BIOCELL is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on molecular and cellular biosciences. The journal welcomes high quality original research articles, review papers, communications, perspectives, commentaries, etc. Topics of interests include but are not limited to: Cellular Biochemistry, Structural & Molecular Biology, Cellular/Molecular Biology, Immunology, Pathology & Neurobiology, Cell Signaling, Regenerative Biology & Stem Cells, Cancer Biology, RNA Biology, Genomics, Transcriptomics, Proteomics & Metabolomics, Plant Molecular & Cellular Biology.
Science Citation Index Expanded (SCIE): 2024 Impact Factor 1.0; Journal Citation Report/Science Edition (JCR); Scopus; Scopus Citescore (Impact per Publication 2024): 2.0; SNIP (Source Normalized Impact per Paper 2024): 0.256; Sociedad Argentina de Investigaciones en Bioquímica y Biología Molecular (SAIB); Portico, etc.
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
BIOCELL, Vol.49, No.11, pp. 2033-2067, 2025, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2025.067661 - 24 November 2025
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Melatonin and Mitochondria: Exploring New Frontiers)
Abstract The development of cancer cell resistance to conventional treatments continues to be a major obstacle in the successful treatment of tumors of many types. The discovery of a highly efficient direct and indirect free radical scavenger, melatonin, in the mitochondrial matrix may be a factor in determining both the occurrence of cancer cell drug insensitivity as well as radioresistance. This relates to two of the known hallmarks of cancer, i.e., exaggerated free radical generation in the mitochondria and the development of Warburg type metabolism (glycolysis). The hypothesis elaborated in this report assumes that the high… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
BIOCELL, Vol.49, No.11, pp. 2069-2091, 2025, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2025.068017 - 24 November 2025
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Mitochondrial Dynamics and Oxidative Stress in Disease: Cellular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Targets)
Abstract The pathogenesis of insulin resistance is influenced by environmental factors, genetic predispositions, and several medications. Various drugs used to manage multiple ailments have been shown to induce insulin resistance, which could lead to Type II Diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Central to drug-induced insulin resistance is mitochondrial dysfunction. Amongst disturbed pathways in drug-induced mitochondrial toxicity is mitophagy, a process that removes dysfunctional mitochondria through the lysosomal pathways to maintain mitochondrial quality. A balance must always be maintained between mitochondrial dynamics and mitophagy, as any alterations may contribute to the pathogenesis of metabolic diseases such as diabetes mellitus.… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
BIOCELL, Vol.49, No.11, pp. 2093-2123, 2025, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2025.069272 - 24 November 2025
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Mechanisms Driving COPD, Atherosclerosis, and Cardiovascular Disease: From Pathogenesis to Therapeutic Innovations)
Abstract Elevated homocysteine is a clinically relevant metabolic signal in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Higher circulating levels track with oxidative stress, endothelial dysfunction, mitochondrial impairment, and pulmonary vascular remodeling, rise with disease severity, and may contribute to the excess cardiovascular risk—although effect sizes and causality remain uncertain. This review centers on the homocysteine–carnitine relationship in COPD pathophysiology. Carnitine deficiency, prevalent in COPD, can worsen mitochondrial bioenergetics, promote accumulation of acyl intermediates, and reduce nitric oxide bioavailability via endothelial nitric oxide synthase uncoupling (eNOS). Conversely, restoring carnitine status in experimental and early clinical settings has been… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
BIOCELL, Vol.49, No.11, pp. 2125-2136, 2025, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2025.070394 - 24 November 2025
Abstract Lewy body diseases (LBD), including Parkinson’s disease (PD) and dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB), are neurodegenerative disorders characterized by the intracellular aggregation and accumulation of α-Synuclein (αSyn), leading to neuronal death. Although these diseases primarily present with symptoms affecting the central nervous system (CNS), such as motor and cognitive impairment, increasing research suggests that their roots may be found in the gut. This review summarizes recent findings and key historical insights into the involvement of the gut in αSyn pathology. The topics covered include pathological observations in patients with LBD, animal models investigating the propagation More >
 Open Access
Open Access
COMMENTARY
BIOCELL, Vol.49, No.11, pp. 2137-2145, 2025, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2025.069216 - 24 November 2025
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Understanding Cellular Mechanisms in Wound Healing During Therapeutic Interventions)
Abstract This commentary analyzes the effect of Exendin-4 on wound healing. After introducing information about the drug, considerations are added regarding its impact on this process. To accelerate wound healing, the drug’s combined effects with stem cells and other factors are examined, aiming to enhance and thus accelerate the process. Finally, the clinical potential of this drug’s effect is considered, not only for wound healing but also in other diseases. Therefore, reading this commentary may provide research perspectives that can stimulate the future reader’s thinking. More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
BIOCELL, Vol.49, No.11, pp. 2147-2166, 2025, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2025.070188 - 24 November 2025
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Modulation of Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Mitochondrial Function: Therapeutic Perspectives Across Diseases)
Abstract Background: Cisplatin (CDDP) is a cornerstone chemotherapeutic agent for many solid tumors, but its clinical use is severely limited by dose-dependent nephrotoxicity, which results in acute kidney injury (AKI) in a significant proportion of patients. CDDP-induced AKI involves interconnected mechanisms, including inflammation, oxidative stress, and tubular cell death. In this study, we aimed to investigate the renoprotective effects of esculetin (ES), a natural antioxidant coumarin, in a murine model of CDDP-induced AKI. Methods: Male C57BL/6 mice (8–10 weeks) received a single intraperitoneal injection of CDDP (20 mg/kg) with or without ES (40 mg/kg/day, oral gavage).… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
BIOCELL, Vol.49, No.11, pp. 2167-2180, 2025, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2025.071827 - 24 November 2025
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Cellular Senescence in Health and Disease)
Abstract Objectives: Targeting epigenetic modifications in anticancer therapy is a promising approach to overcoming cancer cell chemoresistance. The histone deacetylase/DNA methyltransferase inhibitor, parthenolide (PTL), has antitumor activity, but contrasting findings exist on its effect in normal cells. This study aims to examine the non-genomic toxic mechanisms of PTL in human erythrocytes. Methods: Cell death as stimulated by 20–200 μM of PTL for 24 h at 37°C was assessed using fluorescence-assorted cell sorting and spectrophotometric assays. Canonical markers of cell death, including membrane scrambling, oxidative stress, and Ca2+ mobilization, were captured by annexin V-fluorescein isothiocyanate, 2′,7′-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate, and… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
BIOCELL, Vol.49, No.11, pp. 2181-2194, 2025, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2025.070859 - 24 November 2025
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Modulation of Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Mitochondrial Function: Therapeutic Perspectives Across Diseases)
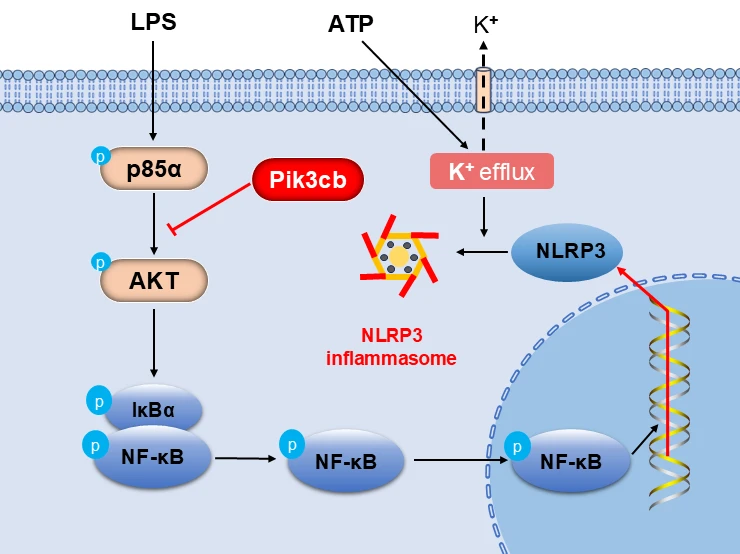
Abstract Objectives: PI3K plays a pivotal role in the inflammatory response by modulating the production and release of inflammatory factors. Pik3cb is one of the subunits of PI3K, and its specific role in myocardium inflammation remains unelucidated. This study aimed to investigate the role of Pik3cb in the inflammatory response and to elucidate the underlying mechanism. Methods: An inflammation model was established using H9c2 cells treated with LPS and ATP, and Pik3cb expression was evaluated in this model system. Subsequently, an overexpression model was constructed by transfecting cells with a Pik3cb overexpression plasmid, after which the… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
BIOCELL, Vol.49, No.11, pp. 2195-2216, 2025, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2025.072716 - 24 November 2025
Abstract Objective: Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are important cells in bone tissue engineering. Bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2) effectively treats bone defects and nonunion. The purpose of this study is to investigate whether BMP-2 promotes bone formation and femoral fracture healing by inhibiting inflammation and promoting osteogenic differentiation of MSCs, in order to provide an experimental basis for developing more efficient fracture treatment strategies. Methods: Bone marrow-derived MSCs (BMSCs) were isolated from rats and treated with OE-BMP-2, the 5′-adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) signal agonist 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleotide (AICAR), and the inhibitor Compound C. Osteogenic differentiation was evaluated through… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
BIOCELL, Vol.49, No.11, pp. 2217-2237, 2025, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2025.068450 - 24 November 2025
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Phytochemicals and Bioactive Monomers from Herbal Medicine: Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms)
Abstract Objectives: An allergy is an exaggerated immune response, and mast cells play central roles in allergic pathologies. Allyl isothiocyanate can suppress inflammatory responses; however, whether allyl isothiocyanate has a suppressive effect on allergic pathologies remains unclear. Methods: 2,4-dinitrofluorobenzen or ovalbumin was used to establish a mouse model of allergic contact dermatitis or food allergy, respectively. The mRNA level of cytokines was determined using real-time polymerase chain reaction. To examine the effects of allyl isothiocyanate on mast cells, degranulation and intracellular calcium measurement, RNA sequencing, real-time polymerase chain reaction, and Western blotting were performed. Results: Allyl isothiocyanate… More >