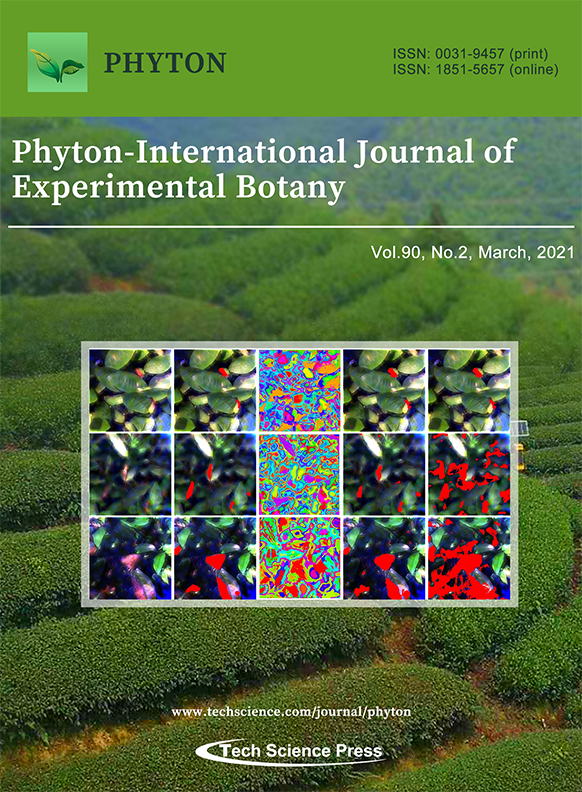
Tea is one of the most famous three traditional beverages. In recent years, hyperspectral imaging technology has shown great potential in detecting and differentiating plant diseases, pests, and some other stresses at the leaf level. However, the lack of studies at canopy level hampers the detection of tea plant stresses at a larger scale. In this issue, Cui et al. proposed a stepwise procedure based on the canopy level hyperspectral imaging data and spectral analysis, image processing, and machine learning approaches. The results show the feasibility of present methods in large-scale detection of stresses in tea plantations.
View this paper