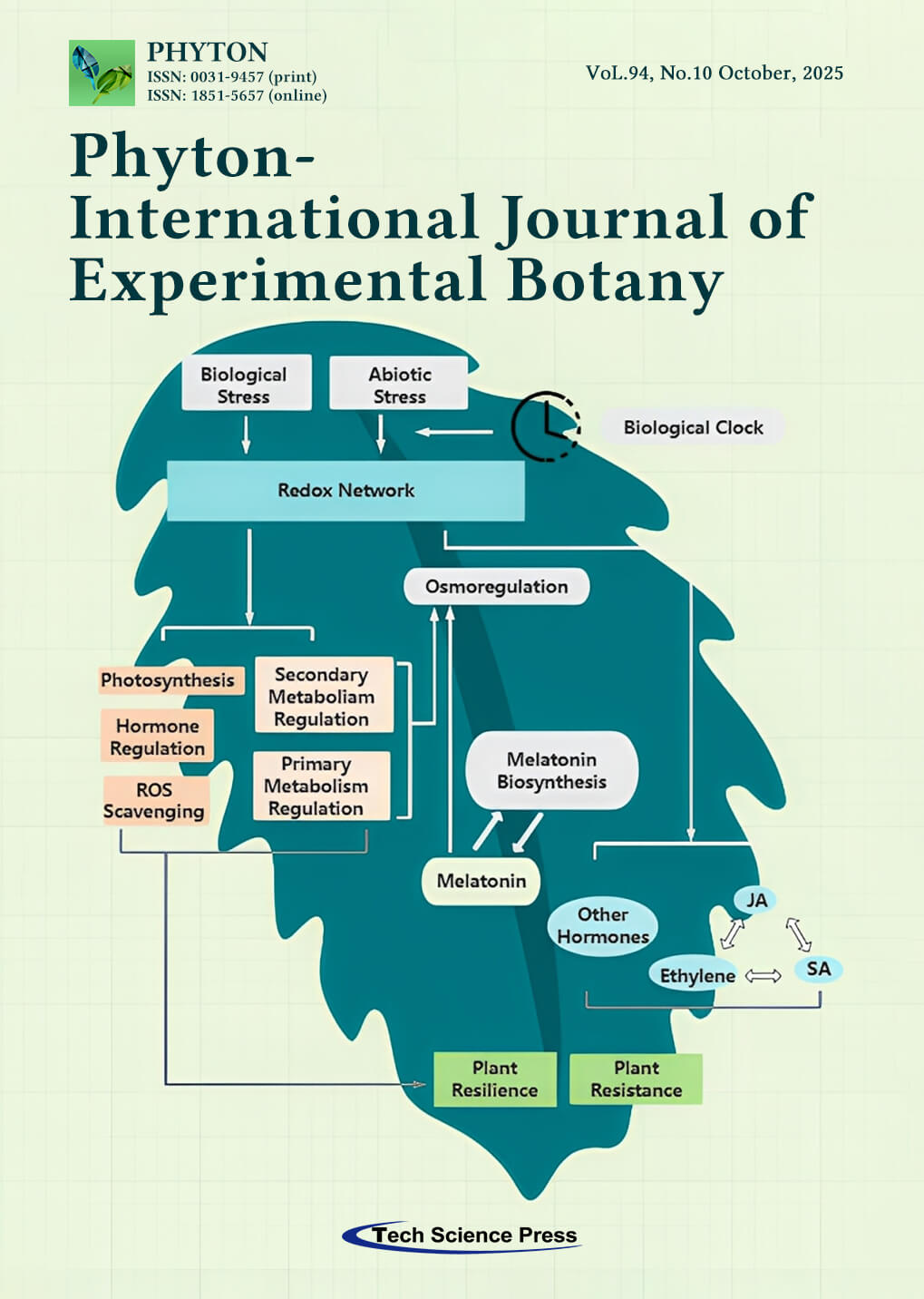
Melatonin plays a bifunctional role in regulating plant resilience and resistance. The synthesis of endogenous melatonin is critically regulated by genes associated with the circadian rhythm pathway. When confronted with biotic or abiotic stresses, plants experience a disruption in membrane pressure homeostasis, leading to the upregulation of crucial genes involved in the synthesis of endogenous hormones and secondary metabolites. This includes the passive synthesis of multiple endogenous hormones, including melatonin. Additionally, these stresses impair photosynthetic capacity, resulting in ROS bursts. Melatonin resynthesis partly counteracts the membrane peroxidation caused by external stresses, thereby enhancing this resilience and stress tolerance.
View this paper