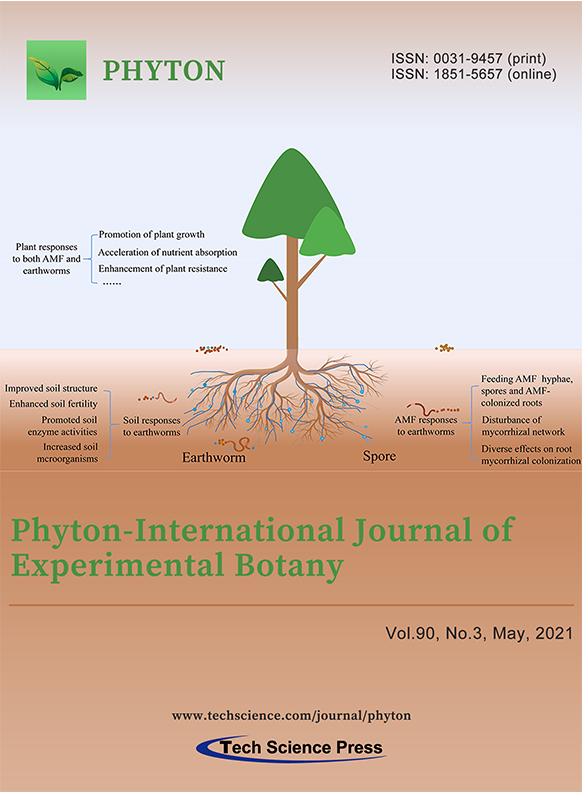
Rhizosphere is the interface between the plant and the soil, where inhabit many organisms. Within these soil organisms, arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) and earthworms belong to the soil community. They are beneficial organisms at different trophic levels improving both soil fertility and structure development, thus collectively promoting plant growth. Earthworm activities redistribute mycorrhizal fungi spores and may give diversified (i.e., positive and negative) effects on root mycorrhizal colonization. Dual inoculation with earthworms and AMF strongly magnifies the response on plant growth. This is through increasing soil enzyme activities and changing soil nutrient availability, collectively mitigating the negative effects of biotic stresses. In this review, we outline the effects of earthworms on AMF root colonization and activitiy. The interaction between earthworms and AMF on plants along with suggested future research are also summarized.
View this paper