KDM6B Regulates the Tumor Microenvironment and Promotes EMT via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling in Differentiated Thyroid Cancer
Jiangtao Yu*, Qingfeng Huo, Xinxin Duan
General Surgery II (thyroid), The Fifth Clinical Medical College of Henan University of Chinese Medicine (Zhengzhou People’s Hospital), Zhengzhou, China
* Corresponding Author: Jiangtao Yu. Email: 
BIOCELL https://doi.org/10.32604/biocell.2026.073331
Received 16 September 2025; Accepted 16 January 2026; Published online 04 February 2026
Abstract
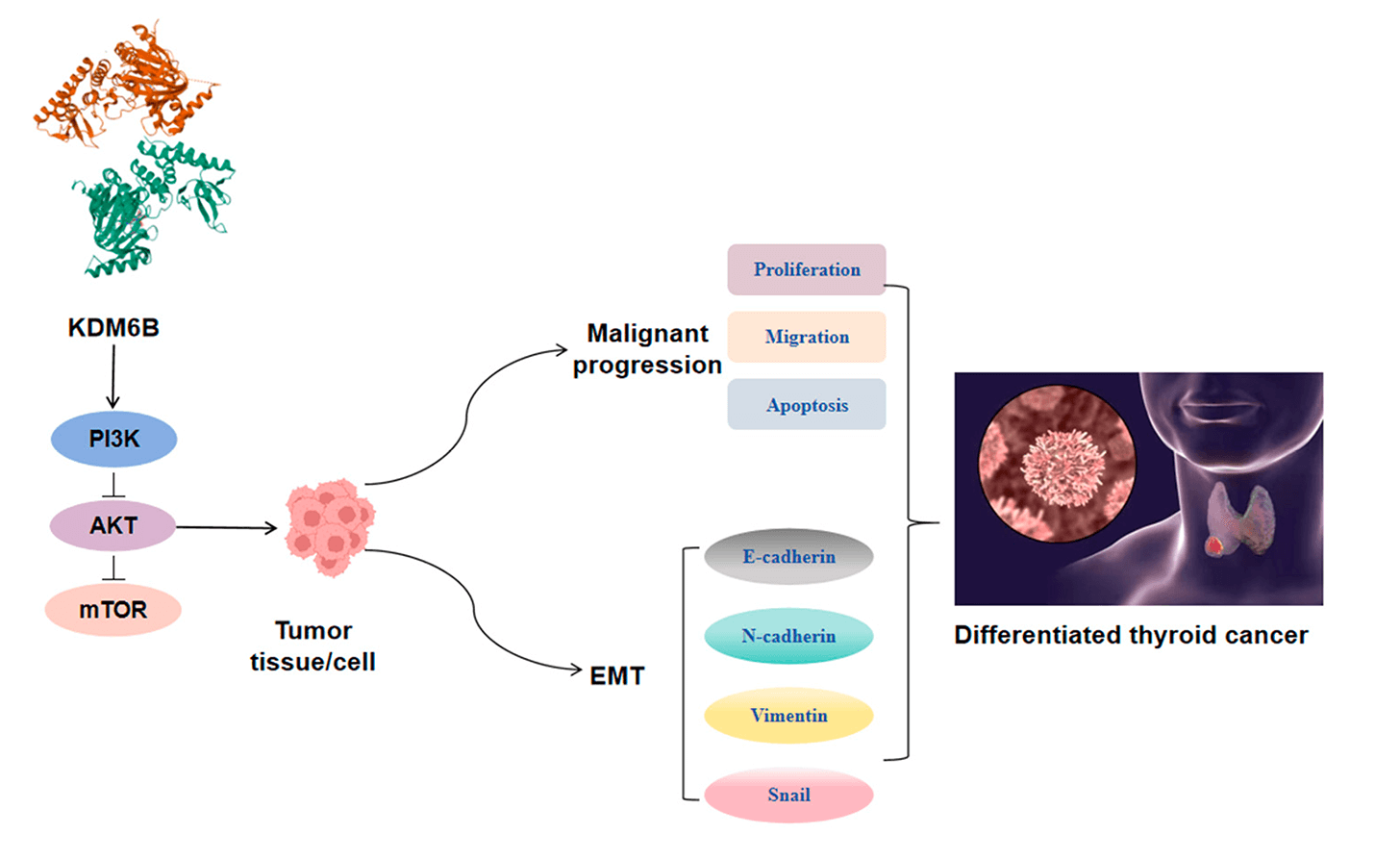
Objectives: The tumor microenvironment and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) are closely linked to the progression of differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC). However, the functional mechanisms of lysine-specific demethylase 6B (KDM6B) in carcinogenesis remain incompletely understood. This study aims to clarify whether KDM6B affects DTC progression and EMT through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B/mammalian target of the rapamycin (PI3K/AKT/mTOR) pathway, providing a potential target for clinical treatment of DTC.
Methods: Tissue samples from DTC patients (n = 39) were collected, and KDM6B expression was determined through Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) and Western blot. Cell counting kit-8 assay, 5-Ethynyl-2
′-deoxyuridine staining, Transwell, Scratch-Wound, and other experiments were used to detect cell biological behavior; flow cytometry and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay were used to investigate its effect on macrophage polarization. A subcutaneous tumor model was constructed in mice, and immunohistochemistry was used to detect nuclear proliferation antigen Ki-67, and a Western blot was used to validate protein expression.
Results: KDM6B level was elevated in DTC tissues and cells compared to normal ones. Knocking down KDM6B inhibited DTC cell proliferation, reduced migratory and invasive capabilities, suppressed M2 macrophage polarization and EMT processes, while overexpression of KDM6B promoted the aforementioned biological behaviors. Knocking down KDM6B blocked the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, while overexpression of KDM6B activated this pathway. PI3K agonists weakened the inhibitory impact of KDM6B knockdown on malignant biological characteristics; the opposite was true for PI3K inhibitors. Additionally, knocking down KDM6B inhibited tumor growth, decreased the Ki67 positivity rate, and inhibited the EMT process and M2 macrophage polarization in mice.
Conclusion: KDM6B regulates the tumor microenvironment and EMT process via PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, thereby influencing DTC progression.
Graphical Abstract
Keywords
Lysine-specific demethylase 6B; phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B/mammalian target of the rapamycin pathway; differentiated thyroid carcinoma; tumor microenvironment; epithelial-mesenchymal transition
 Open Access
Open Access