
Computers, Materials & Continua is a peer-reviewed Open Access journal that publishes all types of academic papers in the areas of computer networks, artificial intelligence, big data, software engineering, multimedia, cyber security, internet of things, materials genome, integrated materials science, and data analysis, modeling, designing and manufacturing of modern functional and multifunctional materials. This journal is published monthly by Tech Science Press.
SCI: 2024 Impact Factor 1.7; Scopus CiteScore (Impact per Publication 2024): 6.1; SNIP (Source Normalized Impact per Paper 2024): 0.675; Ei Compendex; Cambridge Scientific Abstracts; INSPEC Databases; Science Navigator; EBSCOhost; ProQuest Central; Zentralblatt für Mathematik; Portico, etc.
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073519 - 12 January 2026
Abstract Federated Learning (FL) has become a leading decentralized solution that enables multiple clients to train a model in a collaborative environment without directly sharing raw data, making it suitable for privacy-sensitive applications such as healthcare, finance, and smart systems. As the field continues to evolve, the research field has become more complex and scattered, covering different system designs, training methods, and privacy techniques. This survey is organized around the three core challenges: how the data is distributed, how models are synchronized, and how to defend against attacks. It provides a structured and up-to-date review of… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072696 - 12 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Signal Processing for Fault Diagnosis)
Abstract The critical components of gas turbines suffer from prolonged exposure to factors such as thermal oxidation, mechanical wear, and airflow disturbances during prolonged operation. These conditions can lead to a series of issues, including mechanical faults, air path malfunctions, and combustion irregularities. Traditional model-based approaches face inherent limitations due to their inability to handle nonlinear problems, natural factors, measurement uncertainties, fault coupling, and implementation challenges. The development of artificial intelligence algorithms has provided an effective solution to these issues, sparking extensive research into data-driven fault diagnosis methodologies. The review mechanism involved searching IEEE Xplore, ScienceDirect,… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.070684 - 12 January 2026
Abstract The growing developments in 5G and 6G wireless communications have revolutionized communications technologies, providing faster speeds with reduced latency and improved connectivity to users. However, it raises significant security challenges, including impersonation threats, data manipulation, distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks, and privacy breaches. Traditional security measures are inadequate due to the decentralized and dynamic nature of next-generation networks. This survey provides a comprehensive review of how Federated Learning (FL), Blockchain, and Digital Twin (DT) technologies can collectively enhance the security of 5G and 6G systems. Blockchain offers decentralized, immutable, and transparent mechanisms for securing More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073482 - 12 January 2026
Abstract The increasing interconnection of modern industrial control systems (ICSs) with the Internet has enhanced operational efficiency, but also made these systems more vulnerable to cyberattacks. This heightened exposure has driven a growing need for robust ICS security measures. Among the key defences, intrusion detection technology is critical in identifying threats to ICS networks. This paper provides an overview of the distinctive characteristics of ICS network security, highlighting standard attack methods. It then examines various intrusion detection methods, including those based on misuse detection, anomaly detection, machine learning, and specialised requirements. This paper concludes by exploring More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073347 - 12 January 2026
Abstract The rapid advancement of large language models (LLMs) has driven the pervasive adoption of AI-generated content (AIGC), while also raising concerns about misinformation, academic misconduct, biased or harmful content, and other risks. Detecting AI-generated text has thus become essential to safeguard the authenticity and reliability of digital information. This survey reviews recent progress in detection methods, categorizing approaches into passive and active categories based on their reliance on intrinsic textual features or embedded signals. Passive detection is further divided into surface linguistic feature-based and language model-based methods, whereas active detection encompasses watermarking-based and semantic retrieval-based More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072609 - 12 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Computer Vision and Image Processing: Feature Selection, Image Enhancement and Recognition)
Abstract Accurate segmentation of breast cancer in mammogram images plays a critical role in early diagnosis and treatment planning. As research in this domain continues to expand, various segmentation techniques have been proposed across classical image processing, machine learning (ML), deep learning (DL), and hybrid/ensemble models. This study conducts a systematic literature review using the PRISMA methodology, analyzing 57 selected articles to explore how these methods have evolved and been applied. The review highlights the strengths and limitations of each approach, identifies commonly used public datasets, and observes emerging trends in model integration and clinical relevance. More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.071804 - 12 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Object Detection and Recognition)
Abstract This paper presents a unified Unmanned Aerial Vehicle-based (UAV-based) traffic monitoring framework that integrates vehicle detection, tracking, counting, motion prediction, and classification in a modular and co-optimized pipeline. Unlike prior works that address these tasks in isolation, our approach combines You Only Look Once (YOLO) v10 detection, ByteTrack tracking, optical-flow density estimation, Long Short-Term Memory-based (LSTM-based) trajectory forecasting, and hybrid Speeded-Up Robust Feature (SURF) + Gray-Level Co-occurrence Matrix (GLCM) feature engineering with VGG16 classification. Upon the validation across datasets (UAVDT and UAVID) our framework achieved a detection accuracy of 94.2%, and 92.3% detection accuracy when More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072550 - 12 January 2026
Abstract Automatic segmentation of landslides from remote sensing imagery is challenging because traditional machine learning and early CNN-based models often fail to generalize across heterogeneous landscapes, where segmentation maps contain sparse and fragmented landslide regions under diverse geographical conditions. To address these issues, we propose a lightweight dual-stream siamese deep learning framework that integrates optical and topographical data fusion with an adaptive decoder, guided multimodal fusion, and deep supervision. The framework is built upon the synergistic combination of cross-attention, gated fusion, and sub-pixel upsampling within a unified dual-stream architecture specifically optimized for landslide segmentation, enabling efficient… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072514 - 12 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Development and Application of Deep Learning based Object Detection)
Abstract Container transportation is pivotal in global trade due to its efficiency, safety, and cost-effectiveness. However, structural defects—particularly in grapple slots—can result in cargo damage, financial loss, and elevated safety risks, including container drops during lifting operations. Timely and accurate inspection before and after transit is therefore essential. Traditional inspection methods rely heavily on manual observation of internal and external surfaces, which are time-consuming, resource-intensive, and prone to subjective errors. Container roofs pose additional challenges due to limited visibility, while grapple slots are especially vulnerable to wear from frequent use. This study proposes a two-stage automated… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073155 - 12 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Cyberspace Mapping and Anti-Mapping Techniques)
Abstract Topological information is very important for understanding different types of online web services, in particular, for online social networks (OSNs). People leverage such information for various applications, such as social relationship modeling, community detection, user profiling, and user behavior prediction. However, the leak of such information will also pose severe challenges for user privacy preserving due to its usefulness in characterizing users. Large-scale web crawling-based information probing is a representative way for obtaining topological information of online web services. In this paper, we explore how to defend against topological information probing for online web services,… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.074566 - 12 January 2026
Abstract As artificial Intelligence (AI) continues to expand exponentially, particularly with the emergence of generative pre-trained transformers (GPT) based on a transformer’s architecture, which has revolutionized data processing and enabled significant improvements in various applications. This document seeks to investigate the security vulnerabilities detection in the source code using a range of large language models (LLM). Our primary objective is to evaluate the effectiveness of Static Application Security Testing (SAST) by applying various techniques such as prompt persona, structure outputs and zero-shot. To the selection of the LLMs (CodeLlama 7B, DeepSeek coder 7B, Gemini 1.5 Flash,… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.070224 - 12 January 2026
Abstract Wi-Fi technology has evolved significantly since its introduction in 1997, advancing to Wi-Fi 6 as the latest standard, with Wi-Fi 7 currently under development. Despite these advancements, integrating machine learning into Wi-Fi networks remains challenging, especially in decentralized environments with multiple access points (mAPs). This paper is a short review that summarizes the potential applications of federated reinforcement learning (FRL) across eight key areas of Wi-Fi functionality, including channel access, link adaptation, beamforming, multi-user transmissions, channel bonding, multi-link operation, spatial reuse, and multi-basic servic set (multi-BSS) coordination. FRL is highlighted as a promising framework for More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.074871 - 12 January 2026
Abstract As containerized environments become increasingly prevalent in cloud-native infrastructures, the need for effective monitoring and detection of malicious behaviors has become critical. Malicious containers pose significant risks by exploiting shared host resources, enabling privilege escalation, or launching large-scale attacks such as cryptomining and botnet activities. Therefore, developing accurate and efficient detection mechanisms is essential for ensuring the security and stability of containerized systems. To this end, we propose a hybrid detection framework that leverages the extended Berkeley Packet Filter (eBPF) to monitor container activities directly within the Linux kernel. The framework simultaneously collects flow-based network… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073234 - 12 January 2026
Abstract Cloud services, favored by many enterprises due to their high flexibility and easy operation, are widely used for data storage and processing. However, the high latency, together with transmission overheads of the cloud architecture, makes it difficult to quickly respond to the demands of IoT applications and local computation. To make up for these deficiencies in the cloud, fog computing has emerged as a critical role in the IoT applications. It decentralizes the computing power to various lower nodes close to data sources, so as to achieve the goal of low latency and distributed processing.… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072865 - 12 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advancing Edge-Cloud Systems with Software-Defined Networking and Intelligence-Driven Approaches)
Abstract In real-world autonomous driving tests, unexpected events such as pedestrians or wild animals suddenly entering the driving path can occur. Conducting actual test drives under various weather conditions may also lead to dangerous situations. Furthermore, autonomous vehicles may operate abnormally in bad weather due to limitations of their sensors and GPS. Driving simulators, which replicate driving conditions nearly identical to those in the real world, can drastically reduce the time and cost required for market entry validation; consequently, they have become widely used. In this paper, we design a virtual driving test environment capable of More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072436 - 12 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advanced Modeling of Smart and Composite Materials and Structures)
Abstract Artificial intelligence (AI) based models have been used to predict the structural, optical, mechanical, and electrochemical properties of zinc oxide/graphene oxide nanocomposites. Machine learning (ML) models such as Artificial Neural Networks (ANN), Support Vector Regression (SVR), Multilayer Perceptron (MLP), and hybrid, along with fuzzy logic tools, were applied to predict the different properties like wavelength at maximum intensity (444 nm), crystallite size (17.50 nm), and optical bandgap (2.85 eV). While some other properties, such as energy density, power density, and charge transfer resistance, were also predicted with the help of datasets of 1000 (80:20). In… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072495 - 12 January 2026
Abstract This work investigates the effects of deformation mechanisms on the mechanical properties and anisotropy of rolled AZ31B magnesium alloy under uniaxial tension, combining experimental characterization with Visco-Plastic Self Consistent (VPSC) modeling. The research focuses particularly on anisotropic mechanical responses along transverse direction (TD) and rolling direction (RD). Experimental measurements and computational simulations consistently demonstrate that prismatic <a> slip activation significantly reduces the strain hardening rate during the initial stage of tensile deformation. By suppressing the activation of specific deformation mechanisms along RD and TD, the tensile mechanical behavior of the magnesium alloy was further investigated. More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073161 - 12 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Perspective Materials for Science and Industrial: Modeling and Simulation)
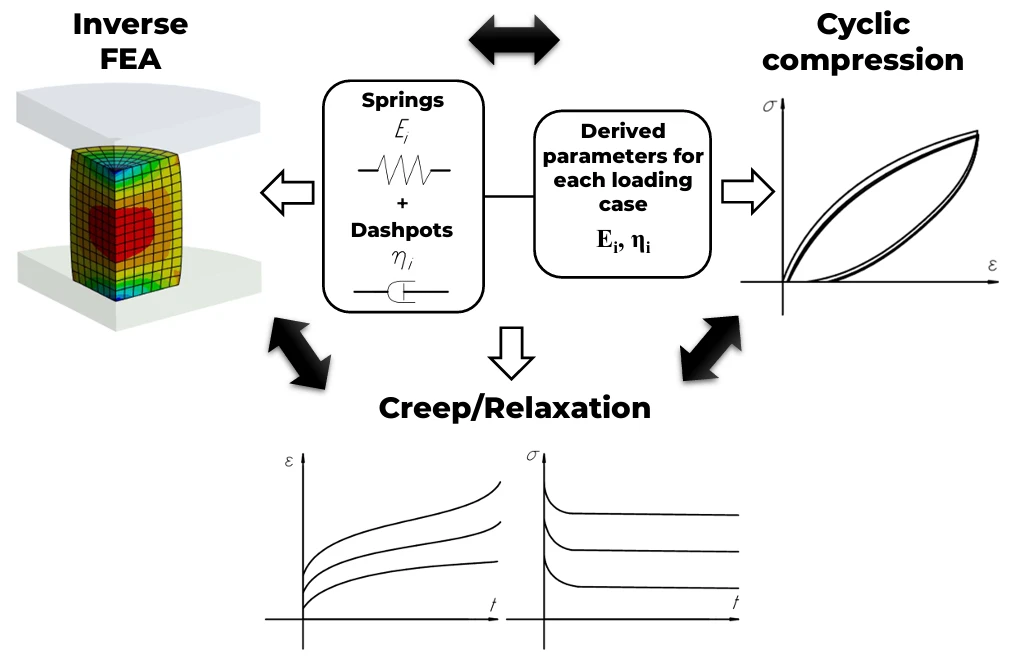
Abstract This study presents and verifies a hybrid methodology for reliable determination of parameters in structural rheological models (Zener, Burgers, and Maxwell) describing the viscoelastic behavior of polyurethane specimens manufactured using extrusion-based 3D printing. Through comprehensive testing, including cyclic compression at strain rates ranging from 0.12 to 120 mm/min (0%–15% strain) and creep/relaxation experiments (10%–30% strain), the lumped parameters were independently determined using both analytical and numerical solutions of the models’ differential equations, followed by cross-verification in additional experiments. Numerical solutions for creep and relaxation problems were obtained using finite element analysis, with the three-parameter Mooney-Rivlin… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073772 - 12 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advanced Computational Modeling and Simulations for Engineering Structures and Multifunctional Materials: Bridging Theory and Practice)
Abstract This study presents a framework involving statistical modeling and machine learning to accurately predict and optimize the mechanical and damping properties of hybrid granite–epoxy (G–E) composites reinforced with cast iron (CI) filler particles. Hybrid G–E composite with added cast iron (CI) filler particles enhances stiffness, strength, and vibration damping, offering enhanced performance for vibration-sensitive engineering applications. Unlike conventional approaches, this work simultaneously employs Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) for high-accuracy property prediction and Response Surface Methodology (RSM) for in-depth analysis of factor interactions and optimization. A total of 24 experimental test data sets of varying input… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.074068 - 12 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Computational Modeling of Mechanical Behavior of Advanced Materials)
Abstract In modern construction, Lightweight Aggregate Concrete (LWAC) has been recognized as a vital material of concern because of its unique properties, such as reduced density and improved thermal insulation. Despite the extensive knowledge regarding its macroscopic properties, there is a wide knowledge gap in understanding the influence of microscale parameters like aggregate porosity and volume ratio on the mechanical response of LWAC. This study aims to bridge this knowledge gap, spurred by the need to enhance the predictability and applicability of LWAC in various construction environments. With the help of advanced numerical methods, including the… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072266 - 12 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advanced Modeling of Smart and Composite Materials and Structures)
Abstract The roller is one of the fundamental elements of ore belt conveyor systems since it supports, guides, and directs material on the belt. This component comprises a body (the external tube) that rotates around a fixed shaft supported by easels. The external tube and shaft of rollers used in ore conveyor belts are mostly made of steel, resulting in high mass, hindering maintenance and replacement. Aiming to achieve mass reduction, we conducted a structural optimization of a roller with a polymeric external tube (hereafter referred to as a polymeric roller), seeking the optimal values for… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072707 - 12 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Applications of Neural Networks in Materials)
Abstract In this study, artificial neural networks (ANNs) were implemented to determine design parameters for an impressed current cathodic protection (ICCP) prototype. An ASTM A36 steel plate was tested in 3.5% NaCl solution, seawater, and NS4 using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) to monitor the evolution of the substrate surface, which affects the current required to reach the protection potential (
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072507 - 12 January 2026
Abstract As circuit feature sizes approach the nanoscale, traditional Copper (Cu) interconnects face significant hurdles posed by rising resistance-capacitance (RC) delay, electromigration, and high power dissipation. These limitations impose constraints on the scalability and reliability of future semiconductor technologies. Our paper describes the new Vertical multilayer Aluminium Boron Nitride Nanoribbon (AlBN) interconnect structure, integrated with Density functional theory (DFT) using first-principles calculations. This study explores AlBN-based nanostructures with doping of 1Cu, 2Cu, 1Fe (Iron), and 2Fe for the application of Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) interconnects. The AlBN structure utilized the advantages of vertical multilayer interconnects… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.071880 - 12 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Efficient Vision Transformers: Architectures, Optimization, and Applications)
Abstract Foreign body classification on coal conveyor belts is a critical component of intelligent coal mining systems. Previous approaches have primarily utilized convolutional neural networks (CNNs) to effectively integrate spatial and semantic information. However, the performance of CNN-based methods remains limited in classification accuracy, primarily due to insufficient exploration of local image characteristics. Unlike CNNs, Vision Transformer (ViT) captures discriminative features by modeling relationships between local image patches. However, such methods typically require a large number of training samples to perform effectively. In the context of foreign body classification on coal conveyor belts, the limited availability… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.071254 - 12 January 2026
Abstract Numerous sectors, such as education, the IT sector, and corporate organizations, transitioned to virtual meetings after the COVID-19 crisis. Organizations now seek to assess participants’ fatigue levels in online meetings to remain competitive. Instructors cannot effectively monitor every individual in a virtual environment, which raises significant concerns about participant fatigue. Our proposed system monitors fatigue, identifying attentive and drowsy individuals throughout the online session. We leverage Dlib’s pre-trained facial landmark detector and focus on the eye landmarks only, offering a more detailed analysis for predicting eye opening and closing of the eyes, rather than focusing… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.071269 - 12 January 2026
Abstract With the development of technology, diffusion model-based solvers have shown significant promise in solving Combinatorial Optimization (CO) problems, particularly in tackling Non-deterministic Polynomial-time hard (NP-hard) problems such as the Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP). However, existing diffusion model-based solvers typically employ a fixed, uniform noise schedule (e.g., linear or cosine annealing) across all training instances, failing to fully account for the unique characteristics of each problem instance. To address this challenge, we present Graph-Guided Diffusion Solvers (GGDS), an enhanced method for improving graph-based diffusion models. GGDS leverages Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) to capture graph structural information… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072093 - 12 January 2026
Abstract Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks pose severe threats to Industrial Control Networks (ICNs), where service disruption can cause significant economic losses and operational risks. Existing signature-based methods are ineffective against novel attacks, and traditional machine learning models struggle to capture the complex temporal dependencies and dynamic traffic patterns inherent in ICN environments. To address these challenges, this study proposes a deep feature-driven hybrid framework that integrates Transformer, BiLSTM, and KNN to achieve accurate and robust DDoS detection. The Transformer component extracts global temporal dependencies from network traffic flows, while BiLSTM captures fine-grained sequential dynamics. The learned… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072426 - 12 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in IoT Security: Challenges, Solutions, and Future Applications)
Abstract Federated Learning (FL) enables joint training over distributed devices without data exchange but is highly vulnerable to attacks by adversaries in the form of model poisoning and malicious update injection. This work proposes Secured-FL, a blockchain-based defensive framework that combines smart contract–based authentication, clustering-driven outlier elimination, and dynamic threshold adjustment to defend against adversarial attacks. The framework was implemented on a private Ethereum network with a Proof-of-Authority consensus algorithm to ensure tamper-resistant and auditable model updates. Large-scale simulation on the Cyber Data dataset, under up to 50% malicious client settings, demonstrates Secured-FL achieves 6%–12% higher accuracy, More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072464 - 12 January 2026
Abstract The integration of High-Altitude Platform Stations (HAPS) with Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces (RIS) represents a critical advancement for next-generation wireless networks, offering unprecedented opportunities for ubiquitous connectivity. However, existing research reveals significant gaps in dynamic resource allocation, joint optimization, and equitable service provisioning under varying channel conditions, limiting practical deployment of these technologies. This paper addresses these challenges by proposing a novel Fairness-Aware Deep Q-Learning (FAIR-DQL) framework for joint resource management and phase configuration in HAPS-RIS systems. Our methodology employs a comprehensive three-tier algorithmic architecture integrating adaptive power control, priority-based user scheduling, and dynamic learning mechanisms. More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.071452 - 12 January 2026
Abstract Cyber-criminals target smart connected devices for spyware distribution and security breaches, but existing Internet of Things (IoT) security standards are insufficient. Major IoT industry players prioritize market share over security, leading to insecure smart products. Traditional host-based protection solutions are less effective due to limited resources. Overcoming these challenges and enhancing the security of IoT Devices requires a security design at the network level that uses lightweight cryptographic parameters. In order to handle control, administration, and security concerns in traditional networking, the Gateway Node offers a contemporary networking architecture. By managing all network-level computations and… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.069718 - 12 January 2026
Abstract As healthcare systems increasingly embrace digitalization, effective management of electronic health records (EHRs) has emerged as a critical priority, particularly in inpatient settings where data sensitivity and real-time access are paramount. Traditional EHR systems face significant challenges, including unauthorized access, data breaches, and inefficiencies in tracking follow-up appointments, which heighten the risk of misdiagnosis and medication errors. To address these issues, this research proposes a hybrid blockchain-based solution for securely managing EHRs, specifically designed as a framework for tracking inpatient follow-ups. By integrating QR code-enabled data access with a blockchain architecture, this innovative approach enhances… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072406 - 12 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Object Detection: Methods and Applications)
Abstract To address the challenge of real-time detection of unauthorized drone intrusions in complex low-altitude urban environments such as parks and airports, this paper proposes an enhanced MBS-YOLO (Multi-Branch Small Target Detection YOLO) model for anti-drone object detection, based on the YOLOv8 architecture. To overcome the limitations of existing methods in detecting small objects within complex backgrounds, we designed a C2f-Pu module with excellent feature extraction capability and a more compact parameter set, aiming to reduce the model’s computational complexity. To improve multi-scale feature fusion, we construct a Multi-Branch Feature Pyramid Network (MB-FPN) that employs a… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.071771 - 12 January 2026
Abstract Manual inspection of onba earing casting defects is not realistic and unreliable, particularly in the case of some micro-level anomalies which lead to major defects on a large scale. To address these challenges, we propose BearFusionNet, an attention-based deep learning architecture with multi-stream, which merges both DenseNet201 and MobileNetV2 for feature extraction with a classification head inspired by VGG19. This hybrid design, figuratively beaming from one layer to another, extracts the enormity of representations on different scales, backed by a pre-preprocessing pipeline that brings defect saliency to the fore through contrast adjustment, denoising, and edge… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.071207 - 12 January 2026
Abstract In multi-modal emotion recognition, excessive reliance on historical context often impedes the detection of emotional shifts, while modality heterogeneity and unimodal noise limit recognition performance. Existing methods struggle to dynamically adjust cross-modal complementary strength to optimize fusion quality and lack effective mechanisms to model the dynamic evolution of emotions. To address these issues, we propose a multi-level dynamic gating and emotion transfer framework for multi-modal emotion recognition. A dynamic gating mechanism is applied across unimodal encoding, cross-modal alignment, and emotion transfer modeling, substantially improving noise robustness and feature alignment. First, we construct a unimodal encoder More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072081 - 12 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Object Detection and Recognition)
Abstract This study addresses the risk of privacy leakage during the transmission and sharing of multimodal data in smart grid substations by proposing a three-tier privacy-preserving architecture based on asynchronous federated learning. The framework integrates blockchain technology, the InterPlanetary File System (IPFS) for distributed storage, and a dynamic differential privacy mechanism to achieve collaborative security across the storage, service, and federated coordination layers. It accommodates both multimodal data classification and object detection tasks, enabling the identification and localization of key targets and abnormal behaviors in substation scenarios while ensuring privacy protection. This effectively mitigates the single-point… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.071124 - 12 January 2026
Abstract Industrial Cyber-Physical Systems (ICPSs) play a vital role in modern industries by providing an intellectual foundation for automated operations. With the increasing integration of information-driven processes, ensuring the security of Industrial Control Production Systems (ICPSs) has become a critical challenge. These systems are highly vulnerable to attacks such as denial-of-service (DoS), eclipse, and Sybil attacks, which can significantly disrupt industrial operations. This work proposes an effective protection strategy using an Artificial Intelligence (AI)-enabled Smart Contract (SC) framework combined with the Heterogeneous Barzilai–Borwein Support Vector (HBBSV) method for industrial-based CPS environments. The approach reduces run time… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.071552 - 12 January 2026
Abstract Message structure reconstruction is a critical task in protocol reverse engineering, aiming to recover protocol field structures without access to source code. It enables important applications in network security, including malware analysis and protocol fuzzing. However, existing methods suffer from inaccurate field boundary delineation and lack hierarchical relationship recovery, resulting in imprecise and incomplete reconstructions. In this paper, we propose
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072692 - 12 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Smart Roads, Smarter Cars, Safety and Security: Evolution of Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks)
Abstract With the continuous advancement of unmanned technology in various application domains, the development and deployment of blind-spot-free panoramic video systems have gained increasing importance. Such systems are particularly critical in battlefield environments, where advanced panoramic video processing and wireless communication technologies are essential to enable remote control and autonomous operation of unmanned ground vehicles (UGVs). However, conventional video surveillance systems suffer from several limitations, including limited field of view, high processing latency, low reliability, excessive resource consumption, and significant transmission delays. These shortcomings impede the widespread adoption of UGVs in battlefield settings. To overcome these… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.071532 - 12 January 2026
Abstract Identifying the community structure of complex networks is crucial to extracting insights and understanding network properties. Although several community detection methods have been proposed, many are unsuitable for social networks due to significant limitations. Specifically, most approaches depend mainly on user–user structural links while overlooking service-centric, semantic, and multi-attribute drivers of community formation, and they also lack flexible filtering mechanisms for large-scale, service-oriented settings. Our proposed approach, called community discovery-based service (CDBS), leverages user profiles and their interactions with consulted web services. The method introduces a novel similarity measure, global similarity interaction profile (GSIP), which… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072404 - 12 January 2026
Abstract To solve the false detection and missed detection problems caused by various types and sizes of defects in the detection of steel surface defects, similar defects and background features, and similarities between different defects, this paper proposes a lightweight detection model named multiscale edge and squeeze-and-excitation attention detection network (MSESE), which is built upon the You Only Look Once version 11 nano (YOLOv11n). To address the difficulty of locating defect edges, we first propose an edge enhancement module (EEM), apply it to the process of multiscale feature extraction, and then propose a multiscale edge enhancement… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.070337 - 12 January 2026
Abstract The generation of high-quality 3D models from single 2D images remains challenging in terms of accuracy and completeness. Deep learning has emerged as a promising solution, offering new avenues for improvements. However, building models from scratch is computationally expensive and requires large datasets. This paper presents a transfer-learning-based approach for category-specific 3D reconstruction from a single 2D image. The core idea is to fine-tune a pre-trained model on specific object categories using new, unseen data, resulting in specialized versions of the model that are better adapted to reconstruct particular objects. The proposed approach utilizes a… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072381 - 12 January 2026
Abstract In the wireless energy transmission service composition optimization problem, a key challenge is accurately capturing users’ preferences for service criteria under complex influencing factors, and optimally selecting a composition solution under their budget constraints. Existing studies typically evaluate satisfaction solely based on energy transmission capacity, while overlooking critical factors such as price and trustworthiness of the provider, leading to a mismatch between optimization outcomes and user needs. To address this gap, we construct a user satisfaction evaluation model for multi-user and multi-provider scenarios, systematically incorporating service price, transmission capacity, and trustworthiness into the satisfaction assessment… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072942 - 12 January 2026
Abstract In image analysis, high-precision semantic segmentation predominantly relies on supervised learning. Despite significant advancements driven by deep learning techniques, challenges such as class imbalance and dynamic performance evaluation persist. Traditional weighting methods, often based on pre-statistical class counting, tend to overemphasize certain classes while neglecting others, particularly rare sample categories. Approaches like focal loss and other rare-sample segmentation techniques introduce multiple hyperparameters that require manual tuning, leading to increased experimental costs due to their instability. This paper proposes a novel CAWASeg framework to address these limitations. Our approach leverages Grad-CAM technology to generate class activation… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.071776 - 12 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Image Recognition: Innovations, Applications, and Future Directions)
Abstract Satellite image segmentation plays a crucial role in remote sensing, supporting applications such as environmental monitoring, land use analysis, and disaster management. However, traditional segmentation methods often rely on large amounts of labeled data, which are costly and time-consuming to obtain, especially in large-scale or dynamic environments. To address this challenge, we propose the Semi-Supervised Multi-View Picture Fuzzy Clustering (SS-MPFC) algorithm, which improves segmentation accuracy and robustness, particularly in complex and uncertain remote sensing scenarios. SS-MPFC unifies three paradigms: semi-supervised learning, multi-view clustering, and picture fuzzy set theory. This integration allows the model to effectively… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072493 - 12 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence for Intrusion Detection Systems)
Abstract With an increase in internet-connected devices and a dependency on online services, the threat of Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks has become a significant concern in cybersecurity. The proposed system follows a multi-step process, beginning with the collection of datasets from different edge devices and network nodes. To verify its effectiveness, experiments were conducted using the CICDoS2017, NSL-KDD, and CICIDS benchmark datasets alongside other existing models. Recursive feature elimination (RFE) with random forest is used to select features from the CICDDoS2019 dataset, on which a BiLSTM model is trained on local nodes. Local models… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.071008 - 12 January 2026
Abstract Federated Learning (FL) protects data privacy through a distributed training mechanism, yet its decentralized nature also introduces new security vulnerabilities. Backdoor attacks inject malicious triggers into the global model through compromised updates, posing significant threats to model integrity and becoming a key focus in FL security. Existing backdoor attack methods typically embed triggers directly into original images and consider only data heterogeneity, resulting in limited stealth and adaptability. To address the heterogeneity of malicious client devices, this paper proposes a novel backdoor attack method named Capability-Adaptive Shadow Backdoor Attack (CASBA). By incorporating measurements of clients’… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.071661 - 12 January 2026
Abstract Social bots are automated programs designed to spread rumors and misinformation, posing significant threats to online security. Existing research shows that the structure of a social network significantly affects the behavioral patterns of social bots: a higher number of connected components weakens their collaborative capabilities, thereby reducing their proportion within the overall network. However, current social bot detection methods still make limited use of topological features. Furthermore, both graph neural network (GNN)-based methods that rely on local features and those that leverage global features suffer from their own limitations, and existing studies lack an effective… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.070948 - 12 January 2026
Abstract Online examinations have become a dominant assessment mode, increasing concerns over academic integrity. To address the critical challenge of detecting cheating behaviours, this study proposes a hybrid deep learning approach that combines visual detection and temporal behaviour classification. The methodology utilises object detection models—You Only Look Once (YOLOv12), Faster Region-based Convolutional Neural Network (RCNN), and Single Shot Detector (SSD) MobileNet—integrated with classification models such as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), Bidirectional Gated Recurrent Unit (Bi-GRU), and CNN-LSTM (Long Short-Term Memory). Two distinct datasets were used: the Online Exam Proctoring (EOP) dataset from Michigan State University and… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072915 - 12 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Nature-Inspired and Metaheuristic Optimization Algorithms: Theory, Applications, and Emerging Trends)
Abstract To address the issue that hybrid flow shop production struggles to handle order disturbance events, a dynamic scheduling model was constructed. The model takes minimizing the maximum makespan, delivery time deviation, and scheme deviation degree as the optimization objectives. An adaptive dynamic scheduling strategy based on the degree of order disturbance is proposed. An improved multi-objective Grey Wolf (IMOGWO) optimization algorithm is designed by combining the “job-machine” two-layer encoding strategy, the timing-driven two-stage decoding strategy, the opposition-based learning initialization population strategy, the POX crossover strategy, the dual-operation dynamic mutation strategy, and the variable neighborhood search… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073492 - 12 January 2026
Abstract Predictive maintenance (PdM) is vital for ensuring the reliability, safety, and cost efficiency of heavy-duty vehicle fleets. However, real-world sensor data are often highly imbalanced, noisy, and temporally irregular, posing significant challenges to model robustness and deployment. Using multivariate time-series data from Scania trucks, this study proposes a novel PdM framework that integrates efficient feature summarization with cost-sensitive hierarchical classification. First, the proposed last_k_summary method transforms recent operational records into compact statistical and trend-based descriptors while preserving missingness, allowing LightGBM to leverage its inherent split rules without ad-hoc imputation. Then, a two-stage LightGBM framework is developed… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072036 - 12 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advancements in Evolutionary Optimization Approaches: Theory and Applications)
Abstract In a wide range of engineering applications, complex constrained multi-objective optimization problems (CMOPs) present significant challenges, as the complexity of constraints often hampers algorithmic convergence and reduces population diversity. To address these challenges, we propose a novel algorithm named Constraint Intensity-Driven Evolutionary Multitasking (CIDEMT), which employs a two-stage, tri-task framework to dynamically integrates problem structure and knowledge transfer. In the first stage, three cooperative tasks are designed to explore the Constrained Pareto Front (CPF), the Unconstrained Pareto Front (UPF), and the
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072710 - 12 January 2026
Abstract Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) in Flying Ad-Hoc Networks (FANETs) are widely used in both civilian and military fields, but they face severe security, trust, and privacy vulnerabilities due to their high mobility, dynamic topology, and open wireless channels. Existing security protocols for Mobile Ad-Hoc Networks (MANETs) cannot be directly applied to FANETs, as FANETs require lightweight, high real-time performance, and strong anonymity. The current FANETs security protocol cannot simultaneously meet the requirements of strong anonymity, high security, and low overhead in high dynamic and resource-constrained scenarios. To address these challenges, this paper proposes an Anonymous Authentication… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.070468 - 12 January 2026
Abstract Breast cancer remains one of the leading causes of cancer mortality world-wide, with accurate molecular subtyping is critical for guiding treatment and improving patient outcomes. Traditional molecular subtyping via immuno-histochemistry (IHC) test is invasive, time-consuming, and may not fully represent tumor heterogeneity. This study proposes a non-invasive approach using digital mammography images and deep learning algorithm for classifying breast cancer molecular subtypes. Four pretrained models, including two Convolutional Neural Networks (MobileNet_V3_Large and VGG-16) and two Vision Transformers (ViT_B_16 and ViT_Base_Patch16_Clip_224) were fine-tuned to classify images into HER2-enriched, Luminal, Normal-like, and Triple Negative subtypes. Hyperparameter tuning,… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072281 - 12 January 2026
Abstract The increased connectivity and reliance on digital technologies have exposed smart transportation systems to various cyber threats, making intrusion detection a critical aspect of ensuring their secure operation. Traditional intrusion detection systems have limitations in terms of centralized architecture, lack of transparency, and vulnerability to single points of failure. This is where the integration of blockchain technology with signature-based intrusion detection can provide a robust and decentralized solution for securing smart transportation systems. This study tackles the issue of database manipulation attacks in smart transportation networks by proposing a signature-based intrusion detection system. The introduced More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072145 - 12 January 2026
Abstract Audio-visual speech recognition (AVSR), which integrates audio and visual modalities to improve recognition performance and robustness in noisy or adverse acoustic conditions, has attracted significant research interest. However, Conformer-based architectures remain computational expensive due to the quadratic increase in the spatial and temporal complexity of their softmax-based attention mechanisms with sequence length. In addition, Conformer-based architectures may not provide sufficient flexibility for modeling local dependencies at different granularities. To mitigate these limitations, this study introduces a novel AVSR framework based on a ReLU-based Sparse and Grouped Conformer (RSG-Conformer) architecture. Specifically, we propose a Global-enhanced Sparse… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.071865 - 12 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Intelligent Computation and Large Machine Learning Models for Edge Intelligence in industrial Internet of Things)
Abstract In scenarios where ground-based cloud computing infrastructure is unavailable, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) act as mobile edge computing (MEC) servers to provide on-demand computation services for ground terminals. To address the challenge of jointly optimizing task scheduling and UAV trajectory under limited resources and high mobility of UAVs, this paper presents PER-MATD3, a multi-agent deep reinforcement learning algorithm with prioritized experience replay (PER) into the Centralized Training with Decentralized Execution (CTDE) framework. Specifically, PER-MATD3 enables each agent to learn a decentralized policy using only local observations during execution, while leveraging a shared replay buffer with More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.069949 - 12 January 2026
Abstract With the recent increase in data volume and diversity, traditional text representation techniques are struggling to capture context, particularly in environments with sparse data. To address these challenges, this study proposes a new model, the Masked Joint Representation Model (MJRM). MJRM approximates the original hypothesis by leveraging multiple elements in a limited context. It dynamically adapts to changes in characteristics based on data distribution through three main components. First, masking-based representation learning, termed selective dynamic masking, integrates topic modeling and sentiment clustering to generate and train multiple instances across different data subsets, whose predictions are… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072172 - 12 January 2026
Abstract Detecting small forest fire targets in unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) images is difficult, as flames typically cover only a very limited portion of the visual scene. This study proposes Context-guided Compact Lightweight Network (CCLNet), an end-to-end lightweight model designed to detect small forest fire targets while ensuring efficient inference on devices with constrained computational resources. CCLNet employs a three-stage network architecture. Its key components include three modules. C3F-Convolutional Gated Linear Unit (C3F-CGLU) performs selective local feature extraction while preserving fine-grained high-frequency flame details. Context-Guided Feature Fusion Module (CGFM) replaces plain concatenation with triplet-attention interactions to… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073227 - 12 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Industrial Big Data and Artificial Intelligence-Driven Intelligent Perception, Maintenance, and Decision Optimization in Industrial Systems-2nd Edition)
Abstract Deep learning-based wind turbine blade fault diagnosis has been widely applied due to its advantages in end-to-end feature extraction. However, several challenges remain. First, signal noise collected during blade operation masks fault features, severely impairing the fault diagnosis performance of deep learning models. Second, current blade fault diagnosis often relies on single-sensor data, resulting in limited monitoring dimensions and ability to comprehensively capture complex fault states. To address these issues, a multi-sensor fusion-based wind turbine blade fault diagnosis method is proposed. Specifically, a CNN-Transformer Coupled Feature Learning Architecture is constructed to enhance the ability to More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.071192 - 12 January 2026
Abstract Recommendation systems have become indispensable for providing tailored suggestions and capturing evolving user preferences based on interaction histories. The collaborative filtering (CF) model, which depends exclusively on user-item interactions, commonly encounters challenges, including the cold-start problem and an inability to effectively capture the sequential and temporal characteristics of user behavior. This paper introduces a personalized recommendation system that combines deep learning techniques with Bayesian Personalized Ranking (BPR) optimization to address these limitations. With the strong support of Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks, we apply it to identify sequential dependencies of user behavior and then incorporate… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.071242 - 12 January 2026
Abstract Underwater images frequently suffer from chromatic distortion, blurred details, and low contrast, posing significant challenges for enhancement. This paper introduces AquaTree, a novel underwater image enhancement (UIE) method that reformulates the task as a Markov Decision Process (MDP) through the integration of Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) and deep reinforcement learning (DRL). The framework employs an action space of 25 enhancement operators, strategically grouped for basic attribute adjustment, color component balance, correction, and deblurring. Exploration within MCTS is guided by a dual-branch convolutional network, enabling intelligent sequential operator selection. Our core contributions include: (1) a More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072625 - 12 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Integrating Split Learning with Tiny Models for Advanced Edge Computing Applications in the Internet of Vehicles)
Abstract Split Learning (SL) has been promoted as a promising collaborative machine learning technique designed to address data privacy and resource efficiency. Specifically, neural networks are divided into client and server sub-networks in order to mitigate the exposure of sensitive data and reduce the overhead on client devices, thereby making SL particularly suitable for resource-constrained devices. Although SL prevents the direct transmission of raw data, it does not alleviate entirely the risk of privacy breaches. In fact, the data intermediately transmitted to the server sub-model may include patterns or information that could reveal sensitive data. Moreover,… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072058 - 12 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Attention Mechanism-based Complex System Pattern Intelligent Recognition and Accurate Prediction)
Abstract Accurate detection of smoke and fire sources is critical for early fire warning and environmental monitoring. However, conventional detection approaches are highly susceptible to noise, illumination variations, and complex environmental conditions, which often reduce detection accuracy and real-time performance. To address these limitations, we propose Lightweight and Precise YOLO (LP-YOLO), a high-precision detection framework that integrates a self-attention mechanism with a feature pyramid, built upon YOLOv8. First, to overcome the restricted receptive field and parameter redundancy of conventional Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), we design an enhanced backbone based on Wavelet Convolutions (WTConv), which expands the… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072343 - 12 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Nature-Inspired Optimization & Applications in Computer Science: From Particle Swarms to Hybrid Metaheuristics)
Abstract Early and accurate detection of bone cancer and marrow cell abnormalities is critical for timely intervention and improved patient outcomes. This paper proposes a novel hybrid deep learning framework that integrates a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) with a Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory (BiLSTM) architecture, optimized using the Firefly Optimization algorithm (FO). The proposed CNN-BiLSTM-FO model is tailored for structured biomedical data, capturing both local patterns and sequential dependencies in diagnostic features, while the Firefly Algorithm fine-tunes key hyperparameters to maximize predictive performance. The approach is evaluated on two benchmark biomedical datasets: one comprising diagnostic data… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.068878 - 12 January 2026
Abstract The performance of data restore is one of the key indicators of user experience for backup storage systems. Compared to the traditional offline restore process, online restore reduces downtime during backup restoration, allowing users to operate on already restored files while other files are still being restored. This approach improves availability during restoration tasks but suffers from a critical limitation: inconsistencies between the access sequence and the restore sequence. In many cases, the file a user needs to access at a given moment may not yet be restored, resulting in significant delays and poor user… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073818 - 12 January 2026
Abstract The cloud-fog computing paradigm has emerged as a novel hybrid computing model that integrates computational resources at both fog nodes and cloud servers to address the challenges posed by dynamic and heterogeneous computing networks. Finding an optimal computational resource for task offloading and then executing efficiently is a critical issue to achieve a trade-off between energy consumption and transmission delay. In this network, the task processed at fog nodes reduces transmission delay. Still, it increases energy consumption, while routing tasks to the cloud server saves energy at the cost of higher communication delay. Moreover, the… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073315 - 12 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Recent Advances in Blockchain Technology and Applications)
Abstract With the development of sharded blockchains, high cross-shard rates and load imbalance have emerged as major challenges. Account partitioning based on hashing and real-time load faces the issue of high cross-shard rates. Account partitioning based on historical transaction graphs is effective in reducing cross-shard rates but suffers from load imbalance and limited adaptability to dynamic workloads. Meanwhile, because of the coupling between consensus and execution, a target shard must receive both the partitioned transactions and the partitioned accounts before initiating consensus and execution. However, we observe that transaction partitioning and subsequent consensus do not require… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072392 - 12 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Enhancing AI Applications through NLP and LLM Integration)
Abstract In multi-domain neural machine translation tasks, the disparity in data distribution between domains poses significant challenges in distinguishing domain features and sharing parameters across domains. This paper proposes a Transformer-based multi-domain-aware mixture of experts model. To address the problem of domain feature differentiation, a mixture of experts (MoE) is introduced into attention to enhance the domain perception ability of the model, thereby improving the domain feature differentiation. To address the trade-off between domain feature distinction and cross-domain parameter sharing, we propose a domain-aware mixture of experts (DMoE). A domain-aware gating mechanism is introduced within the… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073423 - 12 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Privacy-Enhancing Technologies for Secure Data Cooperation and Circulation)
Abstract Attribute-Based Encryption (ABE) has emerged as a fundamental access control mechanism in data sharing, enabling data owners to define flexible access policies. A critical aspect of ABE is key revocation, which plays a pivotal role in maintaining security. However, existing key revocation mechanisms face two major challenges: (1) High overhead due to ciphertext and key updates, primarily stemming from the reliance on revocation lists during attribute revocation, which increases computation and communication costs. (2) Limited universality, as many attribute revocation mechanisms are tailored to specific ABE constructions, restricting their broader applicability. To address these challenges,… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.071301 - 12 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Contrastive Representation Learning for Next-Generation LLMs: Methods and Applications in NLP)
Abstract Knowledge distillation has become a standard technique for compressing large language models into efficient student models, but existing methods often struggle to balance prediction accuracy with explanation quality. Recent approaches such as Distilling Step-by-Step (DSbS) introduce explanation supervision, yet they apply it in a uniform manner that may not fully exploit the different learning dynamics of prediction and explanation. In this work, we propose a task-structured curriculum learning (TSCL) framework that structures training into three sequential phases: (i) prediction-only, to establish stable feature representations; (ii) joint prediction–explanation, to align task outputs with rationale generation; and (iii)… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.070273 - 12 January 2026
Abstract The development of brain-computer interfaces (BCI) based on motor imagery (MI) has greatly improved patients’ quality of life with movement disorders. The classification of upper limb MI has been widely studied and applied in many fields, including rehabilitation. However, the physiological representations of left and right lower limb movements are too close and activated deep in the cerebral cortex, making it difficult to distinguish their features. Therefore, classifying lower limbs motor imagery is more challenging. In this study, we propose a feature extraction method based on functional connectivity, which utilizes phase-locked values to construct a… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072909 - 12 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Omnipresent AI in the Cloud Era Reshaping Distributed Computation and Adaptive Systems for Modern Applications)
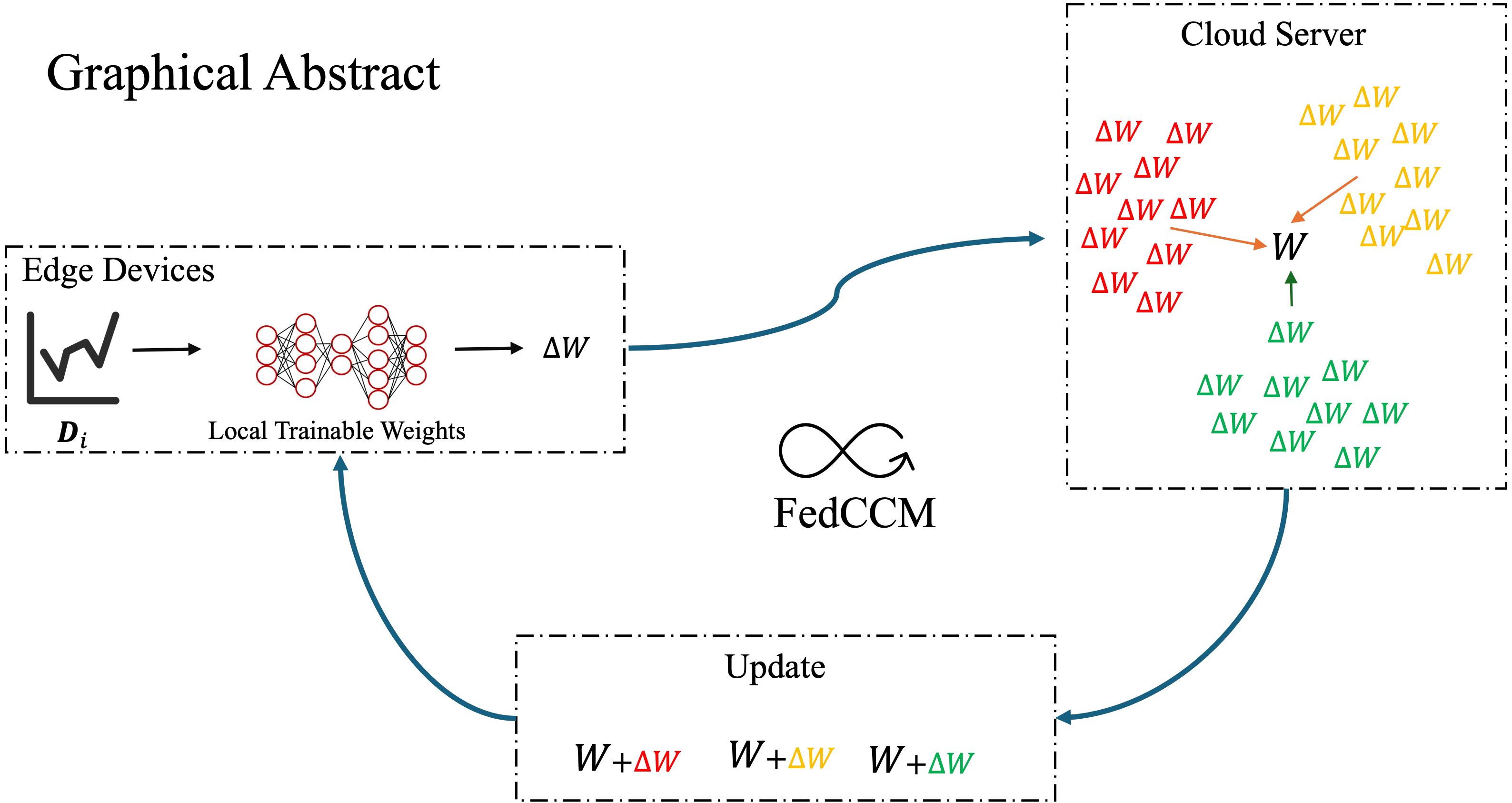
Abstract Federated learning often experiences slow and unstable convergence due to edge-side data heterogeneity. This problem becomes more severe when edge participation rate is low, as the information collected from different edge devices varies significantly. As a result, communication overhead increases, which further slows down the convergence process. To address this challenge, we propose a simple yet effective federated learning framework that improves consistency among edge devices. The core idea is clusters the lookahead gradients collected from edge devices on the cloud server to obtain personalized momentum for steering local updates. In parallel, a global momentum… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.071733 - 12 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Attention Mechanism-based Complex System Pattern Intelligent Recognition and Accurate Prediction)
Abstract Automated Program Repair (APR) techniques have shown significant potential in mitigating the cost and complexity associated with debugging by automatically generating corrective patches for software defects. Despite considerable progress in APR methodologies, existing approaches frequently lack contextual awareness of runtime behaviors and structural intricacies inherent in buggy source code. In this paper, we propose a novel APR approach that integrates attention mechanisms within an autoencoder-based framework, explicitly utilizing structural code affinity and execution context correlation derived from stack trace analysis. Our approach begins with an innovative preprocessing pipeline, where code segments and stack traces are… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072768 - 12 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: AI-Powered Software Engineering)
Abstract Test case prioritization and ranking play a crucial role in software testing by improving fault detection efficiency and ensuring software reliability. While prioritization selects the most relevant test cases for optimal coverage, ranking further refines their execution order to detect critical faults earlier. This study investigates machine learning techniques to enhance both prioritization and ranking, contributing to more effective and efficient testing processes. We first employ advanced feature engineering alongside ensemble models, including Gradient Boosted, Support Vector Machines, Random Forests, and Naive Bayes classifiers to optimize test case prioritization, achieving an accuracy score of
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.069587 - 12 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Emerging Machine Learning Methods and Applications)
Abstract Ensuring the reliability of power transmission networks depends heavily on the early detection of faults in key components such as insulators, which serve both mechanical and electrical functions. Even a single defective insulator can lead to equipment breakdown, costly service interruptions, and increased maintenance demands. While unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) enable rapid and cost-effective collection of high-resolution imagery, accurate defect identification remains challenging due to cluttered backgrounds, variable lighting, and the diverse appearance of faults. To address these issues, we introduce a real-time inspection framework that integrates an enhanced YOLOv10 detector with a Hybrid Quantum-Enhanced More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073159 - 12 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Time Series Analysis, Modelling and Forecasting)
Abstract Marine forecasting is critical for navigation safety and disaster prevention. However, traditional ocean numerical forecasting models are often limited by substantial errors and inadequate capture of temporal-spatial features. To address the limitations, the paper proposes a TimeXer-based numerical forecast correction model optimized by an exogenous-variable attention mechanism. The model treats target forecast values as internal variables, and incorporates historical temporal-spatial data and seven-day numerical forecast results from traditional models as external variables based on the embedding strategy of TimeXer. Using a self-attention structure, the model captures correlations between exogenous variables and target sequences, explores intrinsic More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073171 - 12 January 2026
Abstract In recent years, fog computing has become an important environment for dealing with the Internet of Things. Fog computing was developed to handle large-scale big data by scheduling tasks via cloud computing. Task scheduling is crucial for efficiently handling IoT user requests, thereby improving system performance, cost, and energy consumption across nodes in cloud computing. With the large amount of data and user requests, achieving the optimal solution to the task scheduling problem is challenging, particularly in terms of cost and energy efficiency. In this paper, we develop novel strategies to save energy consumption across… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.071644 - 12 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Industrial Big Data and Artificial Intelligence-Driven Intelligent Perception, Maintenance, and Decision Optimization in Industrial Systems-2nd Edition)
Abstract In order to address the challenges posed by complex background interference, high miss-detection rates of micro-scale defects, and limited model deployment efficiency in photovoltaic (PV) module defect detection, this paper proposes an efficient detection framework based on an improved YOLOv11 architecture. First, a Re-parameterized Convolution (RepConv) module is integrated into the backbone to enhance the model’s sensitivity to fine-grained defects—such as micro-cracks and hot spots—while maintaining high inference efficiency. Second, a Multi-Scale Feature Fusion Convolutional Block Attention Mechanism (MSFF-CBAM) is designed to guide the network toward critical defect regions by jointly modeling channel-wise and spatial… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072681 - 12 January 2026
Abstract With the advent of sixth-generation mobile communications (6G), space–air–ground integrated networks have become mainstream. This paper focuses on collaborative scheduling for mobile edge computing (MEC) under a three-tier heterogeneous architecture composed of mobile devices, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), and macro base stations (BSs). This scenario typically faces fast channel fading, dynamic computational loads, and energy constraints, whereas classical queuing-theoretic or convex-optimization approaches struggle to yield robust solutions in highly dynamic settings. To address this issue, we formulate a multi-agent Markov decision process (MDP) for an air–ground-fused MEC system, unify link selection, bandwidth/power allocation, and task… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072948 - 12 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Deep Learning and Neural Networks: Architectures, Applications, and Challenges)
Abstract Recent advances in deep learning have significantly improved image deblurring; however, existing approaches still suffer from limited global context modeling, inadequate detail restoration, and poor texture or edge perception, especially under complex dynamic blur. To address these challenges, we propose the Multi-Resolution Fusion Network (MRFNet), a blind multi-scale deblurring framework that integrates progressive residual connectivity for hierarchical feature fusion. The network employs a three-stage design: (1) TransformerBlocks capture long-range dependencies and reconstruct coarse global structures; (2) Nonlinear Activation Free Blocks (NAFBlocks) enhance local detail representation and mid-level feature fusion; and (3) an optimized residual subnetwork… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072481 - 12 January 2026
Abstract Malware poses a significant threat to the Internet of Things (IoT). It enables unauthorized access to devices in the IoT environment. The lack of unique architectural standards causes challenges in developing robust malware detection (MD) models. The existing models demand substantial computational resources. This study intends to build a lightweight MD model to detect anomalies in IoT networks. The authors develop a transformation technique, converting the malware binaries into images. MobileNet V2 is fine-tuned using improved grey wolf optimization (IGWO) to extract crucial features of malicious and benign samples. The ResNeXt model is combined with… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073662 - 12 January 2026
Abstract With the rapid development of smart manufacturing, intelligent safety monitoring in industrial workshops has become increasingly important. To address the challenges of complex backgrounds, target scale variation, and excessive model parameters in worker violation detection, this study proposes ADCP-YOLO, an enhanced lightweight model based on YOLOv8. Here, “ADCP” represents four key improvements: Alterable Kernel Convolution (AKConv), Dilated-Wise Residual (DWR) module, Channel Reconstruction Global Attention Mechanism (CRGAM), and Powerful-IoU loss. These components collaboratively enhance feature extraction, multi-scale perception, and localization accuracy while effectively reducing model complexity and computational cost. Experimental results show that ADCP-YOLO achieves a More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072664 - 12 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Extended Reality (XR) and Human-Computer Interaction)
Abstract In recent years, three-dimensional reconstruction technologies that employ multiple cameras have continued to evolve significantly, enabling remote collaboration among users in extended Reality (XR) environments. In addition, methods for deploying multiple cameras for motion capture of users (e.g., performers) are widely used in computer graphics. As the need to minimize and optimize the number of cameras grows to reduce costs, various technologies and research approaches focused on Optimal Camera Placement (OCP) are continually being proposed. However, as most existing studies assume homogeneous camera setups, there is a growing demand for studies on heterogeneous camera setups.… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073850 - 12 January 2026
Abstract In the field of intelligent surveillance, weakly supervised video anomaly detection (WSVAD) has garnered widespread attention as a key technology that identifies anomalous events using only video-level labels. Although multiple instance learning (MIL) has dominated the WSVAD for a long time, its reliance solely on video-level labels without semantic grounding hinders a fine-grained understanding of visually similar yet semantically distinct events. In addition, insufficient temporal modeling obscures causal relationships between events, making anomaly decisions reactive rather than reasoning-based. To overcome the limitations above, this paper proposes an adaptive knowledge-based guidance method that integrates external structured… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.071509 - 12 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Big Data-Driven Intelligent Decision Systems)
Abstract Earthquakes are highly destructive spatio-temporal phenomena whose analysis is essential for disaster preparedness and risk mitigation. Modern seismological research produces vast volumes of heterogeneous data from seismic networks, satellite observations, and geospatial repositories, creating the need for scalable infrastructures capable of integrating and analyzing such data to support intelligent decision-making. Data warehousing technologies provide a robust foundation for this purpose; however, existing earthquake-oriented data warehouses remain limited, often relying on simplified schemas, domain-specific analytics, or cataloguing efforts. This paper presents the design and implementation of a spatio-temporal data warehouse for seismic activity. The framework integrates… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073630 - 12 January 2026
Abstract With the increasing complexity of malware attack techniques, traditional detection methods face significant challenges, such as privacy preservation, data heterogeneity, and lacking category information. To address these issues, we propose Federated Dynamic Prototype Learning (FedDPL) for malware classification by integrating Federated Learning with a specifically designed K-means. Under the Federated Learning framework, model training occurs locally without data sharing, effectively protecting user data privacy and preventing the leakage of sensitive information. Furthermore, to tackle the challenges of data heterogeneity and the lack of category information, FedDPL introduces a dynamic prototype learning mechanism, which adaptively adjusts the More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.071011 - 12 January 2026
Abstract To enhance speech emotion recognition capability, this study constructs a speech emotion recognition model integrating the adaptive acoustic mixup (AAM) and improved coordinate and shuffle attention (ICASA) methods. The AAM method optimizes data augmentation by combining a sample selection strategy and dynamic interpolation coefficients, thus enabling information fusion of speech data with different emotions at the acoustic level. The ICASA method enhances feature extraction capability through dynamic fusion of the improved coordinate attention (ICA) and shuffle attention (SA) techniques. The ICA technique reduces computational overhead by employing depth-separable convolution and an h-swish activation function and More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.071021 - 12 January 2026
Abstract Modern intelligent systems, such as autonomous vehicles and face recognition, must continuously adapt to new scenarios while preserving their ability to handle previously encountered situations. However, when neural networks learn new classes sequentially, they suffer from catastrophic forgetting—the tendency to lose knowledge of earlier classes. This challenge, which lies at the core of class-incremental learning, severely limits the deployment of continual learning systems in real-world applications with streaming data. Existing approaches, including rehearsal-based methods and knowledge distillation techniques, have attempted to address this issue but often struggle to effectively preserve decision boundaries and discriminative features… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072279 - 12 January 2026
Abstract Task scheduling in cloud computing is a multi-objective optimization problem, often involving conflicting objectives such as minimizing execution time, reducing operational cost, and maximizing resource utilization. However, traditional approaches frequently rely on single-objective optimization methods which are insufficient for capturing the complexity of such problems. To address this limitation, we introduce MDMOSA (Multi-objective Dwarf Mongoose Optimization with Simulated Annealing), a hybrid that integrates multi-objective optimization for efficient task scheduling in Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) cloud environments. MDMOSA harmonizes the exploration capabilities of the biologically inspired Dwarf Mongoose Optimization (DMO) with the exploitation strengths of Simulated Annealing (SA), More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073700 - 12 January 2026
Abstract Deep learning has made significant progress in the field of oriented object detection for remote sensing images. However, existing methods still face challenges when dealing with difficult tasks such as multi-scale targets, complex backgrounds, and small objects in remote sensing. Maintaining model lightweight to address resource constraints in remote sensing scenarios while improving task completion for remote sensing tasks remains a research hotspot. Therefore, we propose an enhanced multi-scale feature extraction lightweight network EM-YOLO based on the YOLOv8s architecture, specifically optimized for the characteristics of large target scale variations, diverse orientations, and numerous small objects… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072064 - 12 January 2026
Abstract With the rapid development of digital culture, a large number of cultural texts are presented in the form of digital and network. These texts have significant characteristics such as sparsity, real-time and non-standard expression, which bring serious challenges to traditional classification methods. In order to cope with the above problems, this paper proposes a new ASSC (ALBERT, SVD, Self-Attention and Cross-Entropy)-TextRCNN digital cultural text classification model. Based on the framework of TextRCNN, the Albert pre-training language model is introduced to improve the depth and accuracy of semantic embedding. Combined with the dual attention mechanism, the… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072964 - 12 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Action Recognition: Algorithms, Applications, and Emerging Trends)
Abstract End-to-end Temporal Action Detection (TAD) has achieved remarkable progress in recent years, driven by innovations in model architectures and the emergence of Video Foundation Models (VFMs). However, existing TAD methods that perform full fine-tuning of pretrained video models often incur substantial computational costs, which become particularly pronounced when processing long video sequences. Moreover, the need for precise temporal boundary annotations makes data labeling extremely expensive. In low-resource settings where annotated samples are scarce, direct fine-tuning tends to cause overfitting. To address these challenges, we introduce Dynamic Low-Rank Adapter (DyLoRA), a lightweight fine-tuning framework tailored specifically… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.070741 - 12 January 2026
Abstract Modern industrial environments require uninterrupted machinery operation to maintain productivity standards while ensuring safety and minimizing costs. Conventional maintenance methods, such as reactive maintenance (i.e., run to failure) or time-based preventive maintenance (i.e., scheduled servicing), prove ineffective for complex systems with many Internet of Things (IoT) devices and sensors because they fall short in detecting faults at early stages when it is most crucial. This paper presents a predictive maintenance framework based on a hybrid deep learning model that integrates the capabilities of Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) Networks and Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs). The framework… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.071186 - 12 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Deep Learning: Emerging Trends, Applications and Research Challenges for Image Recognition)
Abstract Medical image segmentation is of critical importance in the domain of contemporary medical imaging. However, U-Net and its variants exhibit limitations in capturing complex nonlinear patterns and global contextual information. Although the subsequent U-KAN model enhances nonlinear representation capabilities, it still faces challenges such as gradient vanishing during deep network training and spatial detail loss during feature downsampling, resulting in insufficient segmentation accuracy for edge structures and minute lesions. To address these challenges, this paper proposes the RE-UKAN model, which innovatively improves upon U-KAN. Firstly, a residual network is introduced into the encoder to effectively… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.071511 - 12 January 2026
Abstract With the rapid development of Internet technology, REST APIs (Representational State Transfer Application Programming Interfaces) have become the primary communication standard in modern microservice architectures, raising increasing concerns about their security. Existing fuzz testing methods include random or dictionary-based input generation, which often fail to ensure both syntactic and semantic correctness, and OpenAPI-based approaches, which offer better accuracy but typically lack detailed descriptions of endpoints, parameters, or data formats. To address these issues, this paper proposes the APIDocX fuzz testing framework. It introduces a crawler tailored for dynamic web pages that automatically simulates user interactions More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.071251 - 12 January 2026
Abstract Deep neural networks have achieved excellent classification results on several computer vision benchmarks. This has led to the popularity of machine learning as a service, where trained algorithms are hosted on the cloud and inference can be obtained on real-world data. In most applications, it is important to compress the vision data due to the enormous bandwidth and memory requirements. Video codecs exploit spatial and temporal correlations to achieve high compression ratios, but they are computationally expensive. This work computes the motion fields between consecutive frames to facilitate the efficient classification of videos. However, contrary… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.069139 - 12 January 2026
Abstract With the increasing complexity of logistics operations, traditional static vehicle routing models are no longer sufficient. In practice, customer demands often arise dynamically, and multi-depot systems are commonly used to improve efficiency. This paper first introduces a vehicle routing problem with the goal of minimizing operating costs in a multi-depot environment with dynamic demand. New customers appear in the delivery process at any time and are periodically optimized according to time slices. Then, we propose a scheduling system TS-DPU based on an improved ant colony algorithm TS-ACO to solve this problem. The classical ant colony More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.069263 - 12 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Nature-Inspired Optimization & Applications in Computer Science: From Particle Swarms to Hybrid Metaheuristics)
Abstract Accurate parameter extraction of photovoltaic (PV) models plays a critical role in enabling precise performance prediction, optimal system sizing, and effective operational control under diverse environmental conditions. While a wide range of metaheuristic optimisation techniques have been applied to this problem, many existing methods are hindered by slow convergence rates, susceptibility to premature stagnation, and reduced accuracy when applied to complex multi-diode PV configurations. These limitations can lead to suboptimal modelling, reducing the efficiency of PV system design and operation. In this work, we propose an enhanced hybrid optimisation approach, the modified Spider Wasp Optimization… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072735 - 12 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Deep Learning and Neural Networks: Architectures, Applications, and Challenges)
Abstract Activation pruning reduces neural network complexity by eliminating low-importance neuron activations, yet identifying the critical pruning threshold—beyond which accuracy rapidly deteriorates—remains computationally expensive and typically requires exhaustive search. We introduce a thermodynamics-inspired framework that treats activation distributions as energy-filtered physical systems and employs the free energy of activations as a principled evaluation metric. Phase-transition–like phenomena in the free-energy profile—such as extrema, inflection points, and curvature changes—yield reliable estimates of the critical pruning threshold, providing a theoretically grounded means of predicting sharp accuracy degradation. To further enhance efficiency, we propose a renormalized free energy technique that More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, Vol.86, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.071994 - 12 January 2026
Abstract Recommendation systems are key to boosting user engagement, satisfaction, and retention, particularly on media platforms where personalized content is vital. Sequential recommendation systems learn from user-item interactions to predict future items of interest. However, many current methods rely on unique user and item IDs, limiting their ability to represent users and items effectively, especially in zero-shot learning scenarios where training data is scarce. With the rapid development of Large Language Models (LLMs), researchers are exploring their potential to enhance recommendation systems. However, there is a semantic gap between the linguistic semantics of LLMs and the… More >