 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Tyler Overholt Daniel1,*, David Thole2, Randy Casals3, Anthony Atala3, Steve Hodges3, Marc Colaco3
Canadian Journal of Urology, DOI:10.32604/cju.2026.074059
Abstract Objectives: Day of surgery cancellations present several workflow challenges that result in delay of care for patients and revenue loss for physicians. This study aimed to further understand same-day pediatric urology surgical cancellations, and the authors assessed identifiable trends for quality improvement over a one-year time period. Methods: Same-day surgical cancellations were prospectively identified at a single tertiary care center, Atrium Health Wake Forest Baptist, from 01 October 2022 to 30 September 2023. Reasons for cancellation were recorded per the parent/legal guardian and categorized as an avoidable or unavoidable cause. Demographic data, surgical rescheduling, and… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Xiaoxiao Guo1,2,#, Mingyu Chang1,2,#, Gangyue Hao1,2, Fengbo Zhang3,*, Haoran Xia1,2,*
Canadian Journal of Urology, DOI:10.32604/cju.2026.075599
Abstract Background: Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is prevalent among aging men. Whether exposure to internet-derived health information is associated with disease awareness and symptom burden at initial diagnosis remains unclear. Methods: We conducted a cross-sectional study of 400 newly diagnosed BPH outpatients. Participants were classified by prior exposure to internet-derived BPH content. BPH awareness and International Prostate Symptom Scores (IPSS) were compared using the Mann-Whitney U test and multivariate linear regression adjusted for age, education, and disposable income. Stratified analyses were performed according to educational attainment, disposable income, and content format. Results: Exposure to internet-derived BPH content… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Daxun Luo#, Bixiao Wang#, Haifeng Song, Chaoyue Ji, Weiguo Hu, Bo Xiao, Boxing Su, Yubao Liu*, Jianxing Li*
Canadian Journal of Urology, DOI:10.32604/cju.2026.076790
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Endoscopic Management of Urolithiasis)
Abstract Objectives: Urinary stone composition critically influences treatment selection and recurrence prevention, yet current intraoperative assessment remains imprecise. This study aims to achieve intraoperative prediction of stone composition by applying a deep convolutional neural network (CNN) to routinely captured endoscopic images. Methods: We retrospectively studied endoscopic images from stone-breaking surgeries in Beijing Tsinghua Changgung Hospital during 2022-12–2024-12. Images were captured before and after laser lithotripsy. Based on postoperative infrared spectroscopy, stones were divided into five categories. In total, 1780 images (1167 from RIRS, 613 from PCNL) were included and split into training and testing sets at… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Jingcheng Lyu1,2,#, Ruiyu Yue1,2,#, Ye Tian1,2,*, Boyu Yang1,2,*
Canadian Journal of Urology, DOI:10.32604/cju.2026.074814
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advancing Early Detection of Prostate Cancer: Innovations, Challenges, and Future Directions)
Abstract Objectives: Patients with a multi-parameter magnetic resonance imaging (mpMRI) prostate imaging report and data system (PI-RADS) score ≤ 3, but with clinically significant prostate cancer (CSPCa) detected by biopsy, are termed MRI-Invisible prostate cancer (MRI(-)PCa). This study aims to explore risk factors for MRI(-)PCa and identify immunohistochemical indicators with predictive significance. Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted on 376 patients with PI-RADS score ≤ 3 who underwent 24-needle systematic prostate biopsy at Beijing Friendship Hospital, Capital Medical University (January 2015 to October 2025). Clinical data, imaging data, and Angiogenic factor with G and FHA domain… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
George Liatsos*, Kalliopi Zioutou, Konstantinos Avramidis, Konstantinos Vamvakaris, Maria Potamiti-Komi, Dimitrios Vassilopoulos
Canadian Journal of Urology, DOI:10.32604/cju.2026.072711
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Bladder and Prostate Cancers and Clinical Trials in Urologic Oncology)
Abstract Objectives: Bladder cancer (BC) is a prevalent malignancy with evolving treatment strategies and an increasingly aging patient population, resulting in a growing and complex burden of hospitalizations that extends beyond urological care and remains insufficiently characterized in real-world Internal Medicine settings. This study aimed to analyze the clinical data and outcomes for patients with BC admitted to the medicine ward. Additionally, this research presents three cases of fever of unknown origin, which all exhibited identical clinical and laboratory findings but ultimately resulted in different disease diagnoses. Methods: This retrospective case-series study included all adult patients… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
CASE REPORT
Jianlin Xie1,#, Jingde Wu1, Qingwei Zhang1, Yuanqi Guo1, Xiande Huang2,*
Canadian Journal of Urology, DOI:10.32604/cju.2026.075856
Abstract Background: Congenital nephrogenic diabetes insipidus (CNDI) is most frequently caused by mutations in the AVPR2 gene. Patients exhibit persistent polyuria due to renal insensitivity to antidiuretic hormone. Chronic high urine output predisposes to bladder dysfunction and upper urinary-tract dilatation, notably hydronephrosis. Although pharmacotherapy can partially reduce urine volume, its capacity to reverse established hydronephrosis is limited. Clean intermittent catheterization (CIC), a mainstay in managing neurogenic bladder, warrants investigation regarding its utility in CNDI-associated hydronephrosis.
Case Description: A 9-year-old Chinese boy presented with lifelong polydipsia and polyuria, with a peak 24-h urine output of approximately 7100 mL. Renal ultrasonography… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Mutlay Sayan1,*, Yetkin Tuac2, Zhiyu Qian3,4, Alexander P. Cole3,4, Jonathan E. Leeman1, Martin T. King1, Paul L. Nguyen1, Anthony V. D’Amico1
Canadian Journal of Urology, DOI:10.32604/cju.2026.074677
Abstract Objectives: Under-grading exists in up to 7% of patients undergoing radical prostatectomy (RP) for prostate cancer (PC). We assessed whether underrepresented race and ethnicity disproportionately increased the odds of adverse pathology at RP in patients with biopsy Gleason score 6 or 7 PC at high-risk for upgrading and/or upstaging at RP based on age and PC indices at presentation. Methods: This retrospective cohort study analyzed 76,474 patients in the National Cancer Database (2015–2021) with biopsy Gleason score 6 or 7 N0M0 PC. Odds ratio (OR) at RP of adverse pathology defined as prostatectomy (p) Gleason… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Mehmet Adıyeke1, Suna Yıldırım Karaca1, S. Anil Ari1, Rüyam Ercenk1, Mücahit Furkan Balci2, İbrahim Karaca1,*
Canadian Journal of Urology, DOI:10.32604/cju.2026.074502
Abstract Objectives: Stress urinary incontinence (SUI) is a prevalent condition that impairs quality of life; while midurethral sling (MUS) surgery is the standard treatment, intraurethral bulking injection offers a minimally invasive alternative. This study aimed to compare the efficacy and safety of intraurethral cross-linked hyaluronic acid/dextranomer (CLHA/Dx, DEXSUI®) injection with midurethral sling surgery in the treatment of stress urinary incontinence in women. Methods: This retrospective study included women who presented with stress urinary incontinence to İzmir Bakırçay University, Çiğli Training and Research Hospital between January 2024 and June 2025. Patients underwent either midurethral sling surgery or intraurethral… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Ernest A. Morton*, Reza Lahiji, Elizabeth Chu, William Luke, Vivian I. Anyaeche, Dattatraya Patil, Akanksha Mehta, Shreyas S. Joshi, Taylor A. Goodstein, Valentina Grajales, Mohammad Hajiha
Canadian Journal of Urology, DOI:10.32604/cju.2026.073853
Abstract Objectives: Prostate cancer (PCa) progression is influenced by a myriad of germline and/or somatic variants estimated to occur in 4.6%–11.8% of patients. Identified pathogenic variants may carry implications for treatment selection and prognosis. Despite the importance of genetic testing, referrals to counselling remain underutilized by urologists. This study aimed to understand referral patterns, testing uptake, and genetic results among men with PCa at a single large academic center. Methods: Records from 2010 to 2022 at Emory University were reviewed to identify men undergoing prostate biopsy and subsequent genetic counselling (CPT 96040). Referrals were confirmed as… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Wei Zhang, Xixi Peng*
Canadian Journal of Urology, DOI:10.32604/cju.2026.072565
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Integrating Multi-Disciplinary Insights in Urological Oncology: A Bridge from Molecular Research to Precision Clinical Practice)
Abstract Background: Observational studies have suggested potential associations between myocardial infarction (MI) and cancer risk, but the causal nature of these relationships remains unclear due to confounding factors and reverse causation. We aimed to investigate the bidirectional causal relationships between MI and urinary system cancers using genetic instruments. Methods: We conducted a two-sample Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis using summary statistics from large-scale genome-wide association studies. Genetic variants associated with MI were used as instrumental variables (n = 19 SNPs for prostate cancer [PCa] and malignant neoplasm of kidney [MRN], n = 6 SNPs for bladder cancer,… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Minkai Xie#, Chong Liu#, Ziwei Wei*, Bin Xu*
Canadian Journal of Urology, DOI:10.32604/cju.2026.073929
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Urinary Tract Injuries: Etiology, Diagnosis, and Management)
Abstract Objectives: Current surgical interventions for pelvic fracture urethral injury (PFUI) are constrained by multiple limitations. This study aimed to introduce the prior exposure maneuvers urethroplasty (PEM-U) in complex posterior anastomotic urethroplasty for PFUI. Methods: From February 2018 to March 2023 at Shanghai Ninth People’s Hospital, 78 patients with complex PFUI underwent transperineal anastomotic urethroplasty, 39 patients of whom underwent classic Webster urethral urethroplasty in which bodies splitting or an inferior pubectomy after transection of bulbar urethra (Group A), and the other 39 patients underwent improved urethral urethroplasty (Group B), in which using PEM-U (corporeal bodies… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Xiangyu Chen#, Congzhe Ren#, Lijun Xie, Xiaoqiang Liu*
Canadian Journal of Urology, DOI:10.32604/cju.2025.069578
Abstract Background: Regional differences in the incidence of prostate cancer (PCa) and prostatitis may be due to different food intake. But which foods affect PCa and prostatitis development or progression remains controversial. This study aims to explore the causal relationship between PCa and prostatitis and 30 different foods using two-sample Mendelian randomization (MR) and multivariable MR (MVMR) analysis. Methods: Data on 30 different foods were screened from the UK Biobank. PCa data came from a large meta-analysis of 140,254 individuals; prostatitis was obtained from the FinnGen consortium. The inverse variance weighted method was the main analysis… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Guancan Liang#, Jian Pan#, Ruixiang Dai, Ziyi Lin, Xunbao Wang, Teng Hou, Zhicheng Luo, Xiaoming Wang*
Canadian Journal of Urology, DOI:10.32604/cju.2026.074252
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: From Mechanisms to Models: Data-Driven Innovation in Urological Disease Research)
Abstract Background: The causal link between mental illness and prostatitis remains inconclusive, largely due to heterogeneity and potential confounders. This study explored the causal link between mental illness and prostatitis in men using Mendelian randomization (MR), and offered recommendations for enhancing future research. Methods: Publicly accessible genome-wide association study (GWAS) data were accessed via the IEU OpenGWAS platform and FinnGen database for this research. The inverse variance weighted (IVW) approach served as the primary Mendelian randomization analysis, while MR-Egger, weighted median, weighted mode, and simple mode methods were additionally applied to evaluate potential relationships between prostatitis… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Shu-Yu Wu1,2, Ching-Chia Li3,4,5, Wen-Jeng Wu3,4,5, Kuan-Hua Huang6,7, Chien-Liang Liu8,9, Shian-Shiang Wang10,11,12, Jian-Ri Li10,11, Han-Yu Weng13, Ta-Yao Tai13, Pi-Che Chen14, Ian-Seng Cheong14, Chung-You Tsai15,16, Pai-Yu Cheng15,17, Jian-Hua Hong18,19, Chung-Hsin Chen19, Jen-Shu Tseng20,21,22, Wun-Rong Lin20,21, Yuan-Hong Jiang2,23, Yu-Khun Lee2,23, Po-Hung Lin24,25,26, See-Tong Pang24, Yung-Tai Chen27, Wei-Chieh Chen28, Chia-Chang Wu29,30,31, Thomas Y. Hsueh32,33, Hsu-Che Huang34,35, Wei-Yu Lin36,37,38, Chia-Cheng Yu39, Jen-Kai Fang40, Chih-Chin Yu1,2, Yao-Chou Tsai1,2,28,*
Canadian Journal of Urology, DOI:10.32604/cju.2025.069390
Abstract Introduction: Upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma (UTUC) is a rare malignancy, particularly in the ureter, and is associated with high rates of recurrence and metastasis. Although body mass index (BMI) has been associated with prognosis in multiple cancer types, its role as a predictive factor in UTUC is still debated. This study aimed to investigate how BMI influences survival outcomes in patients with UTUC treated with radical nephroureterectomy (RNU). Methods: This multi-center retrospective analysis by the Taiwan UTUC Collaboration Group involved 2503 patients who underwent treatment across 19 hospitals from 1988 to 2022. Patients were… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Jaisa Kaufmann1,*, Max Bouvette2, Abdul Qadar1, Dominic Frimberger1, Adam Rensing1, Bhalaajee Meenakshi-Sundaram1
Canadian Journal of Urology, DOI:10.32604/cju.2026.074190
Abstract Background: Pediatric opioid use has been associated with serious adverse effects, including persistent use and overdose. Recent studies have shown that opioid needs may be minimal following outpatient pediatric urologic surgery. Post-operative pain regimens following pediatric penile surgery are not standardized. This study aimed to identify current opioid prescribing practices following hypospadias repair. Methods: An online survey was administered to members of the Societies for Pediatric Urology, including eight questions surrounding physician demographics, hypospadias repair case volume, attitudes regarding opioid prescription in pediatric urology, and post-operative pain regimens. Responses were stratified for analysis. Results: A total… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Sezgin Yeni1,*, Hakan Kilicarslan2, Bertan Tanrıbuyurdu2, Levent Turan2, Hatice Ortac3, Onur Kaygisiz2
Canadian Journal of Urology, DOI:10.32604/cju.2026.072974
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Innovations and Future Directions in the Surgical Management of Urinary Stone Disease)
Abstract Objectives: Retrograde intrarenal surgery (RIRS) has become an increasingly preferred minimally invasive option for the management of kidney stones. However, postoperative pain remains a major clinical concern that may adversely affect patient comfort and recovery. This study aimed to evaluate whether intraluminal administration of lidocaine at the end of RIRS could effectively reduce postoperative pain and analgesic requirements. Methods: A total of 61 patients who underwent RIRS between March and July 2024 were evaluated. Four patients were excluded due to residual stones, and five due to a history of cardiac arrhythmia, leaving 52 patients for… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Sofia Fontanet*, Julio F. Calderón-Cortéz, Edgar Suquilanda, Fernando Gaona, Alejandro García Navarro, Marta Piqueras
Canadian Journal of Urology, DOI:10.32604/cju.2026.074254
Abstract Objectives: Nowadays, bladder neck contracture treatment reported is both bladder neck incisions and resection. Also, different energies have been described. This study aimed to describe and compare surgical techniques and energy sources used in Hospital Universitari de Vic. Methods: retrospective study of patients with a diagnosis of bladder neck contracture that required endoscopic surgical treatment between 2000 and 2024. Preoperative, operative, and postoperative characteristics were analysed. At the end of follow-up, the patient’s status was asymptomatic, under urethral dilatations, or with a permanent catheter. Results: 60 patients were included. Mean age was 71.1 years (SD =… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yubao Liu, Haifeng Song, Zheng Xu, Weiguo Hu, Bo Xiao, Gang Zhang, Boxing Su, Bixiao Wang, Jianxing Li*
Canadian Journal of Urology, DOI:10.32604/cju.2025.070417
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Urolithiasis in Focus: Integrated Perspectives on Infection, Metabolic Dysfunction, and Contemporary Management)
Abstract Objective: The pressure fluctuations during retrograde intrarenal surgery (RIRS) can cause related complications, so precise monitoring and control of intrarenal pressure (IRP) play an important role. This study aimed to assess the clinical value of a Chinese-made disposable pressure-measuring flexible ureteroscope in monitoring IRP during RIRS for upper urinary tract stones <2 cm, and analyze factors affecting IRP. Methods: In this prospective single-arm study, 35 patients (38 renal units) underwent RIRS. Mean age was 42.3 ± 6.1 years, body mass index (BMI) 24.2 ± 2.6 kg/m², and maximum stone diameter 1.6 ± 0.4 cm. Stones… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
James T. Kearns*, Cecilia Chang, Chi Wang, Christopher Ward, Henry M. Dunnenberger, Kristian Novakovic, Alexander P. Glaser, Brian T. Helfand
Canadian Journal of Urology, DOI:10.32604/cju.2025.073852
Abstract Background: Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and prostate cancer (PCa) are common in aging men and are often concomitant. The purpose of the study was to evaluate whether Aquablation in men with BPH and early-stage PCa resulted in improvements in lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) and urinary quality of life (QoL) similar to men with only BPH. Furthermore, we explored active surveillance (AS) cancer outcomes in men undergoing Aquablation compared with a control AS population. Methods: Two prospective IRB (institutional review board)-approved databases were used to investigate outcomes in men with GG1 PCa on AS and… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
CASE REPORT
Angelos Samaras, Stefan Aufderklamm, Bastian Amend, Viktoria Stühler, Arnulf Stenzl, Igor Tsaur, Steffen Rausch*
Canadian Journal of Urology, DOI:10.32604/cju.2025.068588
Abstract Background: Penile fracture is a rare urological emergency, especially when it involves a urethral injury. Case Description: Here, we report the case of a 41-year-old male patient with penile trauma during sexual intercourse, presenting with typical clinical signs of corpus cavernosum rupture and gross hematuria. Emergency surgical exploration revealed an additional partial urethral injury (approximately 1.5 cm in length), which was primarily closed. Surgical management included a vertical penoscrotal incision, evacuation of hematoma, double-layer re-approximation of the urethra, closure of the tunica albuginea, and placement of both transurethral and suprapubic catheters. The postoperative course was uneventful, More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Sin Woo Lee*, Seung-Kwon Choi
Canadian Journal of Urology, DOI:10.32604/cju.2025.073355
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Urolithiasis in Focus: Integrated Perspectives on Infection, Metabolic Dysfunction, and Contemporary Management)
Abstract Background: Postoperative infections are an emerging concern in endourology. This study reports an outbreak of urinary tract infections associated with Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PA) in patients who underwent stone removal surgery using flexible ureteroscopy (FURS) at Seoul Medical Center. Methods: Between August and December 2024, five patients who underwent FURS performed by the same surgeon developed postoperative febrile episodes requiring further treatment. Urine cultures from four patients revealed an outbreak of multidrug-resistant PA, prompting environmental cultures and an inspection of the instrument reprocessing procedures led by the hospital’s infection control department. Results: Although PA was not isolated from… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Manish Kuchakulla1,2,*, Hriday P. Bhambhvani1,2, Robert Fisch1,2, Runzhuo Ma1,2, Jonathan Gal2, Marc Goldstein2
Canadian Journal of Urology, DOI:10.32604/cju.2025.071275
Abstract Objectives: Men with obstructive azoospermia (OA) or infertility often require surgical sperm retrieval for assisted reproductive techniques. While sperm can be successfully obtained from either the testis or epididymis in these patients, sperm DNA integrity may differ between retrieval sites, which could influence reproductive outcomes. This study aimed to determine whether bilateral epididymal and/or testicular sperm extraction is necessary in men with OA or infertility and elevated DNA fragmentation index (DFI). Methods: We retrospectively analyzed men who underwent bilateral testicular biopsy and/or microscopic epididymal sperm aspiration (MESA) by a single surgeon from 2020–2022. TUNEL assays… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Sinan Kılıç*
Canadian Journal of Urology, DOI:10.32604/cju.2025.072049
Abstract Objectives: Testicular torsion is the most common surgical cause of an acute scrotum. Manuel detorsion renewed attention as a practical initial treatment, particularly in the COVID-19 pandemic. This study aims to systematically review and meta-analyze the current literature to determine whether manual detorsion offers a viable alternative to immediate surgery in improving testicular salvage rates. Methods: A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted in accordance with PRISMA guidelines and registered with PROSPERO (CRD420251039489). Studies including ≥30 male patients comparing manual detorsion and surgical exploration were included. Searches were performed in PubMed/MEDLINE, Scopus, TR Index, and… More >
Graphic Abstract
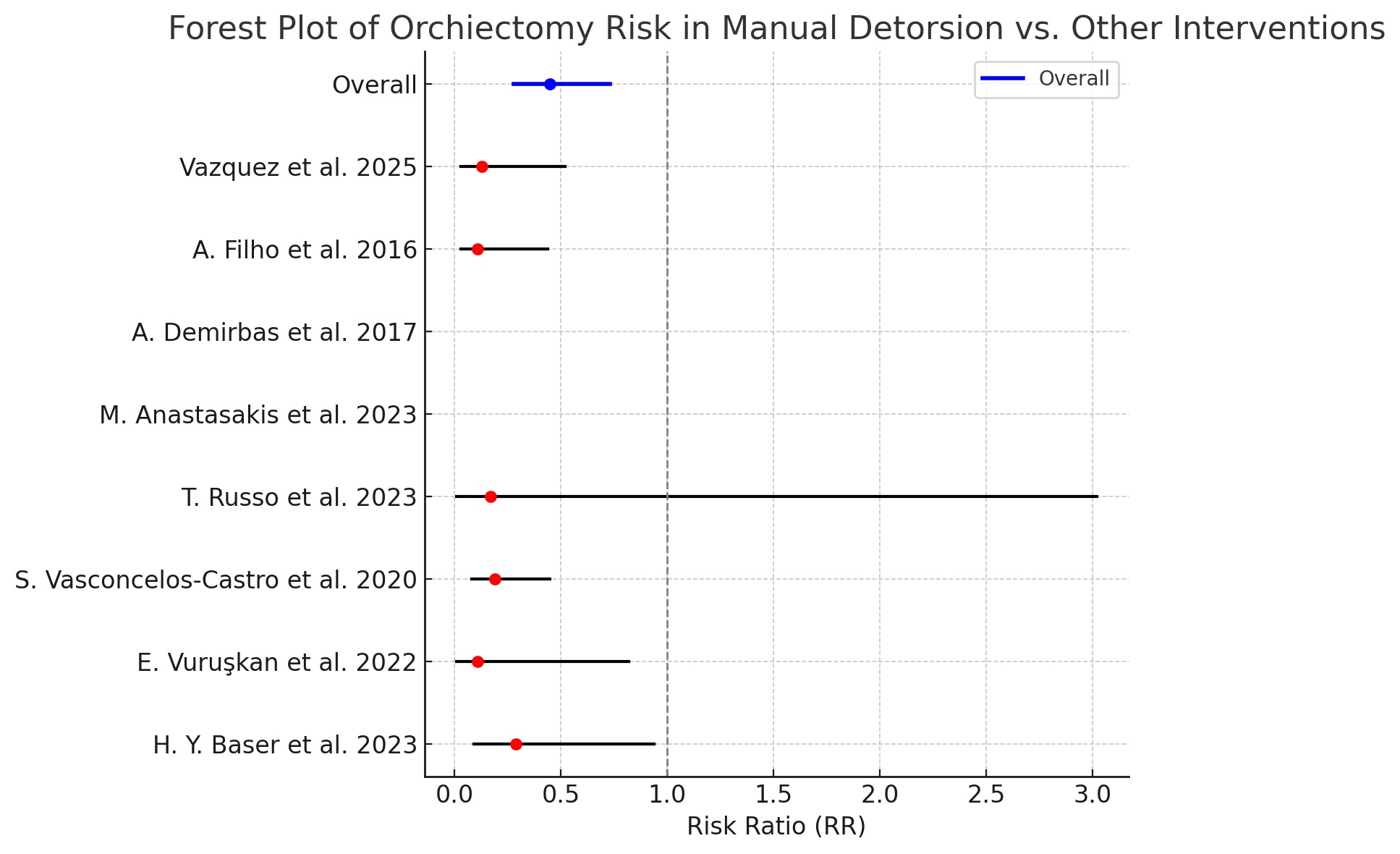
 Open Access
Open Access
CASE REPORT
Shao-Chen Su, Yi-Sheng Lin*, Zhon-Min Huang*, Chao-Yu Hsu, Yen-Chuan Ou
Canadian Journal of Urology, DOI:10.32604/cju.2025.073769
Abstract Background: Tuberculosis (TB) is a globally prevalent infectious disease, including in Taiwan. Prostatic TB is a rare manifestation of genitourinary tuberculosis (GU-TB), which is the third most common extrapulmonary form of the disease. However, due to its insidious onset and non-specific symptoms, prostatic TB is often diagnosed late. Case Description: We report a case of a 72-year-old male patient who presented with lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) and painful scrotal swelling. Following transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), histopathological examination revealed prostatic TB. The patient subsequently had abdominal cramping and diarrhea. A colonoscopy detected an ulcer-like More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Nazım Furkan Günay*, Mücahit Gelmiş, Çağlar Dizdaroğlu, Abdullah Esmeray, Ufuk Çağlar, Ömer Sarılar, Faruk Özgör
Canadian Journal of Urology, DOI:10.32604/cju.2025.072419
Abstract Objectives: Chronic kidney disease (CKD) poses unique challenges in the management of renal stones, and high-quality evidence to guide treatment decisions is limited. This study aimed to compare the effects of flexible ureteroscopy (f-URS) and mini-percutaneous nephrolithotomy (m-PCNL) on perioperative outcomes and long-term renal function in patients with CKD and renal stones. Methods: This prospective randomized study included 60 CKD patients with renal stones measuring 1–4 cm. Participants were randomized into f-URS (n = 24) and m-PCNL (n = 36) groups. Baseline demographics, stone characteristics, and perioperative parameters were recorded. Stone-free rate (SFR) was defined… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Arif Kol1, Hüseyin Günizi2,*, Özlem Ceren Günizi3
Canadian Journal of Urology, DOI:10.32604/cju.2025.070231
Abstract Objective: Sambucus nigra (SN) has been found to exhibit strong antioxidant properties and anti-inflammatory effects. In our study, we aimed to investigate the therapeutic effects of Sambucus nigra extracts (SNe) in interstitial cystitis, a condition in which inflammation plays a significant role in its pathophysiology. Methods: Thirty Wistar albino adult female rats were used in this study. All rats were housed at an average room temperature of 23°C, with a 12-h light/dark cycle, and had ad libitum access to food. The rats were divided into three groups: Group 1 (n = 10): Control (sham) group, Group 2 (n… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
CASE REPORT
Ida Nurwati1, Uki Retno Budihastuti1,2,*, Bhisma Murti3, Teguh Prakosa1,2, Metanolia Sukmawati2
Canadian Journal of Urology, DOI:10.32604/cju.2025.068548
Abstract Background: Varicocele is a common cause of male infertility, often associated with impaired sperm quality, hormonal imbalance, and increased DNA fragmentation. Electroacupuncture (EA) has been proposed as an adjunct therapy to improve reproductive parameters, but clinical evidence remains limited. Case Description: This case report describes a 38-year-old male with a varicocele treated at Dr. Moewardi General Hospital, Indonesia. The patient underwent 16 sessions of EA therapy. Sperm parameters and serum testosterone levels were measured before and after treatment. Following EA, sperm concentration improved from 5.2 to 6.7 × 106/mL, motility increased from 43% to 60%, and More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Jinwei Mao1,, Jie Deng2, Xiqi Peng2, Xunbao Wang2, Song Wu1,*
Canadian Journal of Urology, DOI:10.32604/cju.2025.072113
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: From Mechanisms to Models: Data-Driven Innovation in Urological Disease Research)
Abstract Background: Concealed penis (CP) is a common congenital condition in pediatric urology, and surgical correction remains the mainstay of treatment. The modified Devine procedure (MDP) has been increasingly used, but its comparative safety and effectiveness relative to the traditional Devine procedure (TDP) remain unclear. This study aimed to compare the safety and effectiveness of the MDP with the TDP for the treatment of pediatric CP. Methods: This systematic review and meta-analysis was conducted in accordance with the PRISMA 2020 and AMSTAR guidelines. Prospective, retrospective, and randomized controlled studies comparing MDP and TDP for pediatric CP… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Serkan Özcan1,*, Mertcan Dama2, Enis Mert Yorulmaz1, Osman Köse1, Sacit Nuri Görgel1, Yiğit Akın1
Canadian Journal of Urology, DOI:10.32604/cju.2025.072282
Abstract Objectives: Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate (HoLEP) is an established treatment for benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), but early postoperative dysuria and incontinence remain common concerns. The Virtual Basket (VB) mode has been proposed to reduce tissue trauma. This study evaluated whether VB use improves early postoperative recovery without compromising HoLEP efficacy. Methods: We retrospectively analyzed 168 men who underwent HoLEP between September 2023 and September 2024. Patients were categorized into three groups according to laser settings: 100 W Standard (n = 65), 100 W VB (n = 49), and 80 W VB (n =… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Erdem Öztürk, Tuncel Uzel, Mustafa Işikdoğan*, İsa Dağli, Nurullah Hamİdİ, Halil Başar
Canadian Journal of Urology, DOI:10.32604/cju.2025.071101
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advancing Early Detection of Prostate Cancer: Innovations, Challenges, and Future Directions)
Abstract Background: The European Association of Urology (EAU) recommends transperineal biopsy (TPBx) due to its lower infection risk and higher diagnostic rate for anterior zone tumors. This study aims to assess the learning curve of TPBx using the Perino-Flex® angle-adjustable needle guide under local anesthesia. Methods: A retrospective observational analysis was conducted from November 2023 to March 2024, involving 100 patients who underwent TPBx with coaxial technique under local anesthesia. Data collected included patient demographics, procedure and room times, pain levels, anxiety scores, and complications. The study focused on comparing procedure times, pain scores, and complication rates… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Benedikt Becker1,2, Sophia Hook1, Carla Dapper1, Julius Bergmann1, Christopher Netsch1, Simon Filmar1,*
Canadian Journal of Urology, DOI:10.32604/cju.2025.072386
Abstract Background: Holmium: yttrium-aluminum-garnet (Ho: YAG) laser technology has long been employed for urinary stone fragmentation; however, its limitations have prompted the exploration of alternative systems such as thulium lasers. This study aims to compare a novel pulsed solid-state Thulium: YAG (Tm: YAG) laser to the standard Ho: YAG laser in Mini-percutaneous nephrolithotomy (Mini-PCNL) lithotripsy for renal calculi. Methods: In total, 100 patients undergoing Mini-PCNL were enrolled in this clinical trial. Fifty patients treated with a holmium laser were selected from a retrospective database. These patients were compared to fifty patients who were prospectively enrolled and… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Simone Tammaro1, Francesco Di Fiore2, Felice Crocetto3, Celeste Manfredi1,*, Claudia Collà Ruvolo3, Gianluigi Califano3, Biagio Barone4, Davide Arcaniolo1, Lorenzo Spirito1, Francesco Paolo Calace2, Pasquale Reccia2, Ferdinando Fusco1, Marco De Sio1, Raffaele Balsamo2
Canadian Journal of Urology, DOI:10.32604/cju.2025.072617
Abstract This article has no abstract. More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Mark W. Shilling1, Shawn L. Fernandez2, George J. Ryan1, Juila G. Kim3, David C. Majure4, Frances M. Alba5, Reza Ehsanian1,*
Canadian Journal of Urology, DOI:10.32604/cju.2025.070606
Abstract Background: Individuals with spinal cord injury (SCI) are at high risk for developing neurogenic bladder or neurogenic lower urinary tract dysfunction (NLUTD), which can lead to severe complications and negatively impact quality of life. Despite the critical need for timely urologic care, barriers to access remain poorly understood, particularly in resource-limited settings. This study aims to identify systemic and perceived barriers to urologic follow-up for individuals with SCI treated at an academic medical center. Methods: A single-center, observational study was conducted on individuals presenting with a diagnosis code indicative of complete SCI at an academic… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
CASE REPORT
Francesco Cianflone1, Giuseppe Ottone Cirulli1, Alessio Villano1, Mohammad Eisa Ali1, Mirko Belliato2, Roberto Veronesi2, Germana Bichisao3, Carlo Marchetti1, Simona Secondino4, Paolo Pedrazzoli4,5, Stefano Pelenghi6, Carlo Pellegrini6,7, Andrea Ringressi1, Richard Naspro1,7,*
Canadian Journal of Urology, DOI:10.32604/cju.2025.073002
Abstract Background: Robot-assisted partial nephrectomy (RAPN) is standard for cT1 renal masses, but its feasibility in patients on temporary mechanical circulatory support is poorly documented. We report RAPN performed while a patient was simultaneously supported with venous-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VA ECMO) and Impella®, as part of a staged plan for left ventricular assist device (LVAD) implantation and eventual heart transplantation. Case Presentation: A 51-year-old man presented with ST-elevation myocardial infarction complicated by cardiogenic shock requiring percutaneous coronary intervention with stenting, dual antiplatelet therapy, and combined VA ECMO–Impella® support. During workup for cardiac transplant, computed tomography (CT) staging… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
CASE REPORT
Nicole Handa*, Matthew T. Hudnall, Channa Amarasekera
Canadian Journal of Urology, DOI:10.32604/cju.2025.070415
Abstract Background: Penile constriction rings are most used for sexual pleasure and the management of sexual dysfunction. However, they pose a risk of injury and can be challenging to remove when strangulation occurs. Case Description: We present a case of a patient with urinary retention and a strangulation injury from a penile constriction ring present for 19 h before initial presentation. Multiple attempts to remove the penile ring were unsuccessful, and ultimately, operative management was required. Conclusions: We describe an effective technique for the removal of a stainless-steel penile constriction ring using a Stryker 505 power revision More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Shanhong Luo1, Hongjuan Xu2,*
Canadian Journal of Urology, DOI:10.32604/cju.2025.069884
Abstract Background: Early detection and timely treatment of urinary tract infections (UTIs) can prevent the aggravation of the inflammatory response following a stroke and enhance the recovery of neurological function. This study aimed to develop a simple scoring system by integrating nutritional and inflammatory markers to predict the occurrence of UTIs in patients with acute stroke. Methods: Reviews of 1011 patients with acute stroke were retrieved. The Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index (GNRI) and systemic inflammation response index (SIRI) were utilized to develop a composite score of nutritional-systemic inflammation response index (G-SIRI). The primary endpoint was the… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Zhenzhen Yang1,#, Linxin Jiang2,#, Shan Yin3,*
Canadian Journal of Urology, DOI:10.32604/cju.2025.069717
Abstract Objectives: Kidney stone disease is increasingly prevalent and may be linked to metabolic factors such as insulin resistance, but there is currently no direct evidence connecting estimated glucose disposal rate (eGDR) to kidney stones. This study aimed to investigate the relationship between eGDR and kidney stone prevalence. Methods: We conducted a cross-sectional analysis utilizing data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) from 2007–2018, including 29,753 participants aged 20 years and older. Weighted multivariable logistic regression and nonlinear models were employed to assess the relationship between eGDR and self-reported kidney stone history. Results: Among… More >
Graphic Abstract
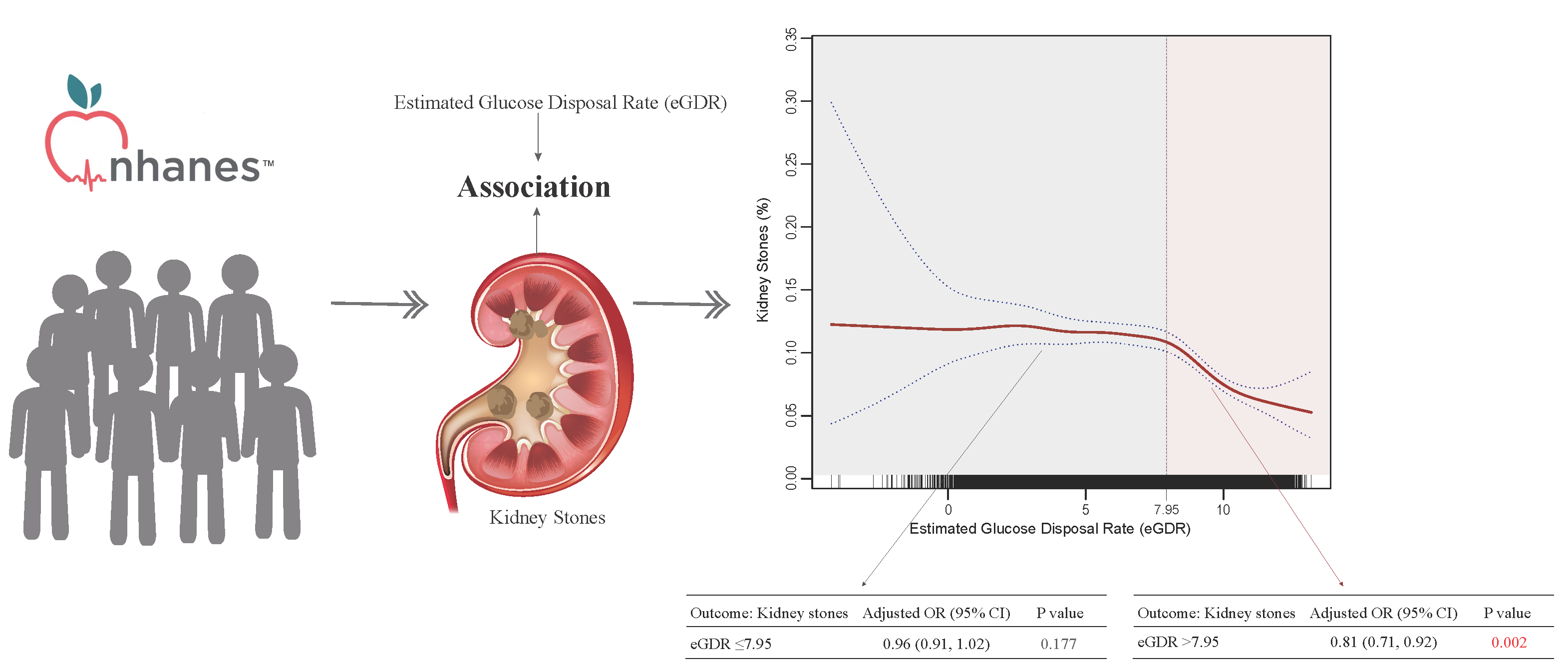
 Open Access
Open Access
CASE REPORT
Kazuki Yanagida1,2, Daisuke Watanabe1,2,3,*, Hazuki Inoue1, Takashi Ujiie1, Akio Mizushima2,3
Canadian Journal of Urology, DOI:10.32604/cju.2025.068677
Abstract Background: Vesicourethral foreign bodies are frequently encountered in urological emergency departments; however, cases of penetrating injury to the corpus spongiosum penis and bulbous urethra are rare. Case Description: A 64-year-old man presented with difficulty removing a foreign body that he had inserted into his urethra for masturbation. Abdominal computed tomography (CT) revealed a rod-shaped foreign body lodged from the bulbous urethra to the posterior wall of the bladder. Cystoscopy confirmed penetration of the foreign body into the urethral sponge at the bulbous urethra. An attempt was made to remove the foreign body transurethrally, but it was… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Jessica L. Wenzel1, Wesley H. Chou1,*, Eric J. Robinson2, Solange Bassale3, Paul Jones4, Sudhir Isharwal1,3, Christopher L. Amling1,3, Kamran P. Sajadi1, Jen-Jane Liu1,3
Canadian Journal of Urology, DOI:10.32604/cju.2025.071079
Abstract This article has no abstract. More >
 Open Access
Open Access
CASE REPORT
Ao Li1,#, Cai Tang2,#, Xin Wei3,*, Feng Liu1,*
Canadian Journal of Urology, DOI:10.32604/cju.2025.070366
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Decoding Renal Development: From Molecular Blueprints to Reconstructive Innovations)
Abstract Background: Ureteroenteric anastomotic stricture is a common complication after ureteral diversion with radical cystectomy, which leads to hydronephrosis, infection, and chronic renal failure. Although ureteroneocystostomy is reliable, its high degree of invasion often causes great damage and postoperative complications in patients. Therefore, we offer a new endoscopic approach with relatively limited invasion for severe obstructions such as ureteroenteric anastomotic atresia. Case Description: A 65-year-old man underwent radical cystectomy and urinary diversion of orthotopic neobladder and standardized chemotherapy for high-risk non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Severe left hydronephrosis was then detected due to ureteroenteric anastomotic atresia. Percutaneous nephrostomy was… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Francesco Claps1,2,*, Miguel Ramírez-Backhaus1, Álvaro Gómez-Ferrer1, Juan Manuel Mascarós1, Argimiro Collado Serra1, Augusto Wong1, Ana Calatrava Fons3, Miguel Ángel Climent4, Antonio Amodeo2, Angelo Porreca5, Jose Rubio-Briones1,6
Canadian Journal of Urology, DOI:10.32604/cju.2025.070162
Abstract Objectives: Residual Disease after adjuvant chemotherapy for non-seminomatous germ cell tumor (NSGCT) poses a significant clinical challenge and difficulties in tailored management. This study aimed to externally validate the Heidenreich criteria among patients eligible for unilateral post-chemotherapy retroperitoneal lymph node dissection (PC-RPLND) for residual masses of NSGCT. Methods: For validation, these criteria were retrospectively applied in 23 patients undergoing PC-RPLND for residual masses of NSGCTs. In patients qualified for unilateral-modified PC-RPLND according to the Heidenreich criteria but treated with fully bilateral dissection, pathological reports were evaluated to identify teratoma or active cancer cells inside the… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
CASE REPORT
Sarah M. Kodres–O’Brien*, Mackenzie Koellermeier, Nayan Shah, Peter Langenstroer
Canadian Journal of Urology, DOI:10.32604/cju.2025.069550
Abstract Background: Retained bullet fragments in the genitourinary tract following gunshot wound is rare and require removal. Case Description: We present the case of a retained bullet in the prostate following a gunshot wound to the pelvis, which was endoscopically removed. A urethral catheter and suprapubic tube were placed. The patient then had migration of a second bullet fragment into the prostatic urethra six weeks later, requiring open removal. Conclusions: This case shows that several approaches can be considered to remove retained bullet fragments from the urinary tract. Furthermore, access to the bladder via a suprapubic tube More >