Salinity Stress in Wheat: Effects, Mechanisms and Management Strategies
Mahmoud F. Seleiman1,2,#,*, Muhammad Talha Aslam3,#, Bushra Ahmed Alhammad4, Muhammad Umair Hassan5, Rizwan Maqbool3, Muhammad Umer Chattha3, Imran Khan3, Harun Ireri Gitari6, Omer S. Uslu7, Rana Roy8, Martin Leonardo Battaglia9
Phyton-International Journal of Experimental Botany, Vol.91, No.4, pp. 667-694, 2022, DOI:10.32604/phyton.2022.017365
- 09 December 2021
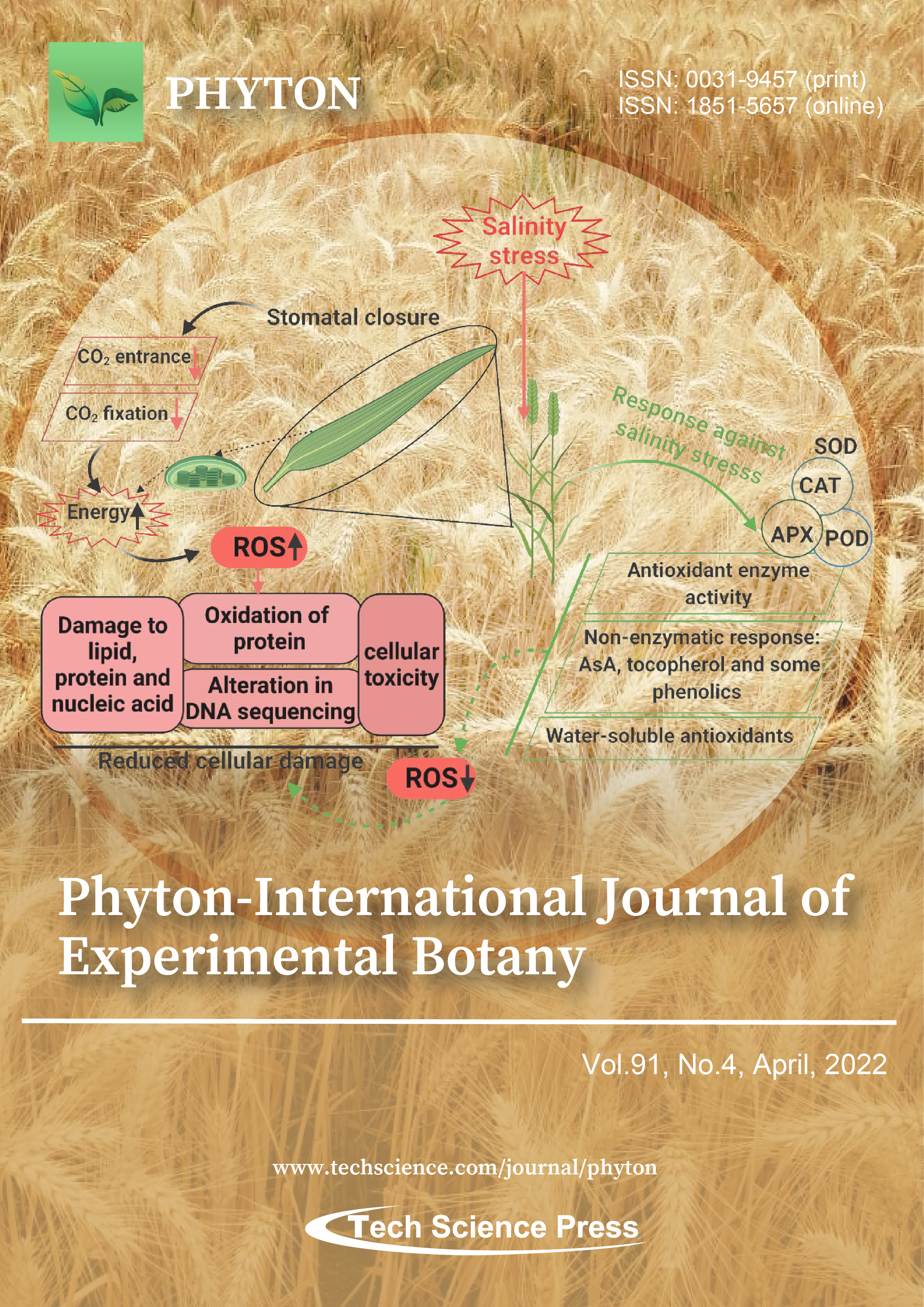
Abstract Salinity stress is a major threat to global food production and its intensity is continuously increasing because of
anthropogenic activities. Wheat is a staple food and a source of carbohydrates and calories for the majority of
people across the globe. However, wheat productivity is adversely affected by salt stress, which is associated with
a reduction in germination, growth, altered reproductive behavior and enzymatic activity, disrupted photosynthesis, hormonal imbalance, oxidative stress, and yield reductions. Thus, a better understanding of wheat (plant)
behavior to salinity stress has essential implications to devise counter and alleviation measures to cope… More >