfined Compressive Strength (UCS) is a key parameter for the assessment of the stability and performance of stabilized soils, yet traditional laboratory testing is both time and resource intensive. In this study, an interpretable machine learning approach to UCS prediction is presented, pairing five models (Random Forest (RF), Gradient Boosting (GB), Extreme Gradient Boosting (XGB), CatBoost, and K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN)) with SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP) for enhanced interpretability and to guide feature removal. A complete dataset of 12 geotechnical and chemical parameters, i.e., Atterberg limits, compaction properties, stabilizer chemistry, dosage, curing time, was used to… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2026.076381 - 26 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Artificial Intelligence and Advanced Numerical Modeling Integration Techniques in Tunnel and Underground Engineering)
Abstract In-situ enlargement of super-large-span tunnels can intensify excavation-induced unloading in the surrounding rock, increasing deformation demand and failure risk during construction. This study combines laboratory model tests with FLAC3D simulations to evaluate the stabilizing role of prestressed anchor cables and to establish an energy-balance framework for support optimization. Comparative model tests of existing and enlarged tunnel sections, with and without anchors, show that reinforcement increases load-carrying capacity, reduces displacement, and confines damage to more localized zones. The numerical simulations reproduce displacement fields, shear-strain localization, and plastic-zone evolution with good agreement against the experimental observations. The energy More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2026.077616 - 26 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Computational Advances in Nanofluids: Modelling, Simulations, and Applications)
Abstract A high-order hybrid numerical framework is developed by coupling a three-stage exponential time integrator with a Runge–Kutta scheme for the efficient solution of partial differential equations involving first-order time derivatives. The proposed scheme attains third-order temporal accuracy and is rigorously validated through stability and convergence analyses for both scalar and coupled systems. Its effectiveness is demonstrated by simulating unsteady Eyring-Prandtl non-Newtonian nanofluid flow over a Riga plate with coupled heat and mass transfer under electromagnetic actuation. The physical model accounts for Brownian motion and thermophoresis, and the nanofluid considered is a Prandtl-type non-Newtonian base fluid… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2026.076115 - 26 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Applications of Modelling and Simulation in Nanofluids)
Abstract This study investigates the enhancement of convective heat transfer in a serpentine pipe using ferrofluid flow influenced by dual non-uniform magnetic sources. The primary objective is to improve thermal performance in compact cooling systems, such as those used in heat exchangers. A two-dimensional, steady-state Computational Fluid Dynamic (CFD) model is developed in ANSYS Fluent to simulate the behavior of an incompressible ferrofluid under applied constant heat flux and magnetic fields. The magnetic force is modeled using the Kelvin force, which acts on magnetized nanoparticles in response to spatially varying electromagnetic fields generated by two strategically… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.073292 - 26 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Applied Artificial Intelligence: Advanced Solutions for Engineering Real-World Challenges)
Abstract There is a need for accurate prediction of heat and mass transfer in aerodynamically designed, non-Newtonian nanofluids across aerodynamically designed, high-flux biomedical micro-devices for thermal management and reactive coating processes, but existing work is not uncharacteristically remiss regarding viscoelasticity, radiative heating, viscous dissipation, and homogeneous–heterogeneous reactions within a single scheme that is calibrated. This research investigates the flow of Williamson nanofluid across a dynamically wedged surface under conditions that include viscous dissipation, thermal radiation, and homogeneous-heterogeneous reactions. The paper develops a detailed mathematical approach that utilizes boundary layers to transform partial differential equations into ordinary… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2026.075040 - 26 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Applied Artificial Intelligence: Advanced Solutions for Engineering Real-World Challenges)
Abstract Accurate photovoltaic (PV) power generation forecasting is essential for the efficient integration of renewable energy into power grids. However, the nonlinear and non-stationary characteristics of PV power signals, driven by fluctuating weather conditions, pose significant challenges for reliable prediction. This study proposes a DOEP (Decomposition–Optimization–Error Correction–Prediction) framework, a hybrid forecasting approach that integrates adaptive signal decomposition, machine learning, metaheuristic optimization, and error correction. The PV power signal is first decomposed using CEEMDAN to extract multi-scale temporal features. Subsequently, the hyperparameters and window sizes of the LSSVM are optimized using a Segment-based EBQPSO strategy. The main… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.073821 - 26 February 2026
Abstract Accurate estimation of photovoltaic (PV) parameters is essential for optimizing solar module performance and enhancing resource efficiency in renewable energy systems. This study presents a process innovation by introducing, for the first time, the Triangulation Topology Aggregation Optimizer (TTAO) integrated with parallel computing to address PV parameter estimation challenges. The effectiveness and robustness of TTAO are rigorously evaluated using two standard benchmark datasets (KC200GT and R.T.C. France solar cells) and a real-world dataset (Poly70W solar module) under single-, double-, and triple-diode configurations. Results show that TTAO consistently achieves superior accuracy by producing the lowest RMSE More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.069931 - 26 February 2026
Abstract This research proposes an improved Puma optimization algorithm (IPuma) as a novel dynamic reconfiguration tool for a photovoltaic (PV) array linked in total-cross-tied (TCT). The proposed algorithm utilizes the Newton-Raphson search rule (NRSR) to boost the exploration process, especially in search spaces with more local regions, and boost the exploitation with adaptive parameters alternating with random parameters in the original Puma. The effectiveness of the introduced IPuma is confirmed through comprehensive evaluations on the CEC’20 benchmark problems. It shows superior performance compared to both established and modern metaheuristic algorithms in terms of effectively navigating the… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2026.077872 - 26 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advanced Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Methods Applied to Energy Systems)
Abstract Inspections of power transmission lines (PTLs) conducted using unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) are complicated by the fine structure of the lines and complex backgrounds, making accurate and efficient segmentation challenging. This study presents the Wavelet-Guided Transformer U-Net (WGT-UNet) model, a new hybrid network that combines Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT), and Transformer architectures. The model’s primary contribution is based on spatial and channel attention mechanisms derived from wavelet subbands to guide the Transformer’s self-attention structure. Thus, low and high frequency components are separated at each stage using DWT, suppressing structural noise and… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2026.075269 - 26 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advanced Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Methods Applied to Energy Systems)
Abstract Various factors, including weak tie-lines into the electric power system (EPS) networks, can lead to low-frequency oscillations (LFOs), which are considered an instant, non-threatening situation, but slow-acting and poisonous. Considering the challenge mentioned, this article proposes a clustering-based machine learning (ML) framework to enhance the stability of EPS networks by suppressing LFOs through real-time tuning of key power system stabilizer (PSS) parameters. To validate the proposed strategy, two distinct EPS networks are selected: the single-machine infinite-bus (SMIB) with a single-stage PSS and the unified power flow controller (UPFC) coordinated SMIB with a double-stage PSS. To… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.075178 - 26 February 2026
Abstract Robust teleoperation in image-guided interventions faces critical challenges from latency, deformation, and the quasi-periodic nature of physiological motion. This paper presents a fully integrated, latency-aware visual servoing system leveraging stereo vision, hand–eye calibration, and learning-based prediction for motion-compensated teleoperation. The system combines a calibrated binocular camera setup, dual robotic arms, and a predictive control loop incorporating Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) and Temporal Convolutional Network (TCN) models. Through experiments using both in vivo and phantom datasets, we quantitatively assess the prediction accuracy and motion-compensation performance of both models. Results show that TCNs deliver more stable and precise More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2026.074687 - 26 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Applied Artificial Intelligence: Advanced Solutions for Engineering Real-World Challenges)
Abstract In Human–Robot Interaction (HRI), generating robot trajectories that accurately reflect user intentions while ensuring physical realism remains challenging, especially in unstructured environments. In this study, we develop a multimodal framework that integrates symbolic task reasoning with continuous trajectory generation. The approach employs transformer models and adversarial training to map high-level intent to robotic motion. Information from multiple data sources, such as voice traits, hand and body keypoints, visual observations, and recorded paths, is integrated simultaneously. These signals are mapped into a shared representation that supports interpretable reasoning while enabling smooth and realistic motion generation. Based… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.073488 - 26 February 2026
Abstract Business Process Modelling (BPM) is essential for analyzing, improving, and automating the flow of information within organizations, but traditional approaches based on manual interpretation are slow, error-prone, and require a high level of expertise. This article proposes an innovative alternative solution that overcomes these limitations by automatically generating comprehensive Business Process Modelling and Notation (BPMN) diagrams solely from verbal descriptions of the processes to be modeled, utilizing Large Language Models (LLMs) and multimodal Artificial Intelligence (AI). Experimental results, based on video recordings of process explanations provided by an expert from an organization (in this case,… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2026.077574 - 26 February 2026
Abstract The modern world remains vulnerable to natural disasters, including floods, earthquakes, wildfires, and others. These events remain unpredictable and inevitable, and recovering quickly and effectively requires significant effort and expense. Monitoring is becoming more efficient thanks to technologies such as Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), which can access hard-to-reach areas and provide real-time data. However, in disaster-affected areas, these monitoring systems may encounter many obstacles when communicating with servers or transmitting monitored data. This paper proposes an adaptive communication model to overcome the challenges faced in disaster-affected areas. A base station is responsible for collecting data… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2026.078206 - 26 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Computational Models and Applications of Multi-Agent Systems in Control Engineering and Information Science)
Abstract Researchers are increasingly focused on enabling groups of multiple unmanned vehicles to operate cohesively in complex, real-world environments, where coordinated formation control and obstacle avoidance are essential for executing sophisticated collective tasks. This paper presents a Distributed Formation Control and Obstacle Avoidance (DFCOA) framework for multi-unmanned ground vehicles (UGV). DFCOA integrates a virtual leader structure for global guidance, an improved A* path planning algorithm with an advanced cost function for efficient path planning, and a repulsive-force- based improved vector field histogram star(VFH*) technique for collision avoidance. The virtual leader generates a reference trajectory while enabling… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2026.074428 - 26 February 2026
Abstract Domain adaptation aims to reduce the distribution gap between the training data (source domain) and the target data. This enables effective predictions even for domains not seen during training. However, most conventional domain adaptation methods assume a single source domain, making them less suitable for modern deep learning settings that rely on diverse and large-scale datasets. To address this limitation, recent research has focused on Multi-Source Domain Adaptation (MSDA), which aims to learn effectively from multiple source domains. In this paper, we propose Efficient Domain Transition for Multi-source (EDTM), a novel and efficient framework designed… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2026.071669 - 26 February 2026
Abstract Human Activity Recognition (HAR) is a novel area for computer vision. It has a great impact on healthcare, smart environments, and surveillance while is able to automatically detect human behavior. It plays a vital role in many applications, such as smart home, healthcare, human computer interaction, sports analysis, and especially, intelligent surveillance. In this paper, we propose a robust and efficient HAR system by leveraging deep learning paradigms, including pre-trained models, CNN architectures, and their average-weighted fusion. However, due to the diversity of human actions and various environmental influences, as well as a lack of… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2026.077373 - 26 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Recent Advances in Signal Processing and Computer Vision)
Abstract Arrhythmias are a frequently occurring phenomenon in clinical practice, but how to accurately distinguish subtle rhythm abnormalities remains an ongoing difficulty faced by the entire research community when conducting ECG-based studies. From a review of existing studies, two main factors appear to contribute to this problem: the uneven distribution of arrhythmia classes and the limited expressiveness of features learned by current models. To overcome these limitations, this study proposes a dual-path multimodal framework, termed DM-EHC (Dual-Path Multimodal ECG Heartbeat Classifier), for ECG-based heartbeat classification. The proposed framework links 1D ECG temporal features with 2D time–frequency More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2026.076332 - 26 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Machine Learning and Deep Learning-Based Pattern Recognition)
Abstract Automated detection of Motor Imagery (MI) tasks is extremely useful for prosthetic arms and legs of stroke patients for their rehabilitation. Prediction of MI tasks can be performed with the help of Electroencephalogram (EEG) signals recorded by placing electrodes on the scalp of subjects; however, accurate prediction of MI tasks remains a challenge due to noise that is incurred during the EEG signal recording process, the extraction of a feature vector with high interclass variance, and accurate classification. The proposed method consists of preprocessing, feature extraction, and classification. First, EEG signals are denoised using a… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2026.077714 - 26 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Machine Learning and Deep Learning-Based Pattern Recognition)
Abstract Most Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) interpretation techniques visualize only the dominant cues that the model relies on, but there is no guarantee that these represent all the evidence the model uses for classification. This limitation becomes critical when hidden secondary cues—potentially more meaningful than the visualized ones—remain undiscovered. This study introduces CasCAM (Cascaded Class Activation Mapping) to address this fundamental limitation through counterfactual reasoning. By asking “if this dominant cue were absent, what other evidence would the model use?”, CasCAM progressively masks the most salient features and systematically uncovers the hierarchy of classification evidence hidden More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2026.075732 - 26 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Artificial Intelligence Models in Healthcare: Challenges, Methods, and Applications)
Abstract Parkinson’s disease remains a major clinical issue in terms of early detection, especially during its prodromal stage when symptoms are not evident or not distinct. To address this problem, we proposed a new deep learning 2-based approach for detecting Parkinson’s disease before any of the overt symptoms develop during their prodromal stage. We used 5 publicly accessible datasets, including UCI Parkinson’s Voice, Spiral Drawings, PaHaW, NewHandPD, and PPMI, and implemented a dual stream CNN–BiLSTM architecture with Fisher-weighted feature merging and SHAP-based explanation. The findings reveal that the model’s performance was superior and achieved 98.2%, a More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2026.074800 - 26 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Data-Driven Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Computational Modelling for Engineering and Applied Sciences)
Abstract Mortality prediction in respiratory health is challenging, especially when using large-scale clinical datasets composed primarily of categorical variables. Traditional digital twin (DT) frameworks often rely on longitudinal or sensor-based data, which are not always available in public health contexts. In this article, we propose a novel proto-DT framework for mortality prediction in respiratory health using a large-scale categorical biomedical dataset. This dataset contains 415,711 severe acute respiratory infection cases from the Brazilian Unified Health System, including both COVID-19 and non-COVID-19 patients. Four classification models—extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost), logistic regression, random forest, and a deep neural… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2026.074283 - 26 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Exploring the Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Healthcare: Insights into Data Management, Integration, and Ethical Considerations)
Abstract Visual diagnosis of skin cancer is challenging due to subtle inter-class similarities, variations in skin texture, the presence of hair, and inconsistent illumination. Deep learning models have shown promise in assisting early detection, yet their performance is often limited by the severe class imbalance present in dermoscopic datasets. This paper proposes CANNSkin, a skin cancer classification framework that integrates a convolutional autoencoder with latent-space oversampling to address this imbalance. The autoencoder is trained to reconstruct lesion images, and its latent embeddings are used as features for classification. To enhance minority-class representation, the Synthetic Minority Oversampling… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2026.076798 - 26 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Exploring the Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Healthcare: Insights into Data Management, Integration, and Ethical Considerations)
Abstract Colorectal cancer is the third most diagnosed cancer worldwide, and immune checkpoint inhibitors have shown promising therapeutic outcomes in selected patient groups. This study performed a comprehensive analysis of multi-omics data from The Cancer Genome Atlas colorectal adenocarcinoma cohort (TCGA-COADREAD), accessed through cBioPortal, to develop machine learning models for predicting progression-free survival (PFS) following immunotherapy. The dataset included clinical variables, genomic alterations in Kirsten Rat Sarcoma Viral Oncogene Homolog (KRAS), B-Raf Proto-Oncogene (BRAF), and Neuroblastoma RAS Viral Oncogene Homolog (NRAS), microsatellite instability (MSI) status, tumor mutation burden (TMB), and expression of immune checkpoint genes. Kaplan–Meier… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2026.073473 - 26 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Intelligent Medical Decision Support Systems: Methods and Applications)
Abstract Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) have become valuable tools in medical imaging, enabling realistic image synthesis for enhancement, augmentation, and restoration. However, their integration into clinical workflows raises concerns, particularly the risk of subtle distortions or hallucinations that may undermine diagnostic accuracy and weaken trust in AI-assisted decision-making. To address this challenge, we propose a hybrid deep learning framework designed to detect GAN-induced artifacts in medical images, thereby reinforcing the reliability of AI-driven diagnostics. The framework integrates low-level statistical descriptors, including high-frequency residuals and Gray-Level Co-occurrence Matrix (GLCM) texture features, with high-level semantic representations extracted from… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.072603 - 26 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Cutting-Edge Security and Privacy Solutions for Next-Generation Intelligent Mobile Internet Technologies and Applications)
Abstract In this paper, we propose a new privacy-aware transmission scheduling algorithm for 6G ad hoc networks. This system enables end nodes to select the optimum time and scheme to transmit private data safely. In 6G dynamic heterogeneous infrastructures, unstable links and non-uniform hardware capabilities create critical issues regarding security and privacy. Traditional protocols are often too computationally heavy to allow 6G services to achieve their expected Quality-of-Service (QoS). As the transport network is built of ad hoc nodes, there is no guarantee about their trustworthiness or behavior, and transversal functionalities are delegated to the extreme nodes. However, More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.075239 - 26 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Emerging Artificial Intelligence Technologies and Applications-II)
Abstract Graph neural networks (GNN) have shown strong performance in node classification tasks, yet most existing models rely on uniform or shared weight aggregation, lacking flexibility in modeling the varying strength of relationships among nodes. This paper proposes a novel graph coupling convolutional model that introduces an adaptive weighting mechanism to assign distinct importance to neighboring nodes based on their similarity to the central node. Unlike traditional methods, the proposed coupling strategy enhances the interpretability of node interactions while maintaining competitive classification performance. The model operates in the spatial domain, utilizing adjacency list structures for efficient… More >